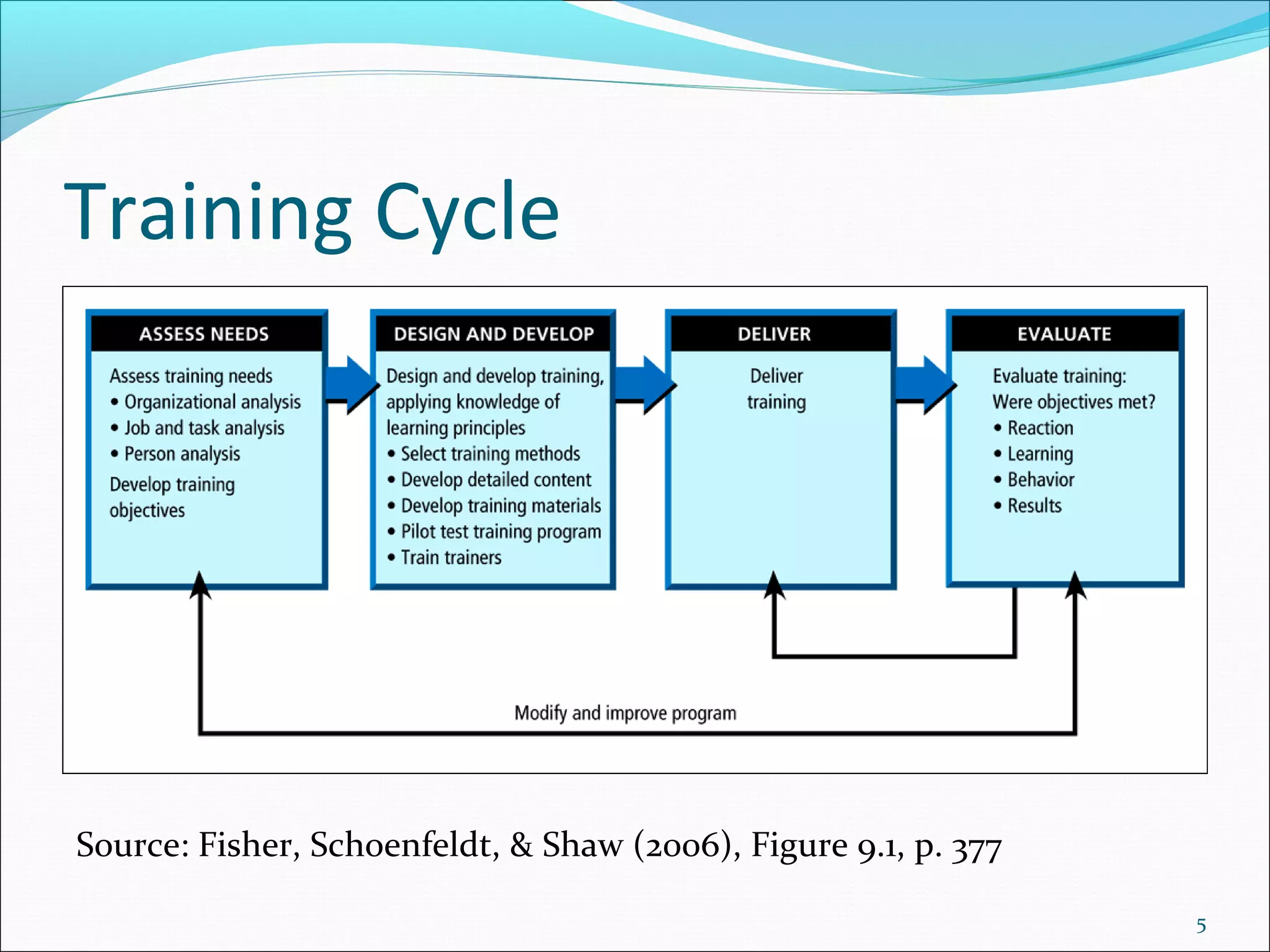
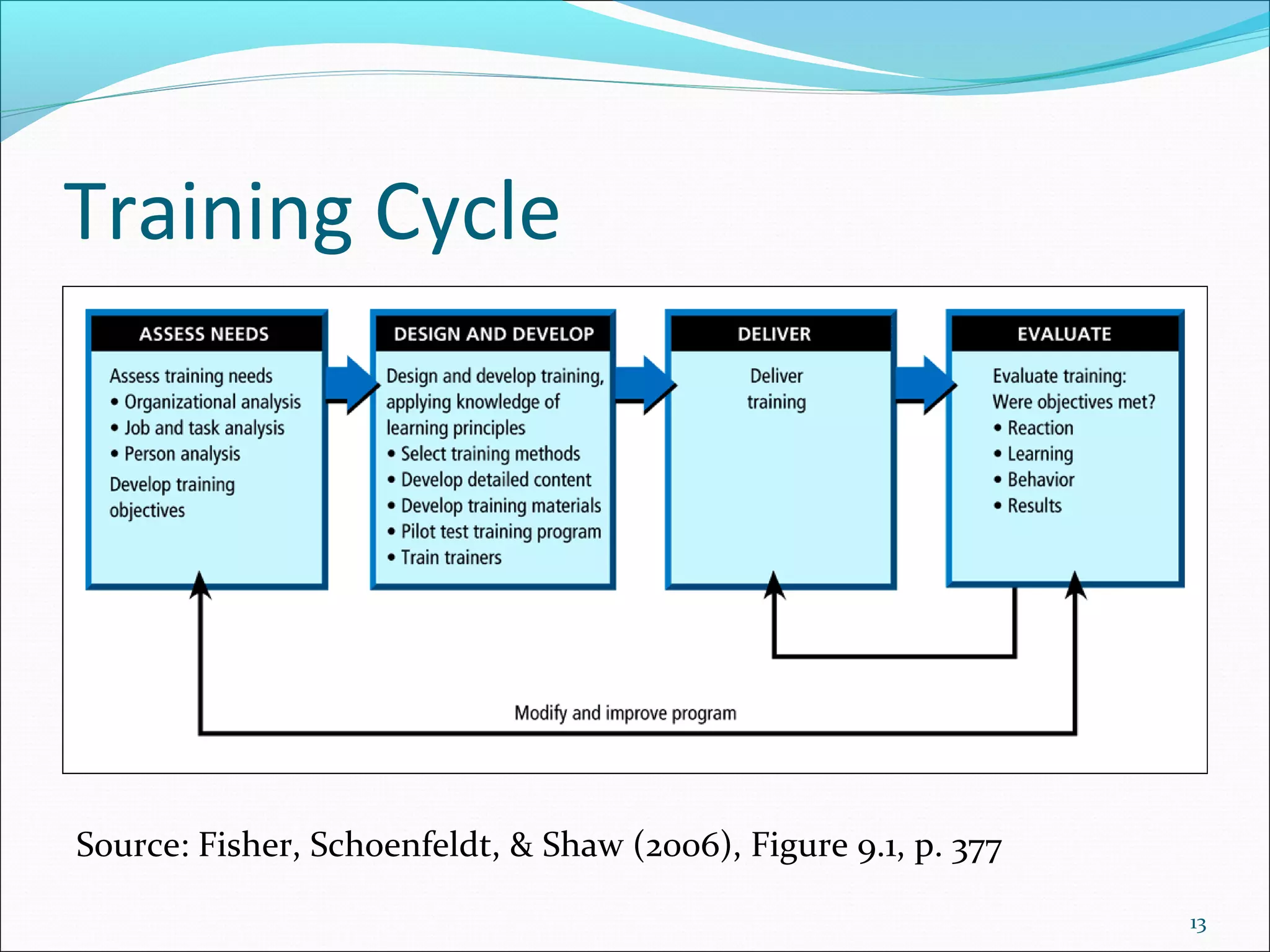
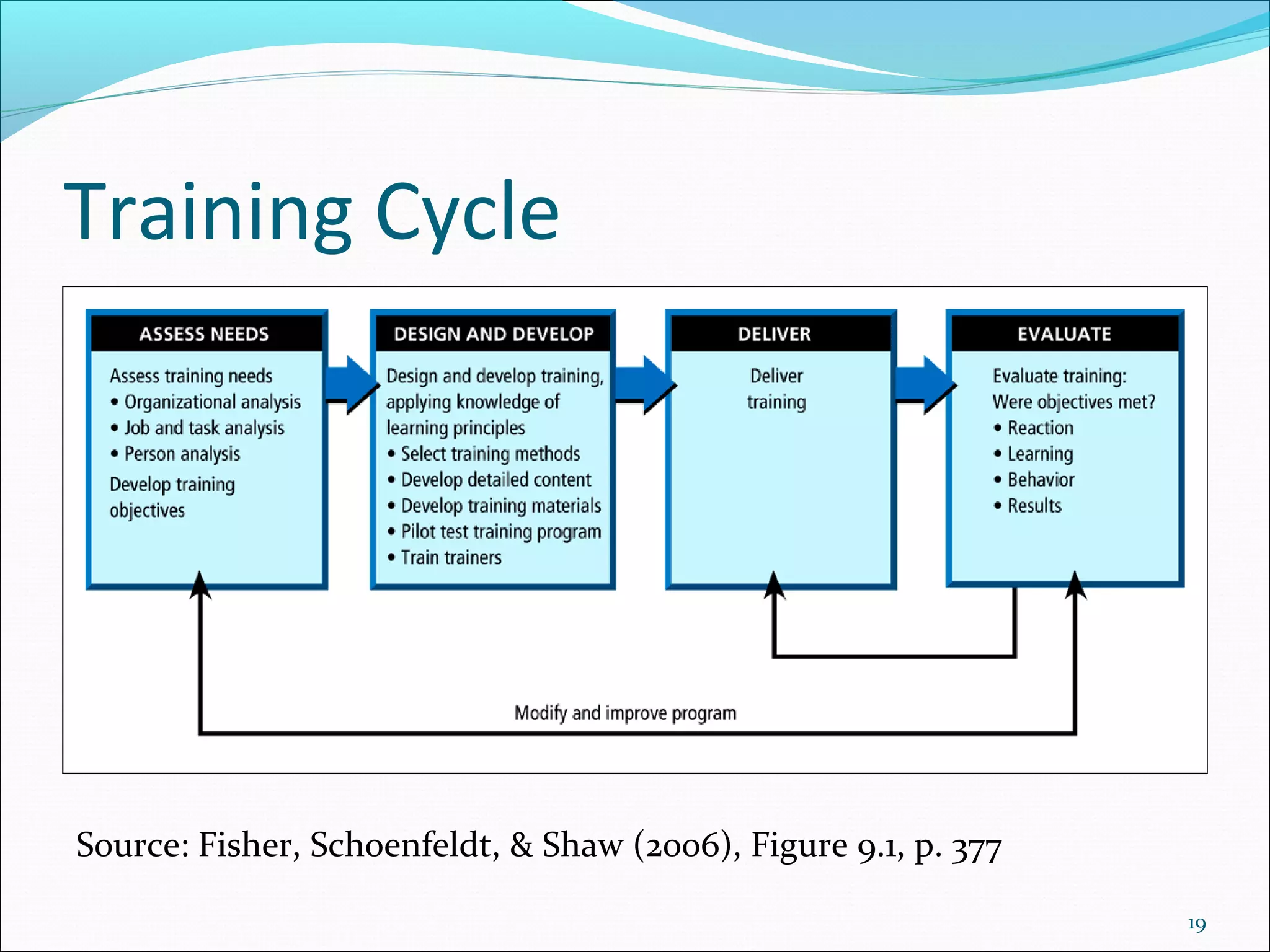
