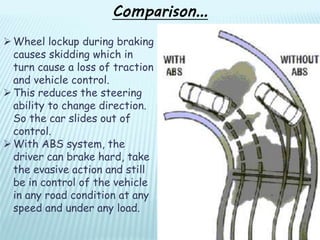
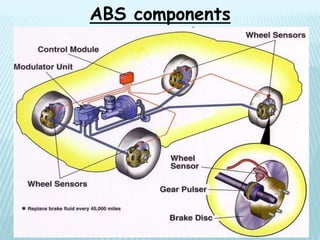
The document presents information about anti-lock braking systems (ABS). It begins with an introduction that defines ABS and describes how it works to improve vehicle control and stopping distances. The document then discusses the history of ABS development from the 1920s to modern systems. It provides details on the working principles of ABS, including how electronic control units and wheel speed sensors allow ABS to continuously monitor and modulate brake pressure to prevent wheel lockup. The document concludes by discussing the advantages of ABS in maintaining vehicle stability and control during braking.