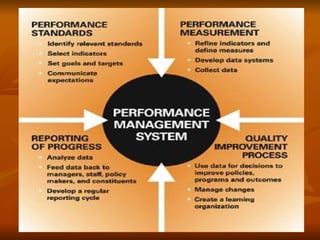
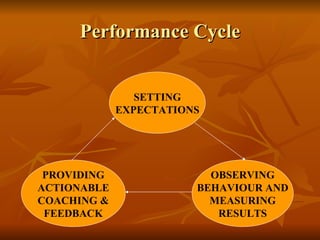
The document discusses performance management systems (PMS), which provide a structured approach to communicate business strategy, establish performance expectations, facilitate management, and measure and motivate performance. A key part of PMS is setting employee performance expectations, maintaining ongoing performance dialogue, and conducting annual performance appraisals. PMS also includes procedures for addressing underperformance, encouraging development, training managers, and resolving disputes. The goals of PMS are to guide employee efforts, assess individuals, teams, and the organization, and inform decisions around promotions, pay, and training needs.