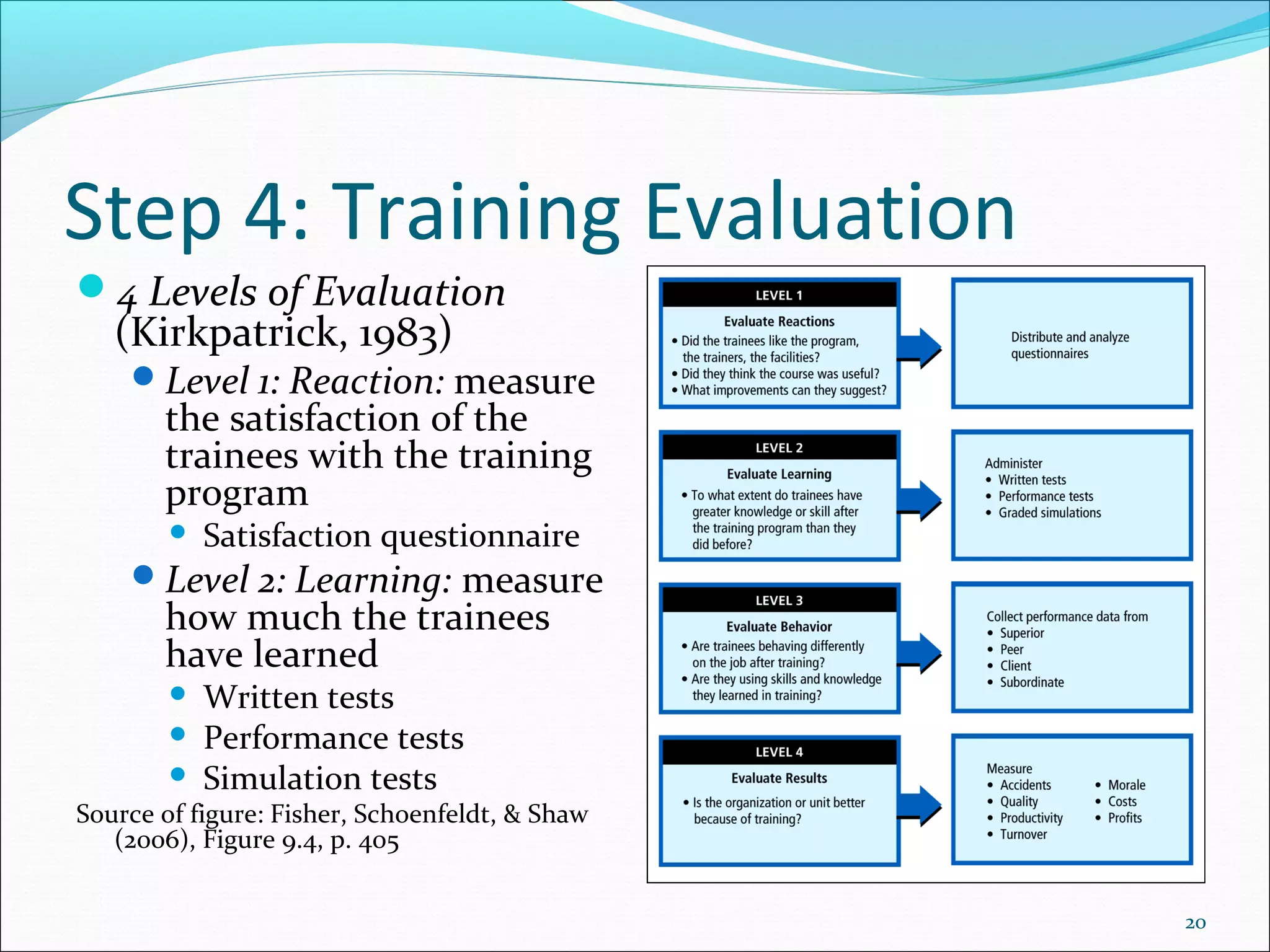
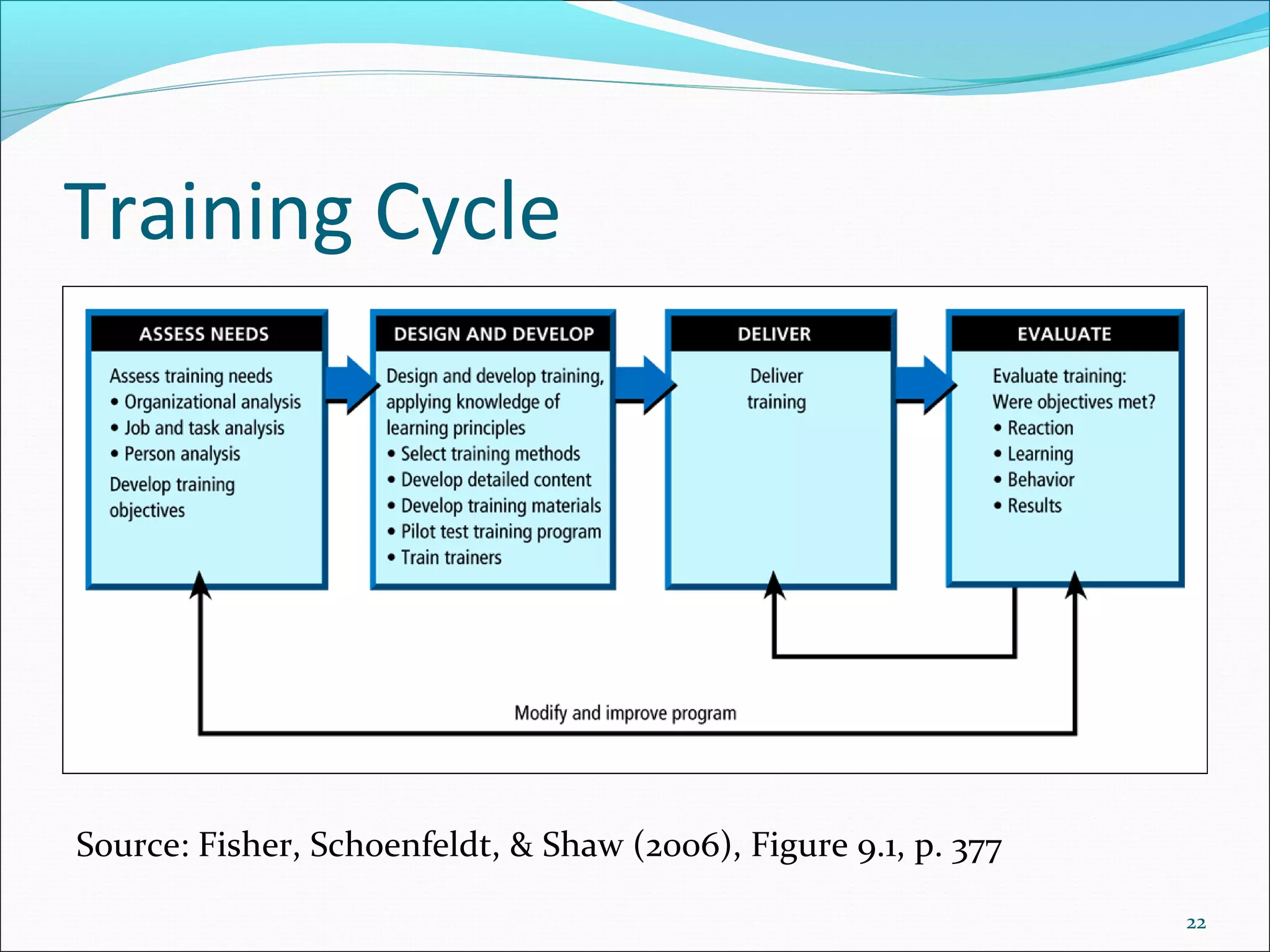
The document outlines the typical training cycle which includes 4 steps: 1) conducting a needs analysis to identify training needs at the organizational, job, and individual level, 2) designing and developing the training program using various training methods and considering how people learn, 3) delivering the training, and 4) evaluating the training using Kirkpatrick's 4 levels which measure reaction, learning, behavior, and results.