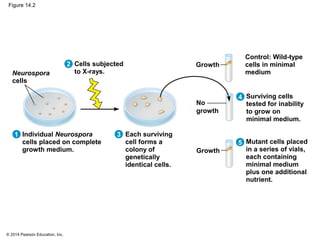
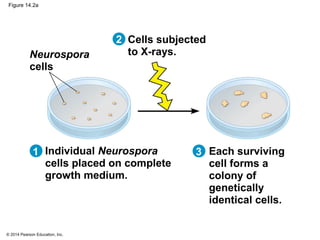
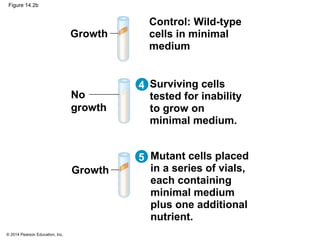
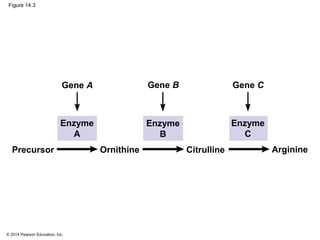
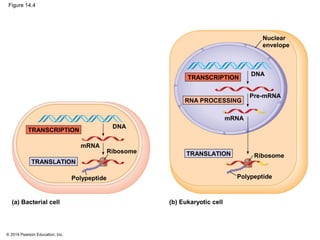
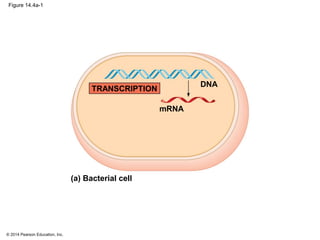
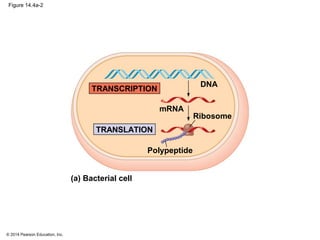
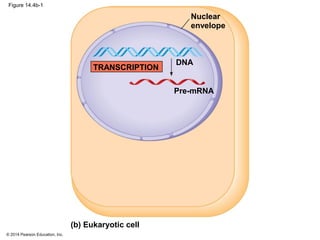
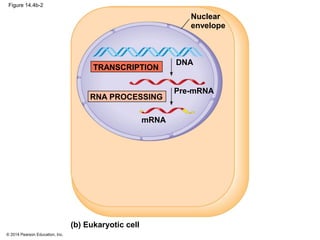
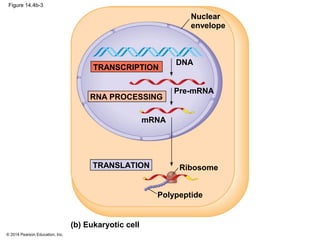
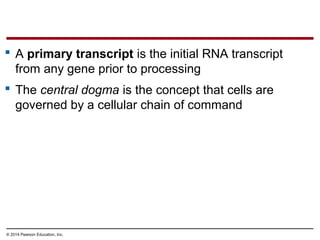
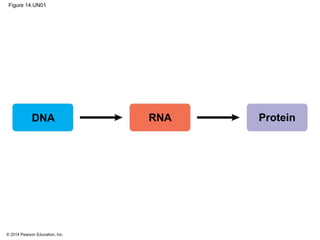
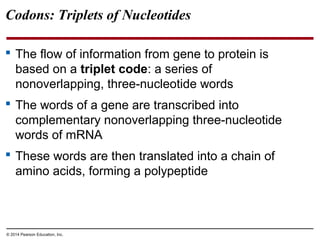
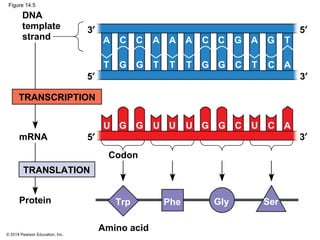
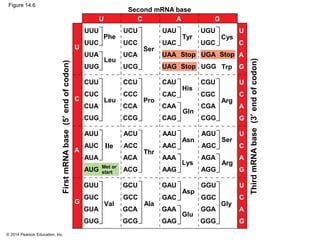
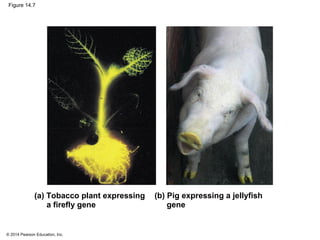
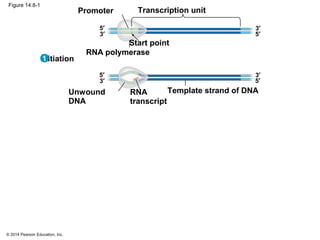
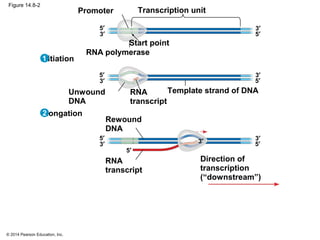
