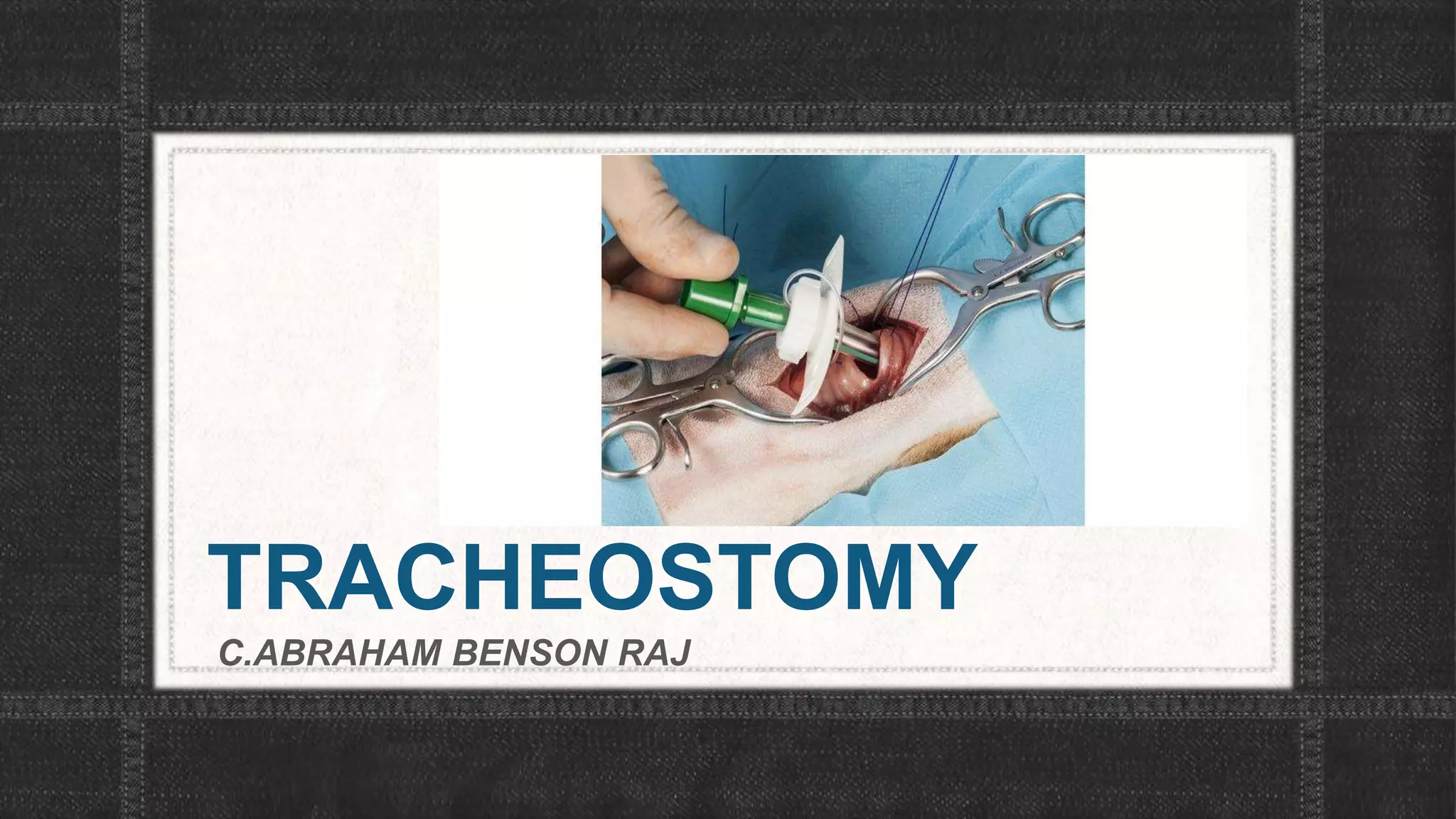
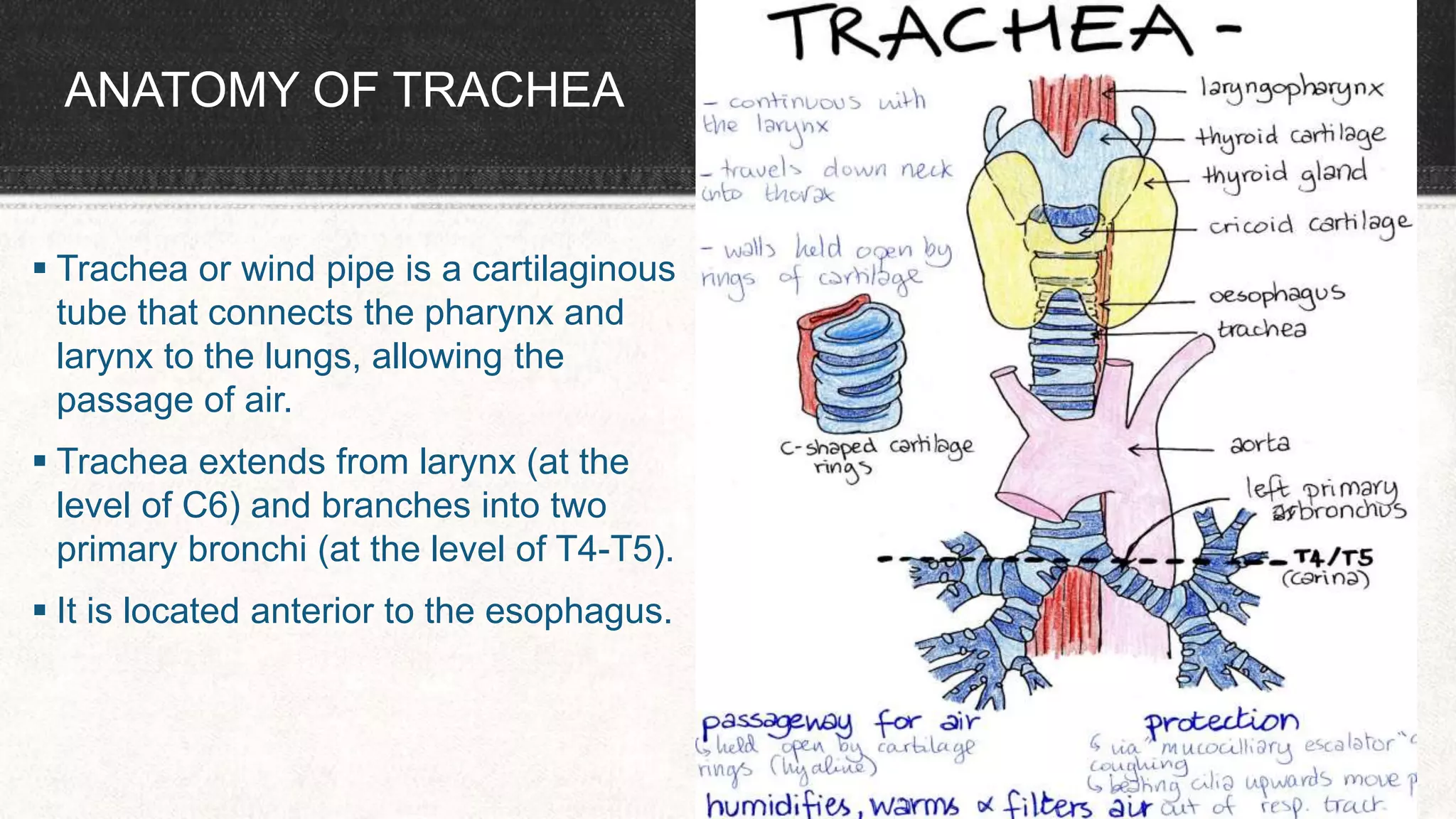
