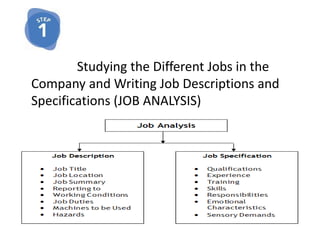
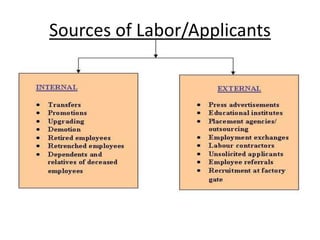
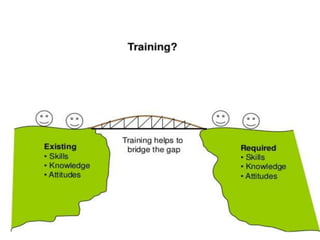
The document discusses the key aspects of staffing, which includes recruiting, selecting, and training employees. It describes staffing as an important managerial function that is pervasive and continuous. The basis of effective staffing is the efficient management of human resources through proper recruitment and selection procedures to place the right employees in the right jobs. The document then covers the different steps involved in recruitment, selection, and training employees. It discusses various training methods commonly used like on-the-job training, classroom training, and management development programs. Finally, it mentions some types of personnel movements like transfer, promotion, and separation.