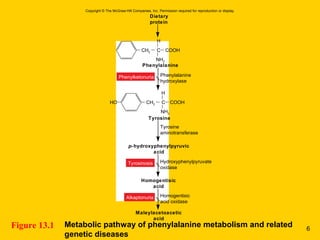
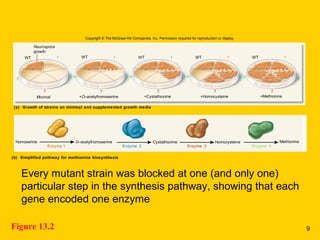
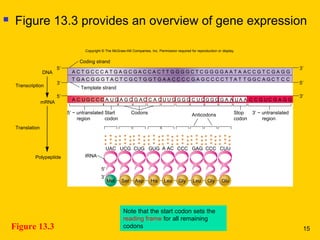
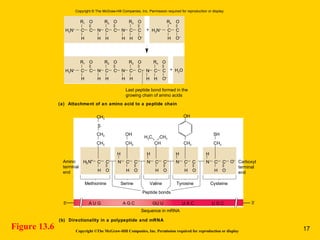
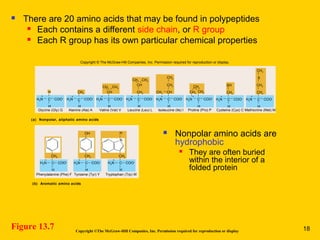
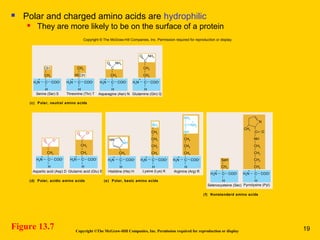
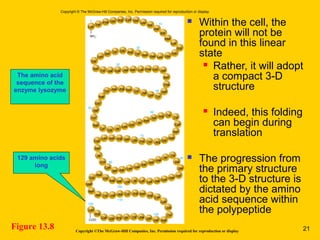
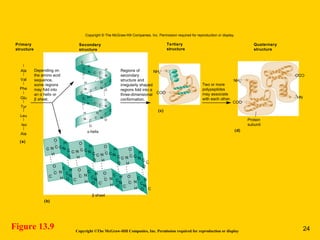
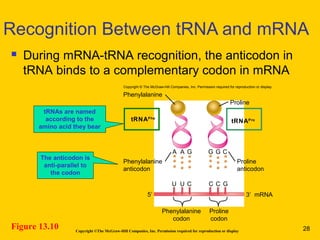
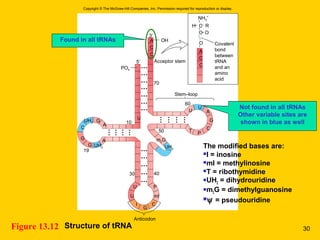
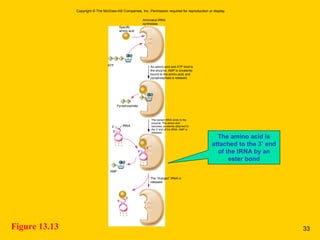
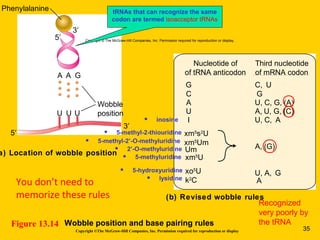
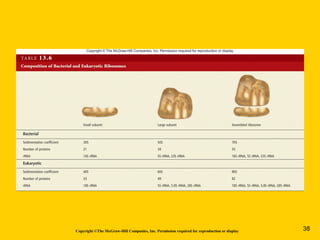
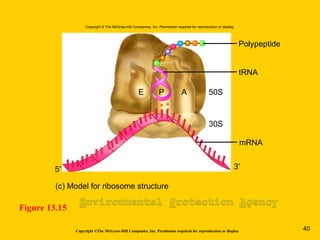
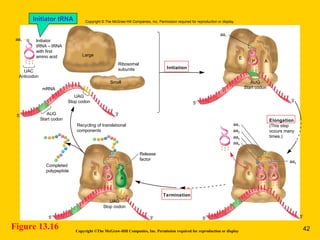
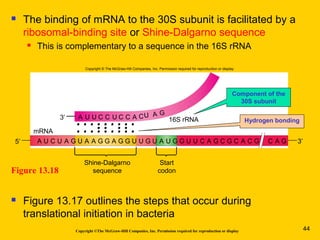
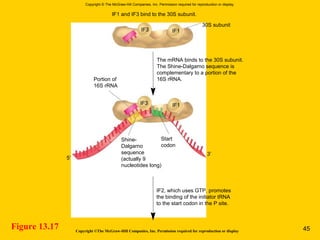
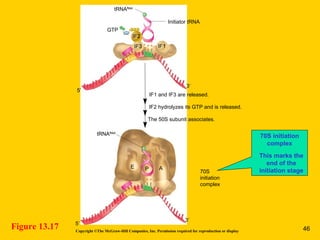
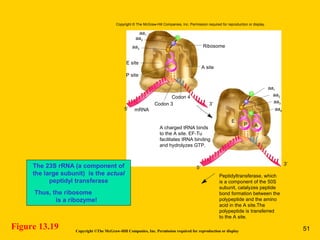
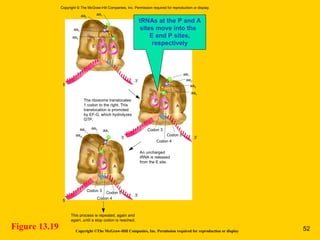
The document discusses the genetic basis for protein synthesis. It begins by explaining how genes encode proteins through transcription of DNA into mRNA and translation of mRNA codons into amino acid sequences. Early scientists like Garrod and Beadle and Tatum established through experiments that genes encode enzymes through a one gene-one polypeptide hypothesis. The genetic code is then explained, where mRNA codons specify 20 amino acids. Translation follows the codon sequences to produce a polypeptide with directionality from N-terminal to C-terminal end.