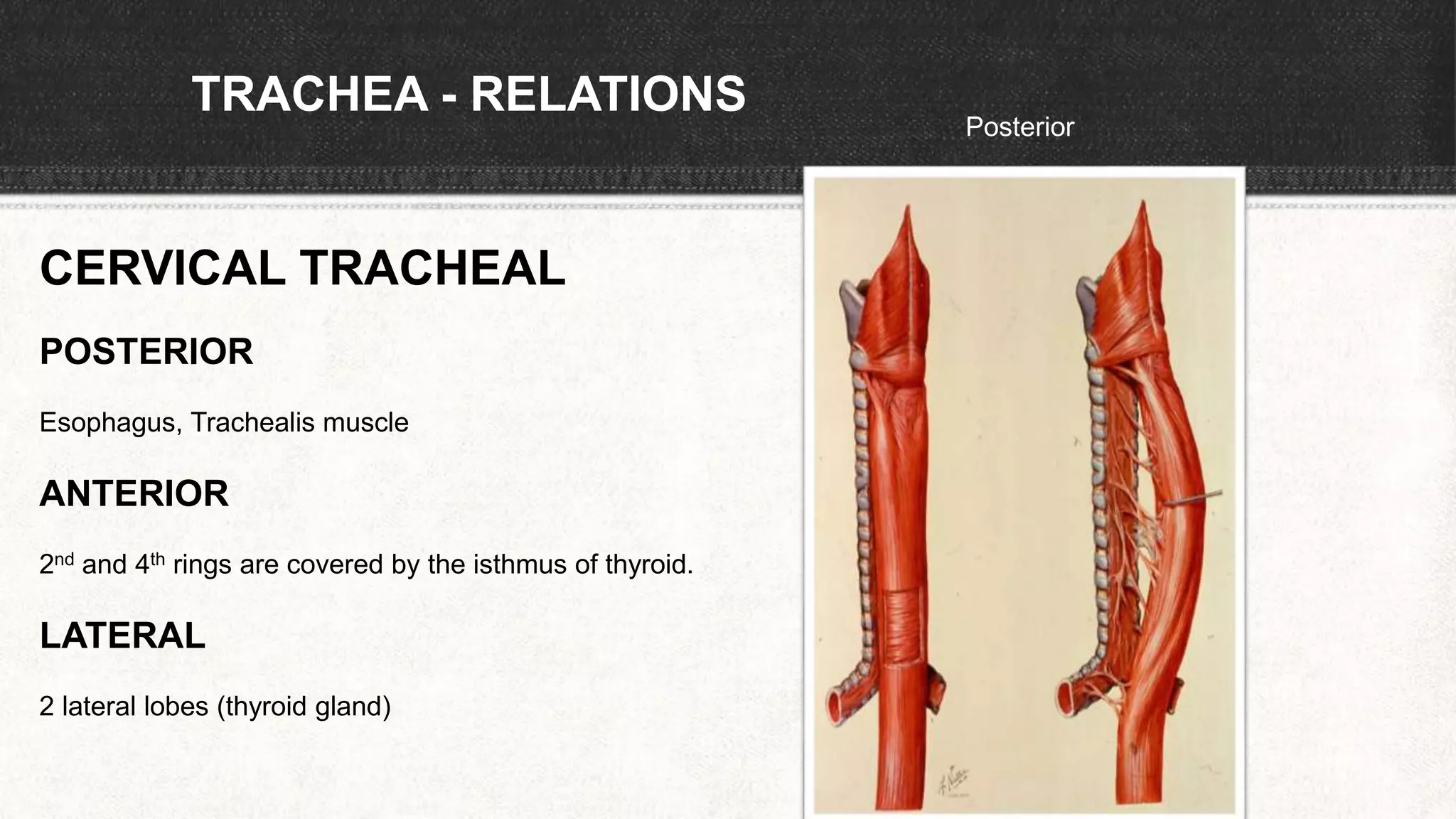
