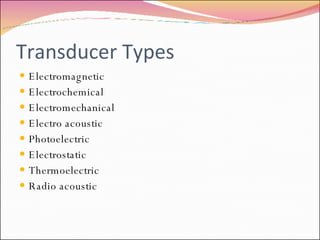
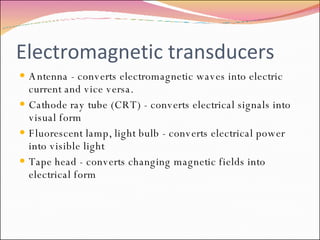
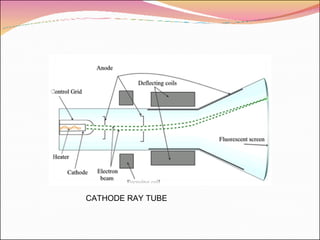
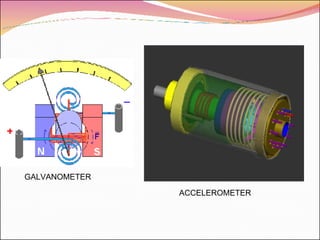
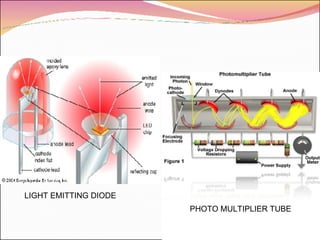
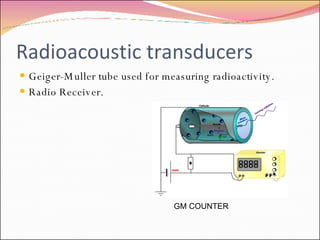
A transducer is a device that converts one form of energy to another. There are several types of transducers including electromagnetic, electrochemical, electromechanical, electroacoustic, photoelectric, electrostatic, thermoelectric, and radioacoustic transducers. Examples of transducers include antennas, microphones, loudspeakers, thermometers, pH probes, accelerometers, light emitting diodes, photomultiplier tubes, electrometers, resistance temperature detectors, and Geiger-Muller tubes. Transducer efficiency is defined as the ratio of output power to input power, with no transducer achieving 100% efficiency due to power losses in the conversion process.