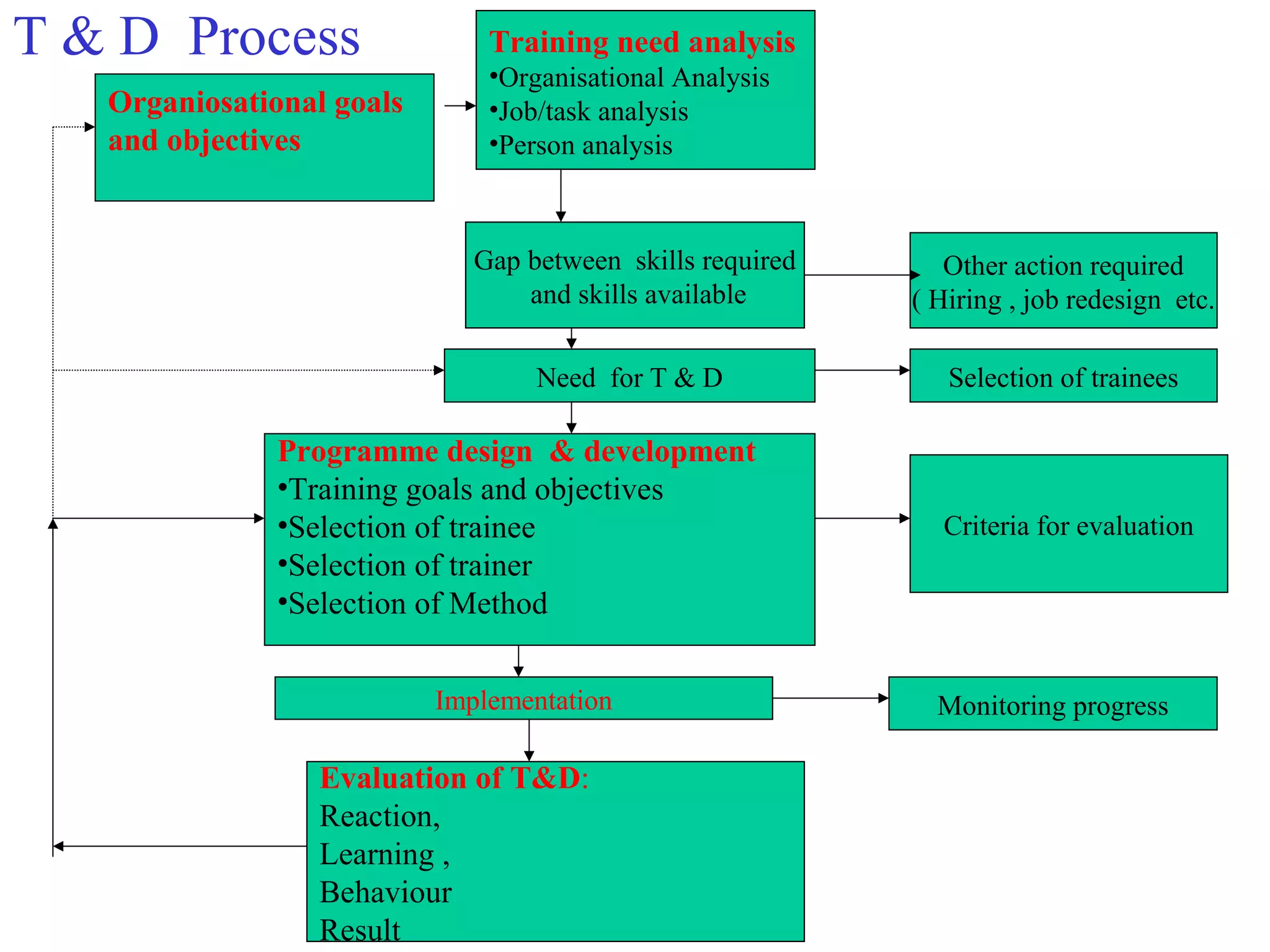
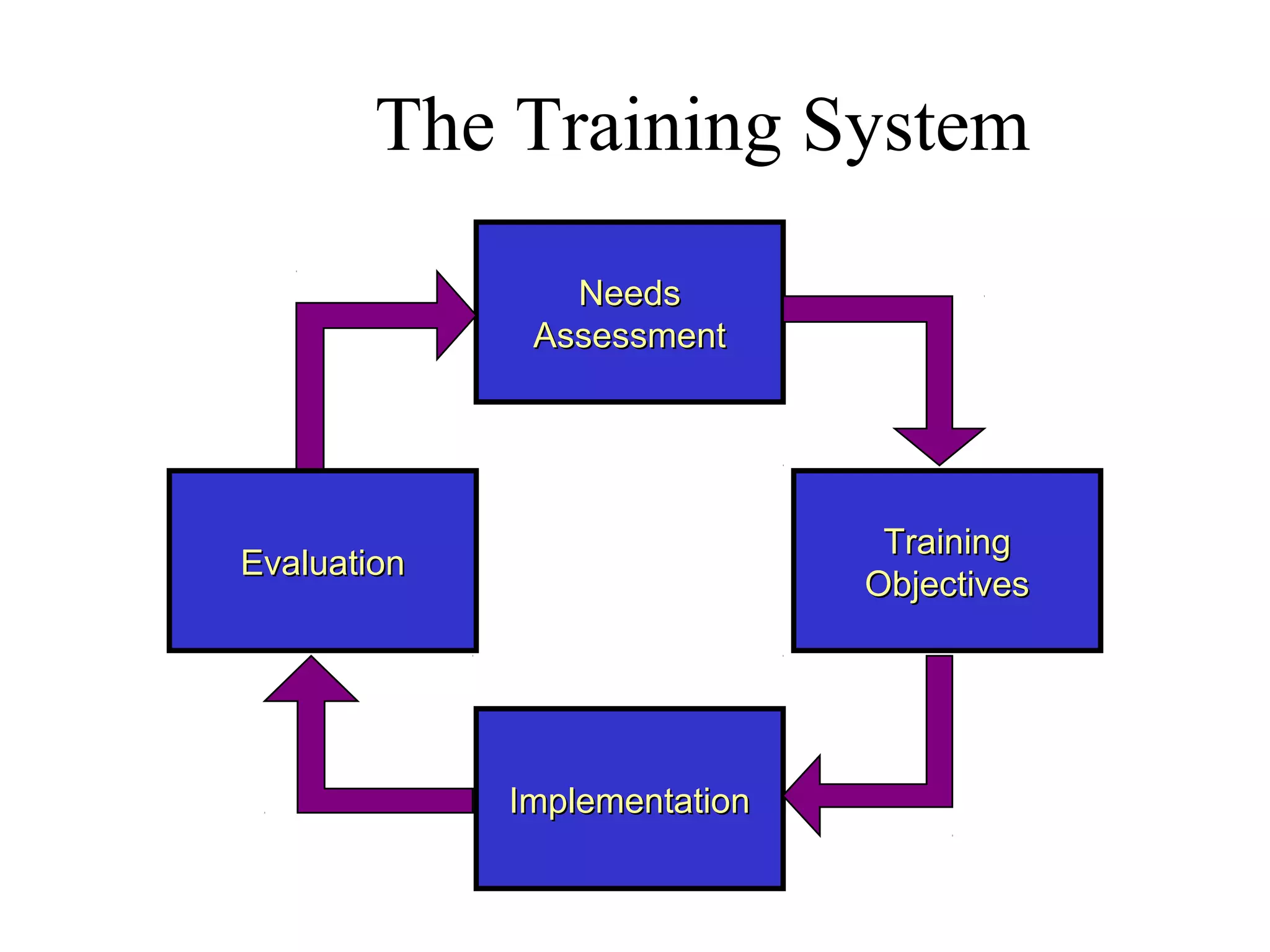
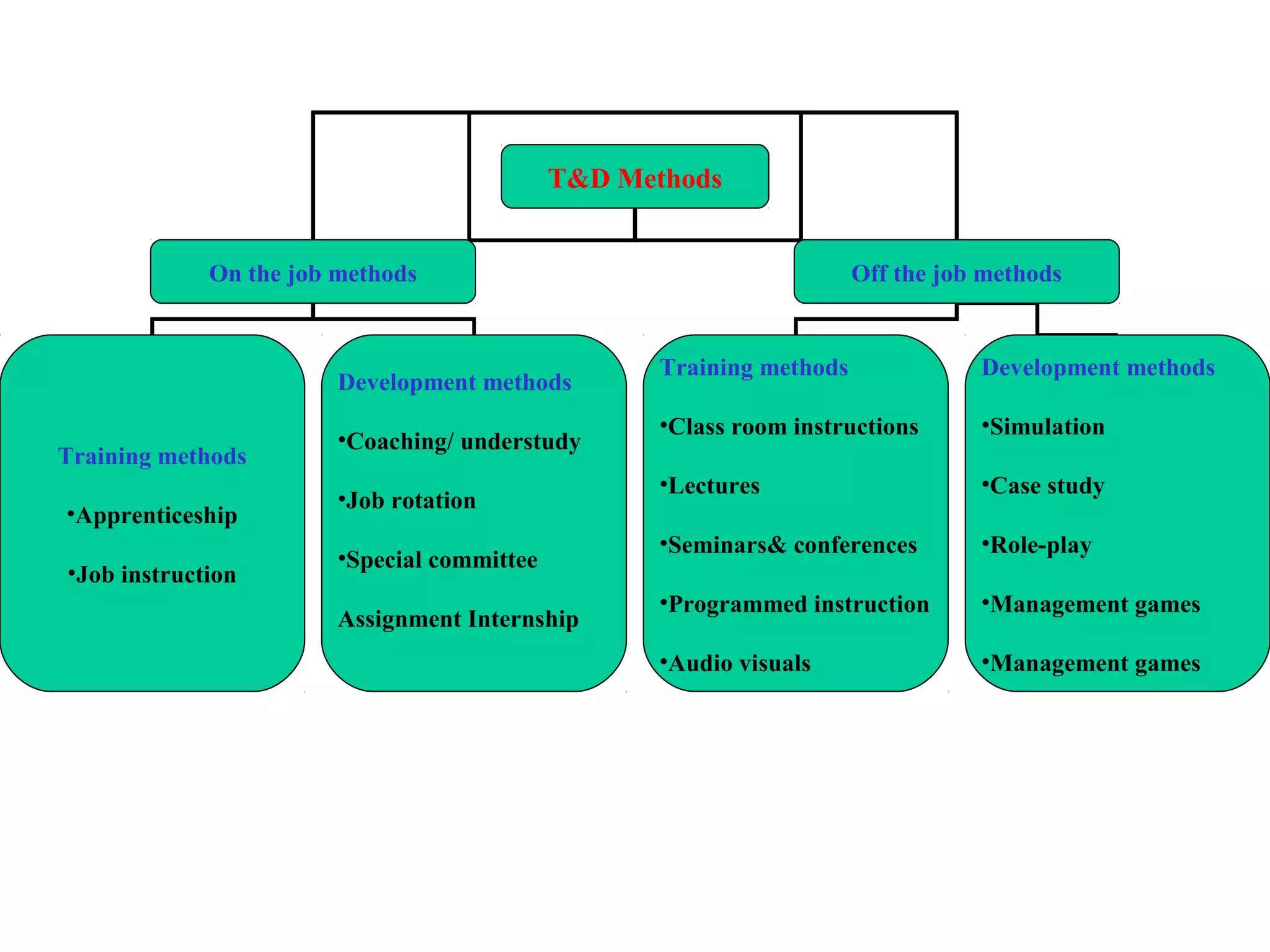
The document compares training and development. Training aims to improve current job performance through imparting technical skills, while development focuses on acquiring skills for future roles through broad, managerial training. Examples of each are provided. The importance, purpose, process, methods, benefits and types of training and development are also outlined.