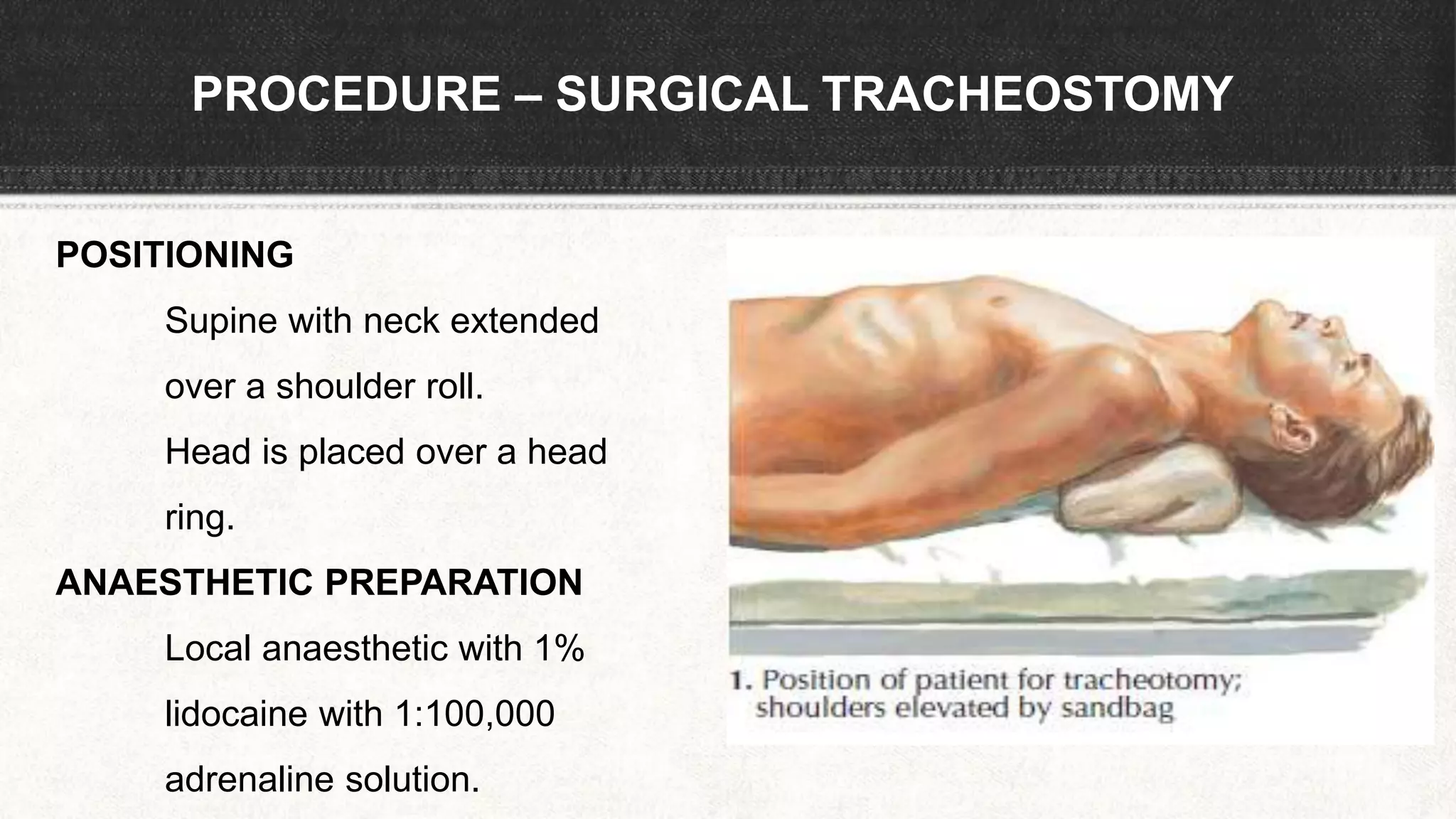
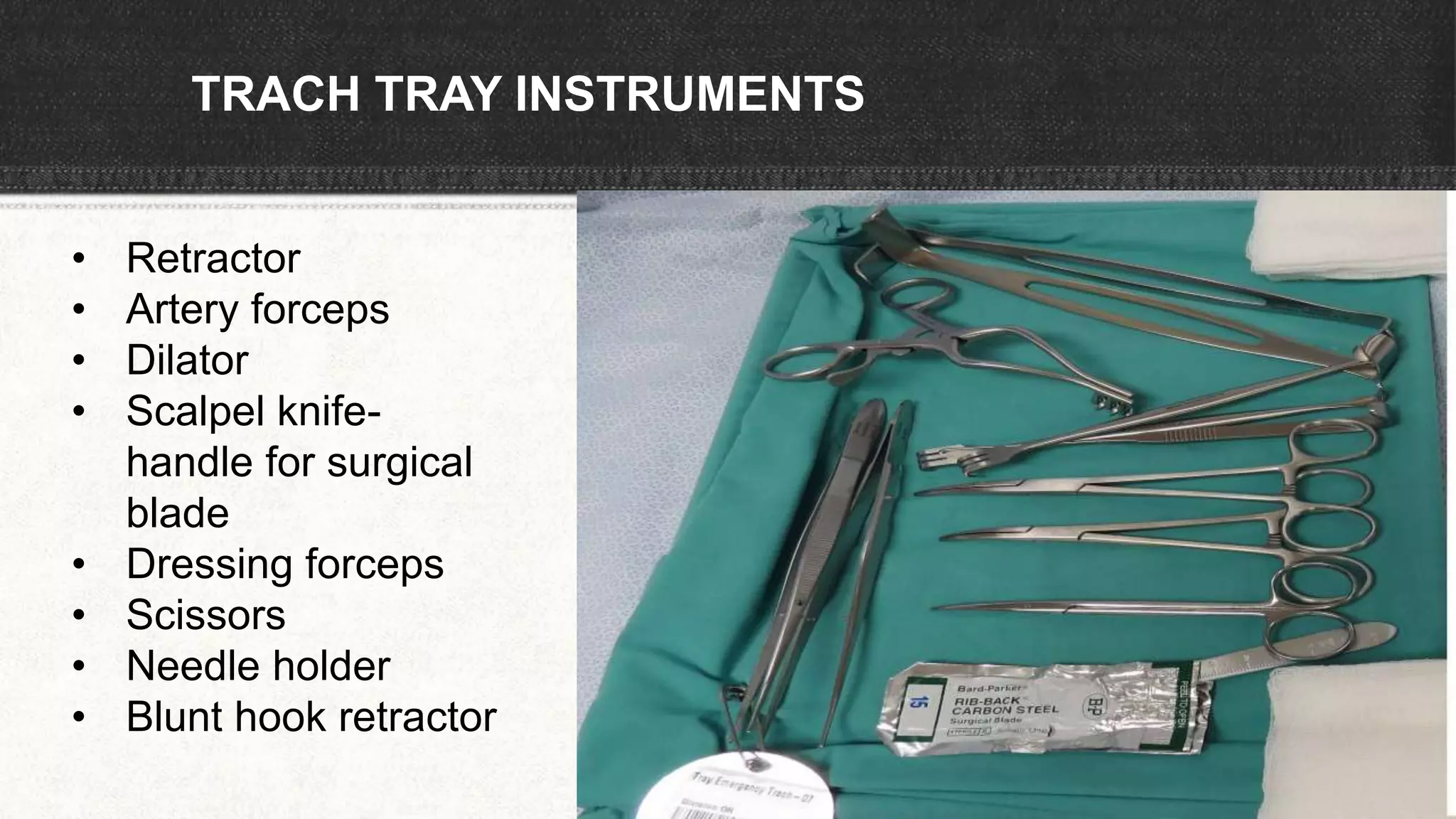