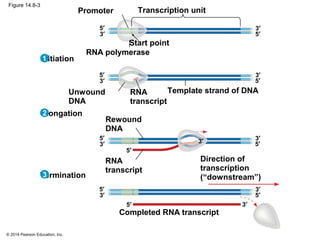
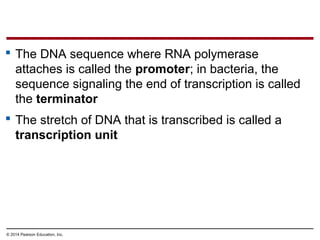
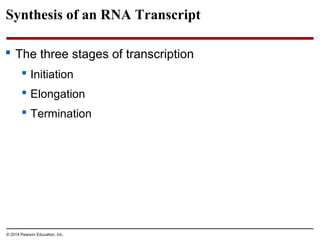
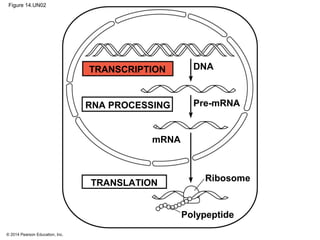
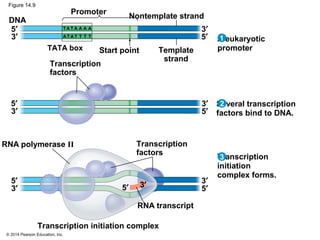
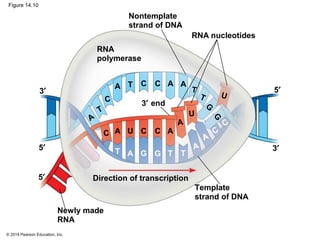
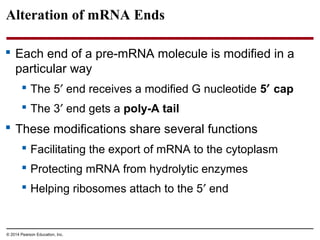
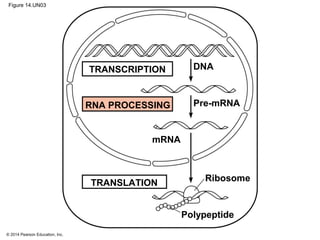
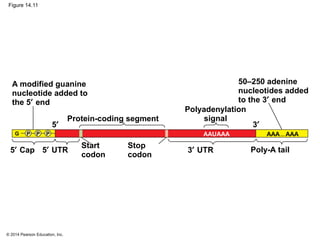
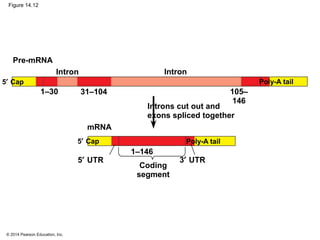
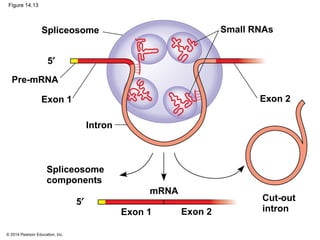
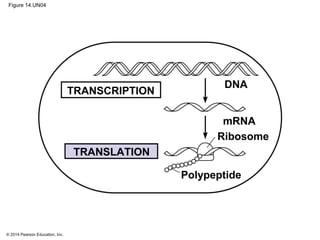
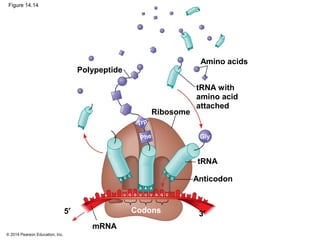
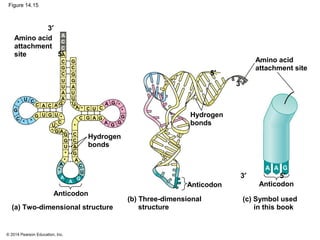
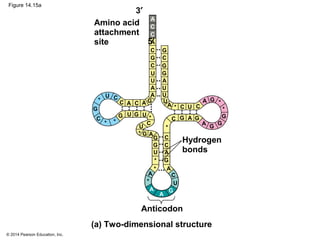
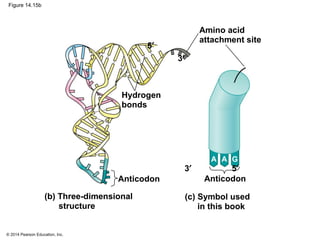
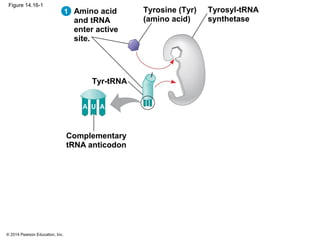
