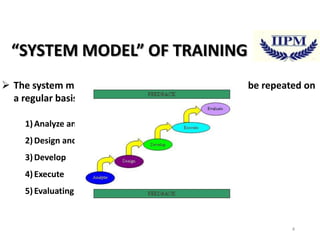
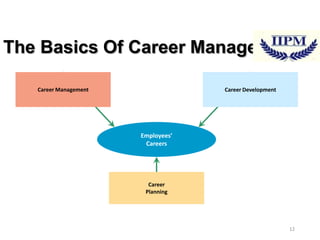
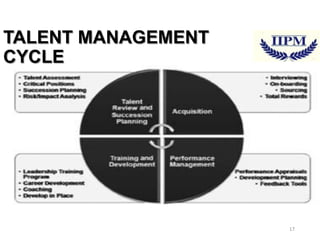
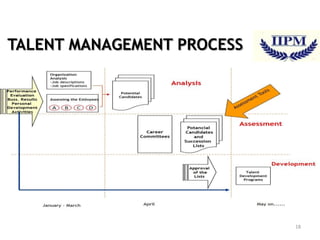
The document discusses training and talent management, outlining the importance of training for skill acquisition and career development. It details various training methods, both on-the-job and off-the-job, along with their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of effective talent management in aligning workforce capabilities with organizational goals.