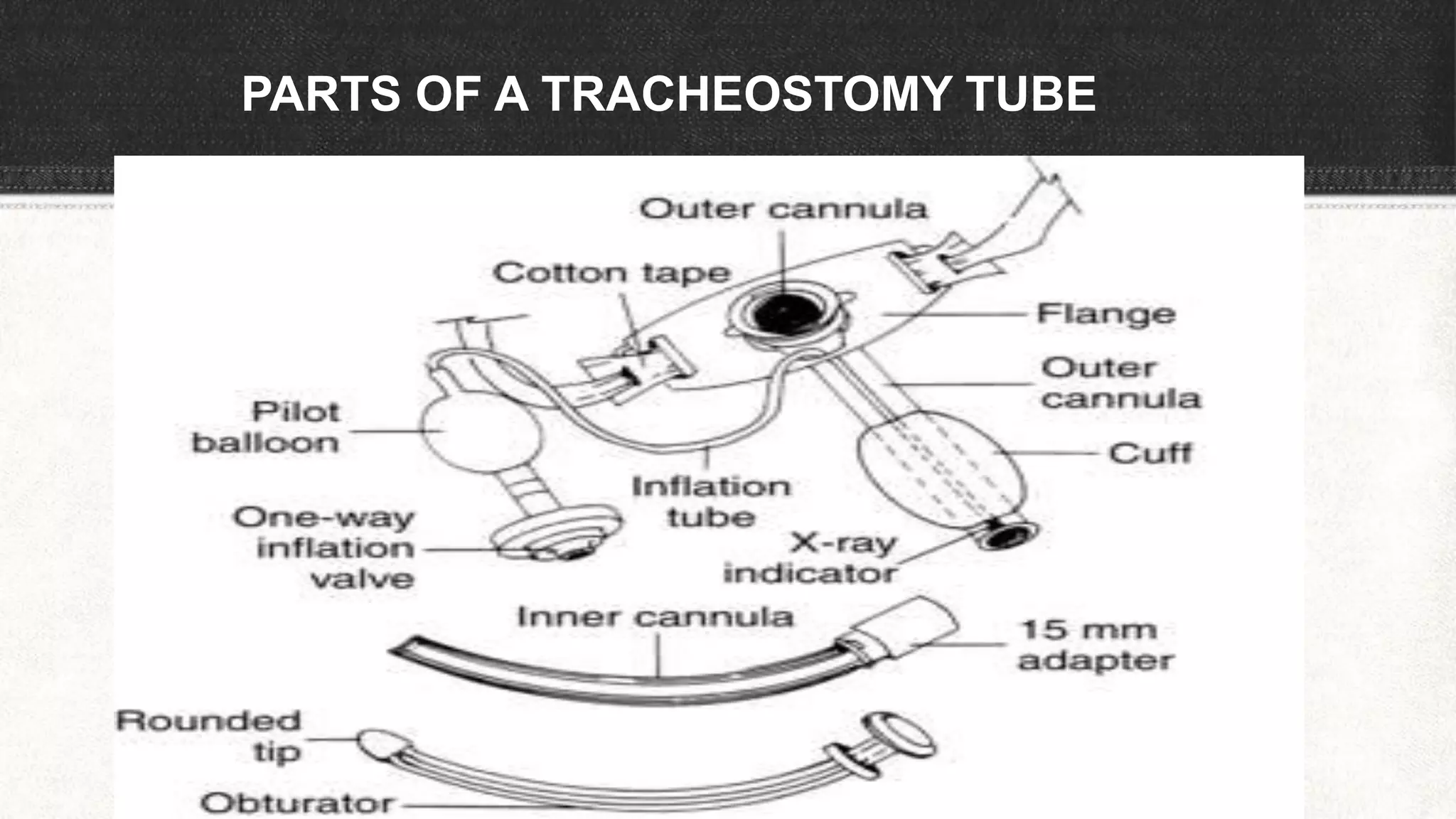
