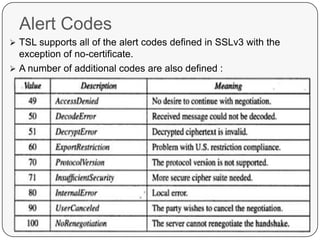
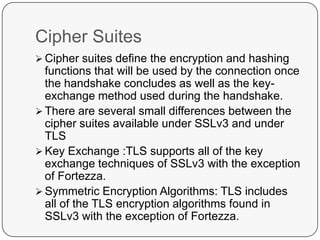
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a standard security protocol that ensures secure connections on the Internet. It is based on the earlier SSL protocol with minor differences in record format version numbers, use of HMAC for message authentication codes, and additional alert codes. The goals of TLS are to establish a secure connection through cryptographic security, allow for interoperability between independent implementations, and provide an extensible framework to incorporate new encryption methods. TLS uses the record layer to encapsulate and process messages through steps like fragmentation, encryption, integrity checks. It generates cryptographic secrets through pseudorandom functions and data expansion functions.









![Message Authentication Code
The Message Authentication Code (MAC) used for TLS is
HMAC
HMAC is expressed by the following equation,
HMACK(M) = H[(K+ opad)||H[(K+
ipad)||M]]
Where:
: is concatenation
M
: is the plain-text to be encrypted
H
: is the hashing function (either MD-5 or SHA-1)
K+ : secret key padded with zeros on the left so that the result
is equal to the block length of the hash code (for MD-5 and SHA1 block length is 512 bits)
ipad : 00110110 (36 in hexa decimal) repeated 64 times (512
bits)
opad : 01011101 (5c in hexa decimal) repeated 64 times (512
bits)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transportlayersecurity-140125013918-phpapp02/85/Transport-layer-security-11-320.jpg)