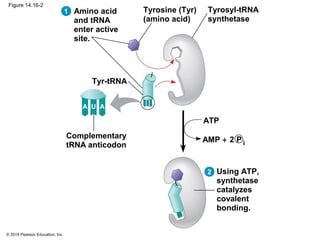
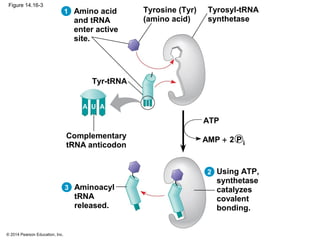
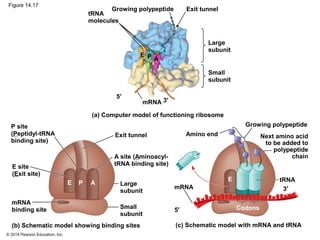
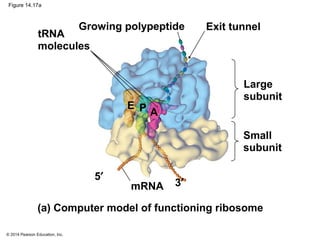
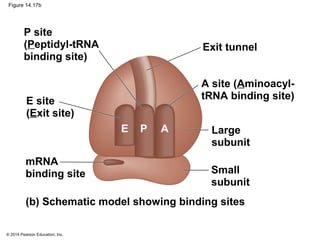
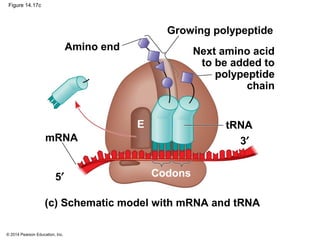
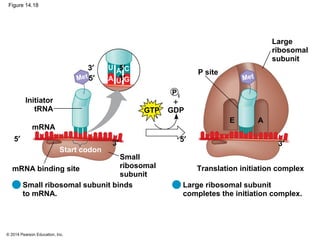
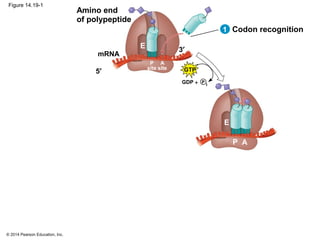
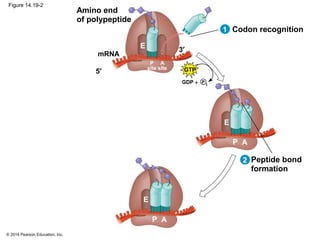
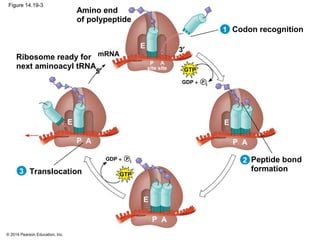
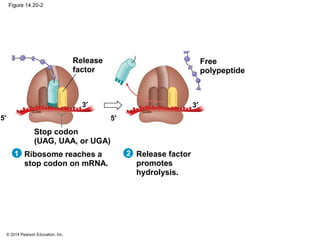
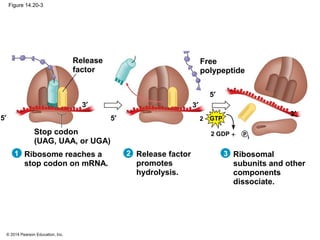
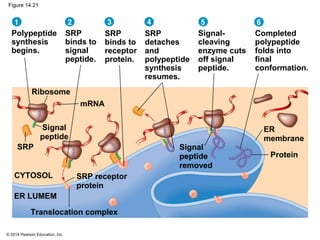
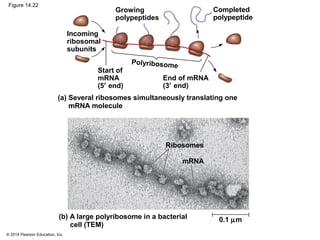
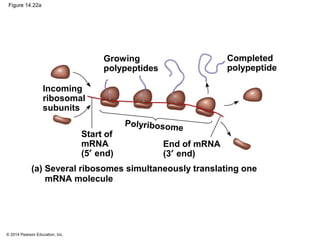
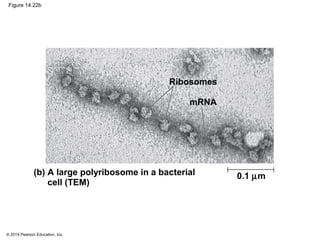
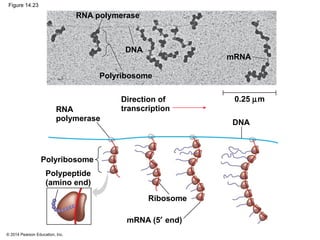
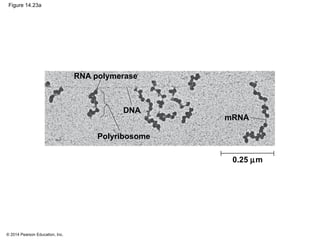