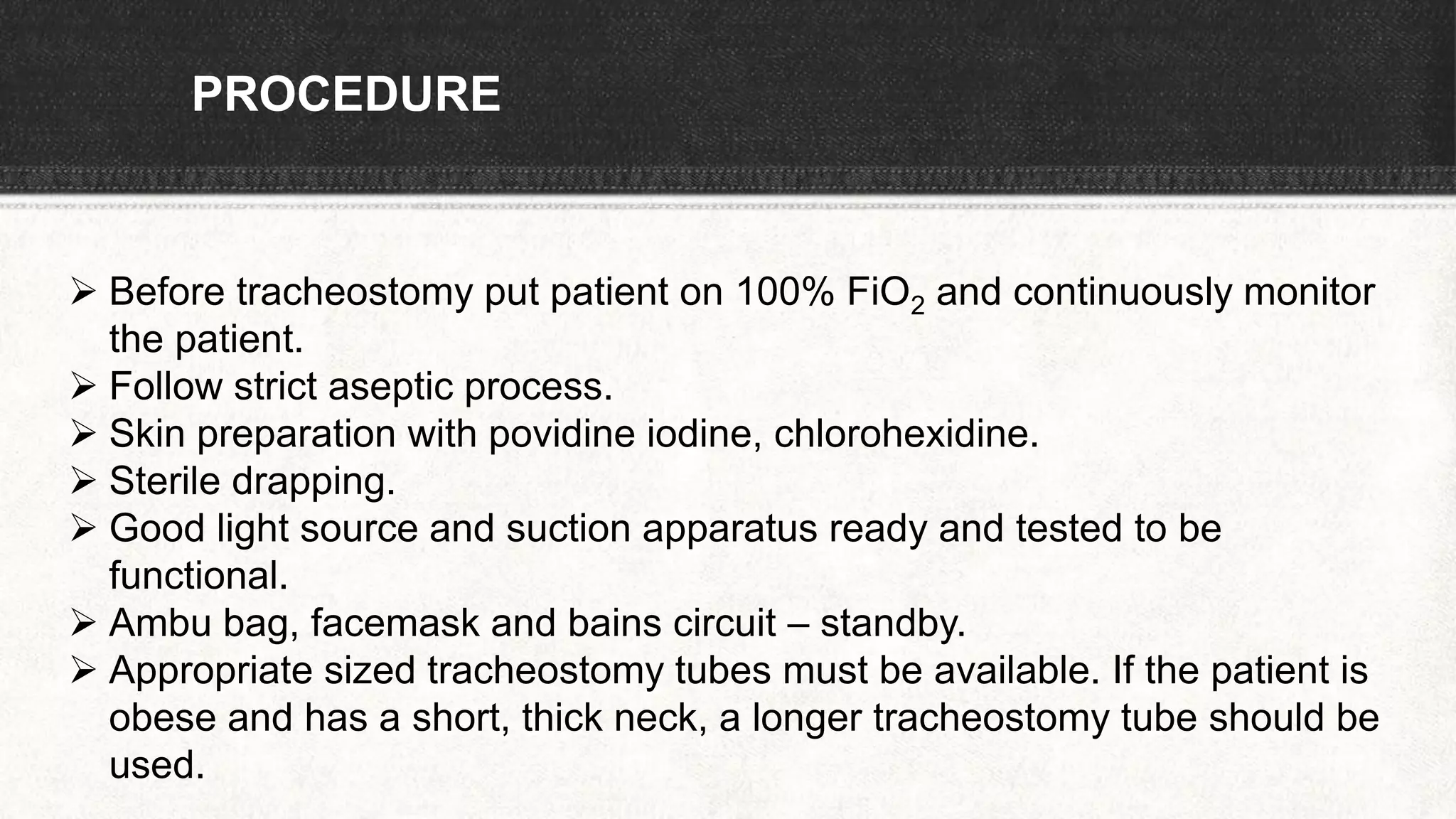
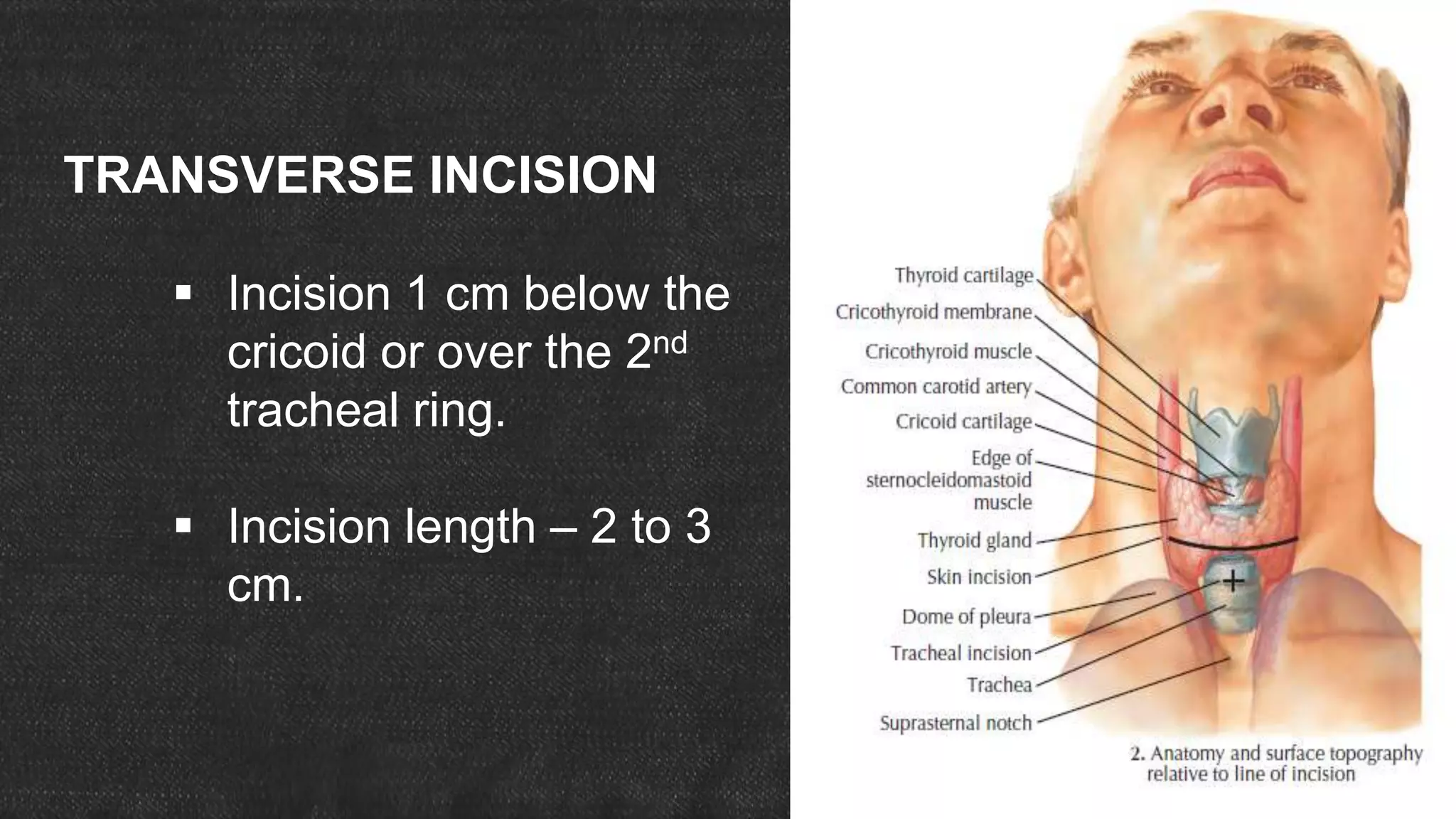
