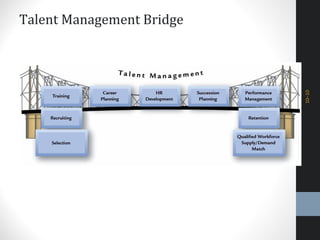
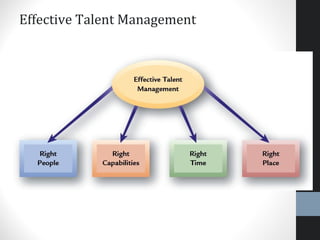
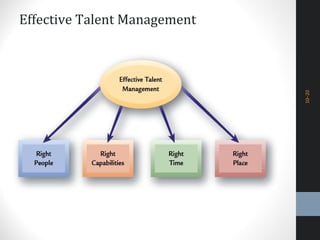
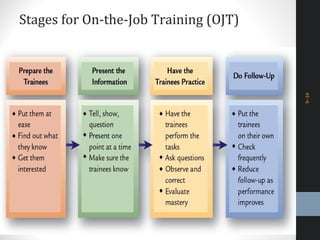
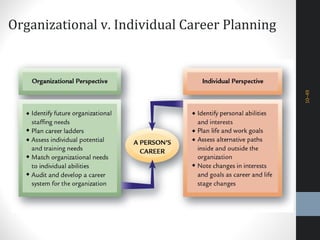
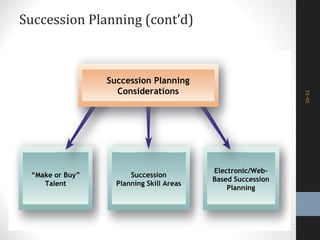
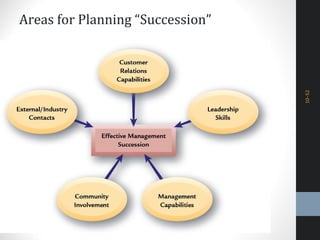
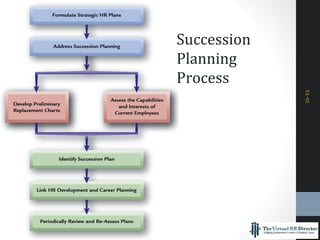
The document outlines a comprehensive talent management strategy for organizations, detailing processes from recruitment to employee onboarding, performance management, and career development. Key elements include creating a strategic plan, effective recruitment methodologies, onboarding practices, and establishing performance management systems aligned with organizational goals. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of employee engagement and succession planning to enhance retention and organizational effectiveness.