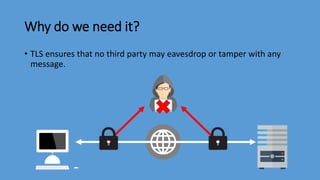
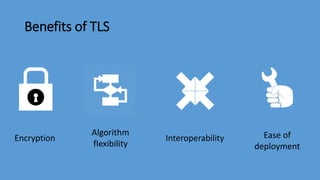
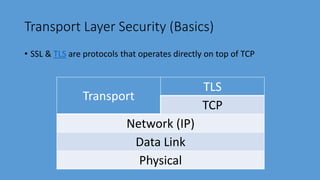
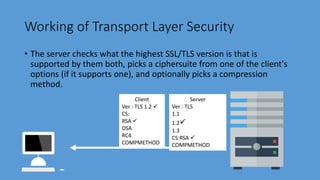
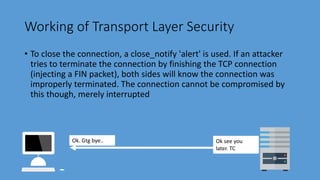
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is the successor to Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and ensures privacy and security between communicating applications on the internet. TLS encrypts data transmission, works with most browsers and servers, supports flexible encryption algorithms, and is easy to deploy on many systems transparently. It operates directly above TCP and establishes an encrypted connection by negotiating a cipher suite and exchanging certificates and keys between the client and server. Once handshake is complete, both sides can communicate securely until closing the connection. TLS version and cipher suite used can be viewed in browser.