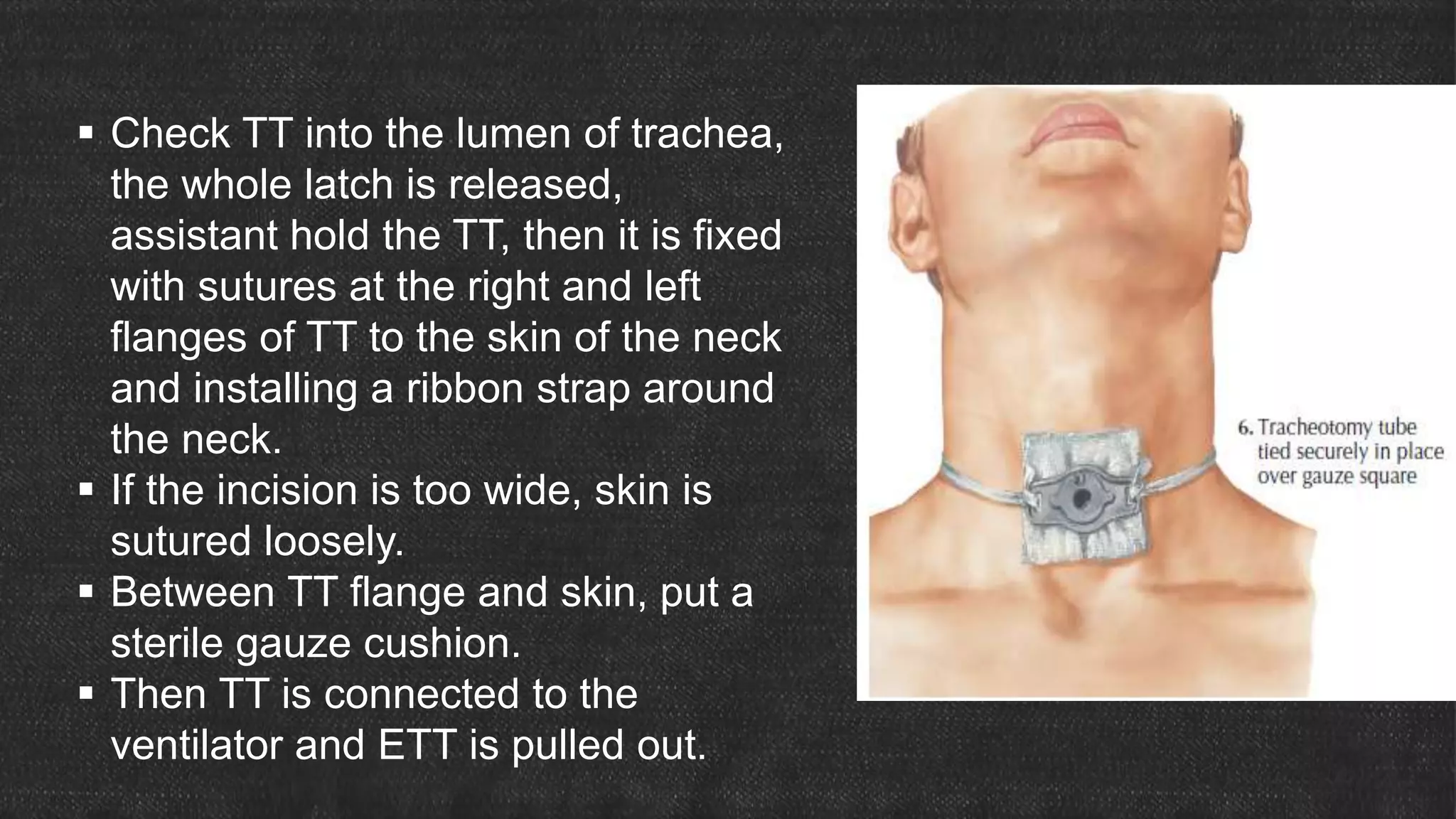
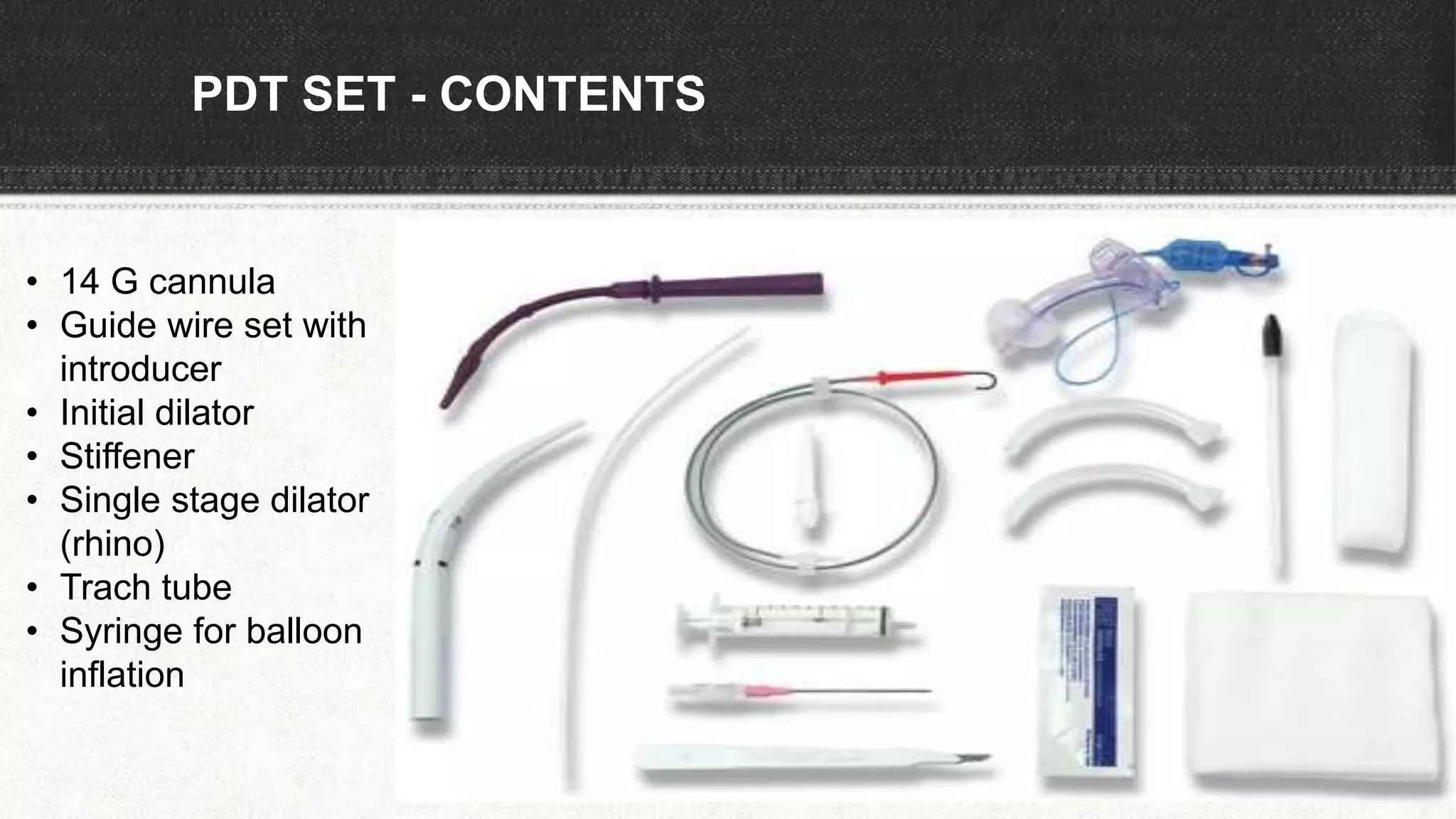
