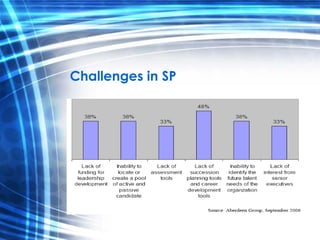
The document discusses talent management and career development, emphasizing a systematic approach to succession planning to build leadership capabilities within organizations. It highlights the importance of developing internal talent to align with strategic goals, addressing contemporary challenges such as changing demographics and the evolving nature of work. Additionally, it outlines the characteristics of a protean career, which is self-driven and adaptable to change.