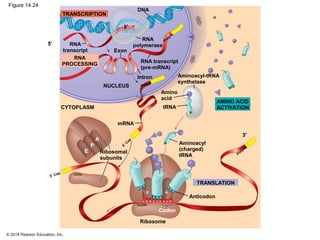
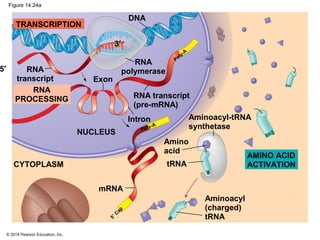
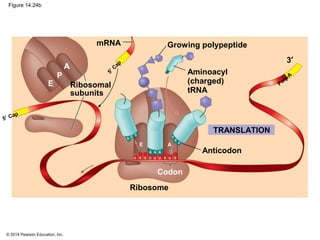
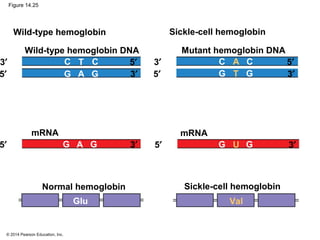
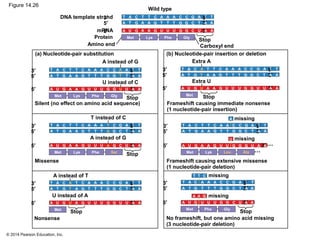
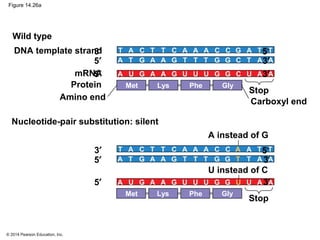
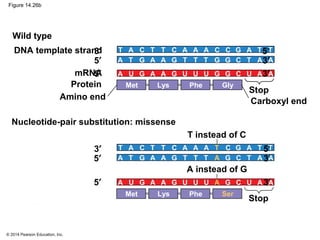
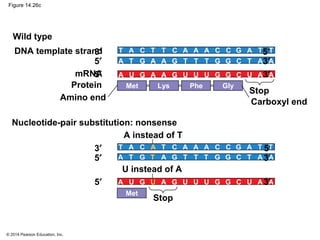
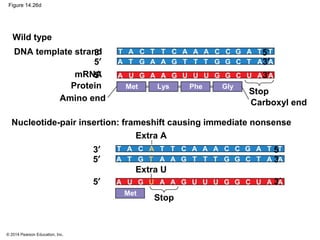
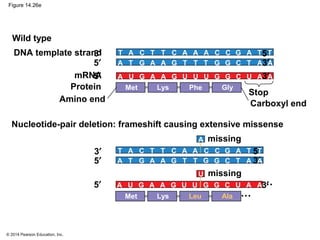
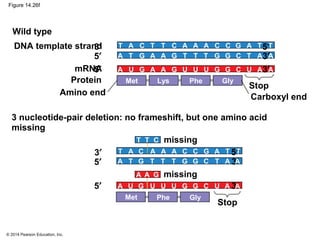
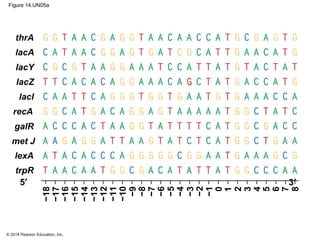
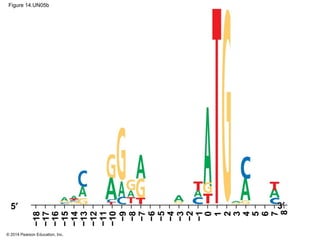
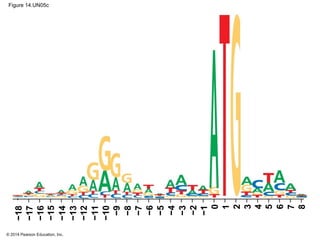
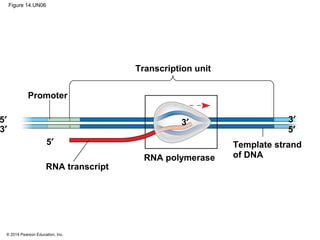
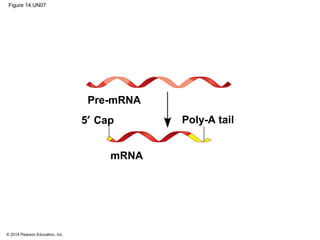
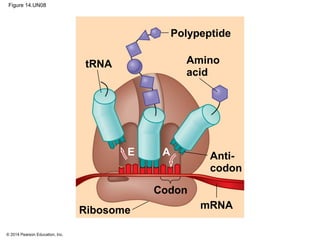
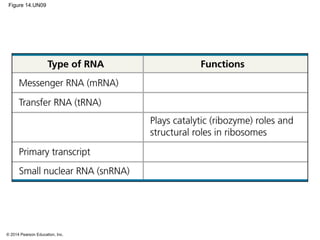
The document discusses gene expression from DNA to protein. It begins by outlining the central dogma that DNA is transcribed into RNA which is then translated into protein. The relationship between genes and proteins was discovered through studies of metabolic defects in bread mold by Beadle and Tatum. Their one gene-one enzyme hypothesis showed that genes dictate phenotypes by encoding enzymes for metabolic pathways. The document then describes the processes of transcription and translation, including the roles of promoters, RNA polymerase, codons, and the universal genetic code. It discusses how the genetic code is cracked and evolution of the nearly universal code across species.