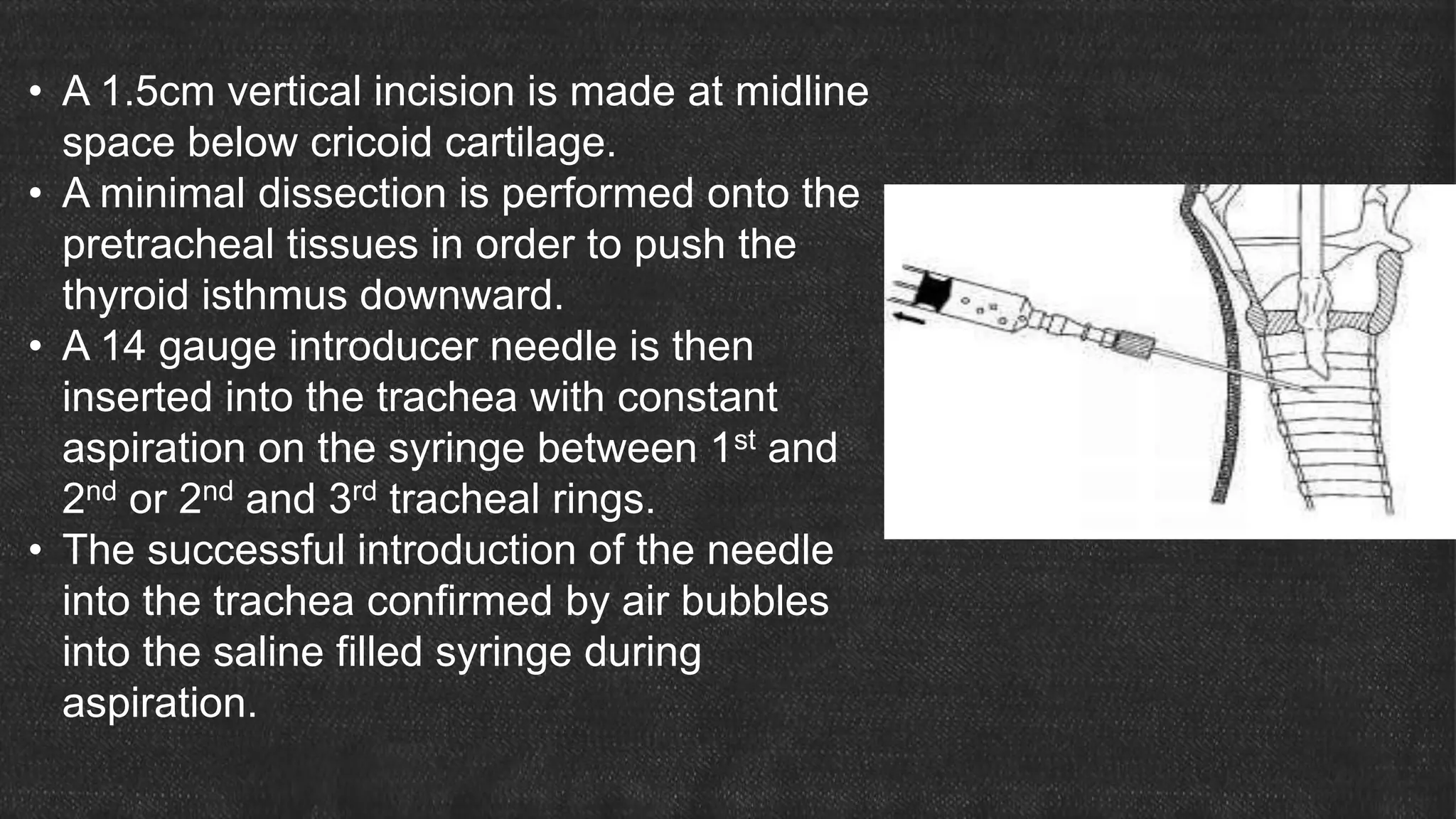
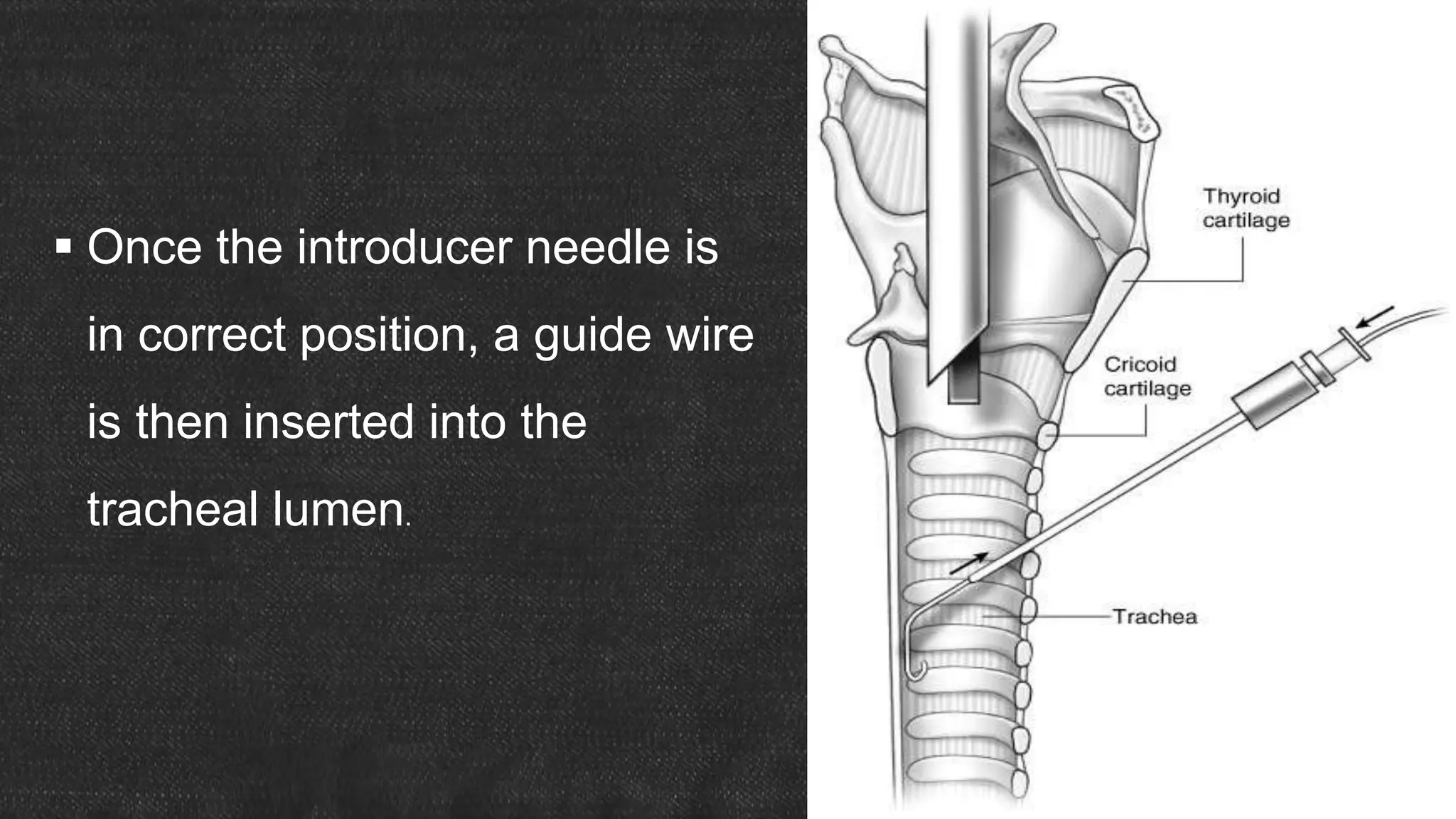
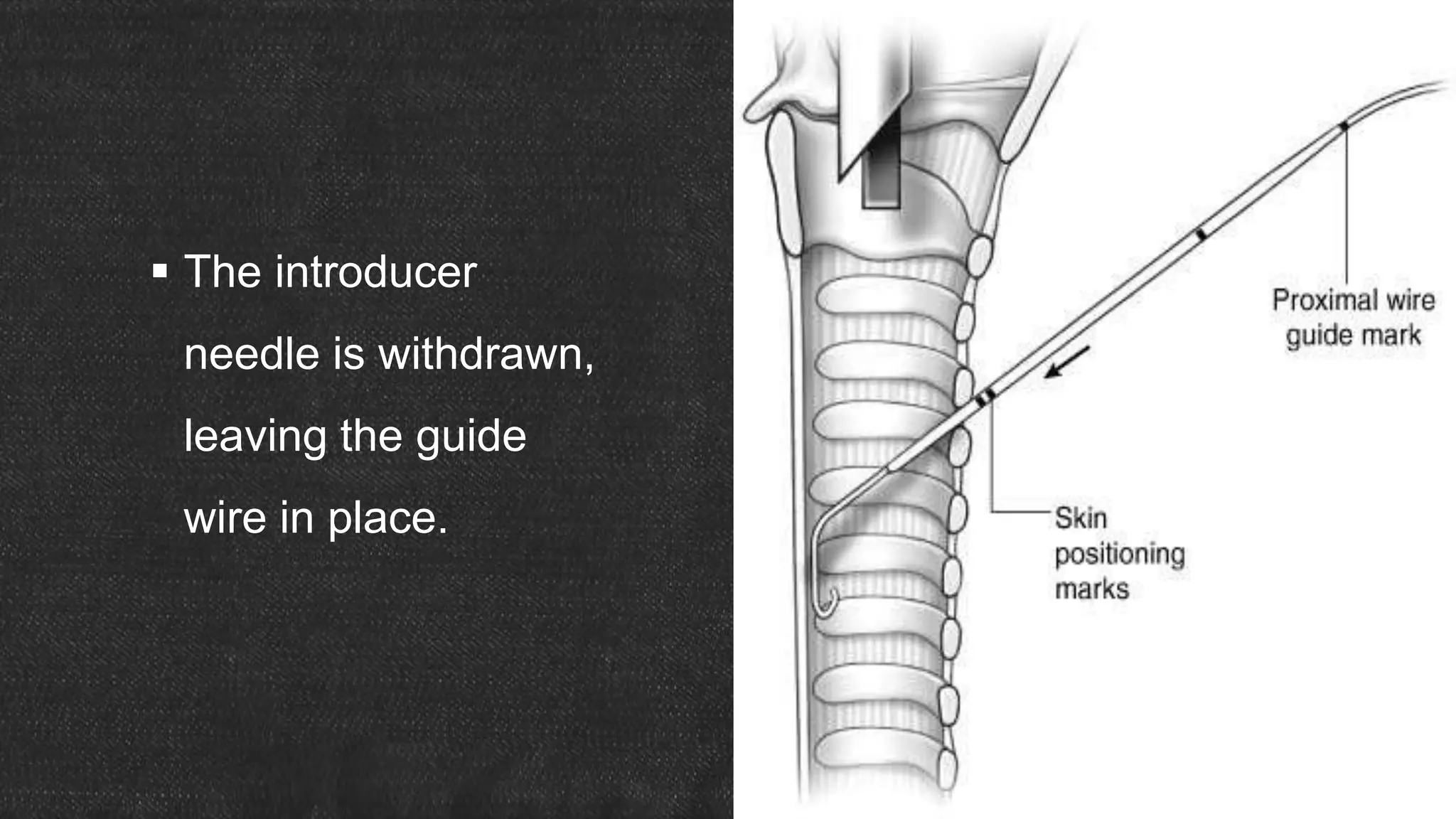
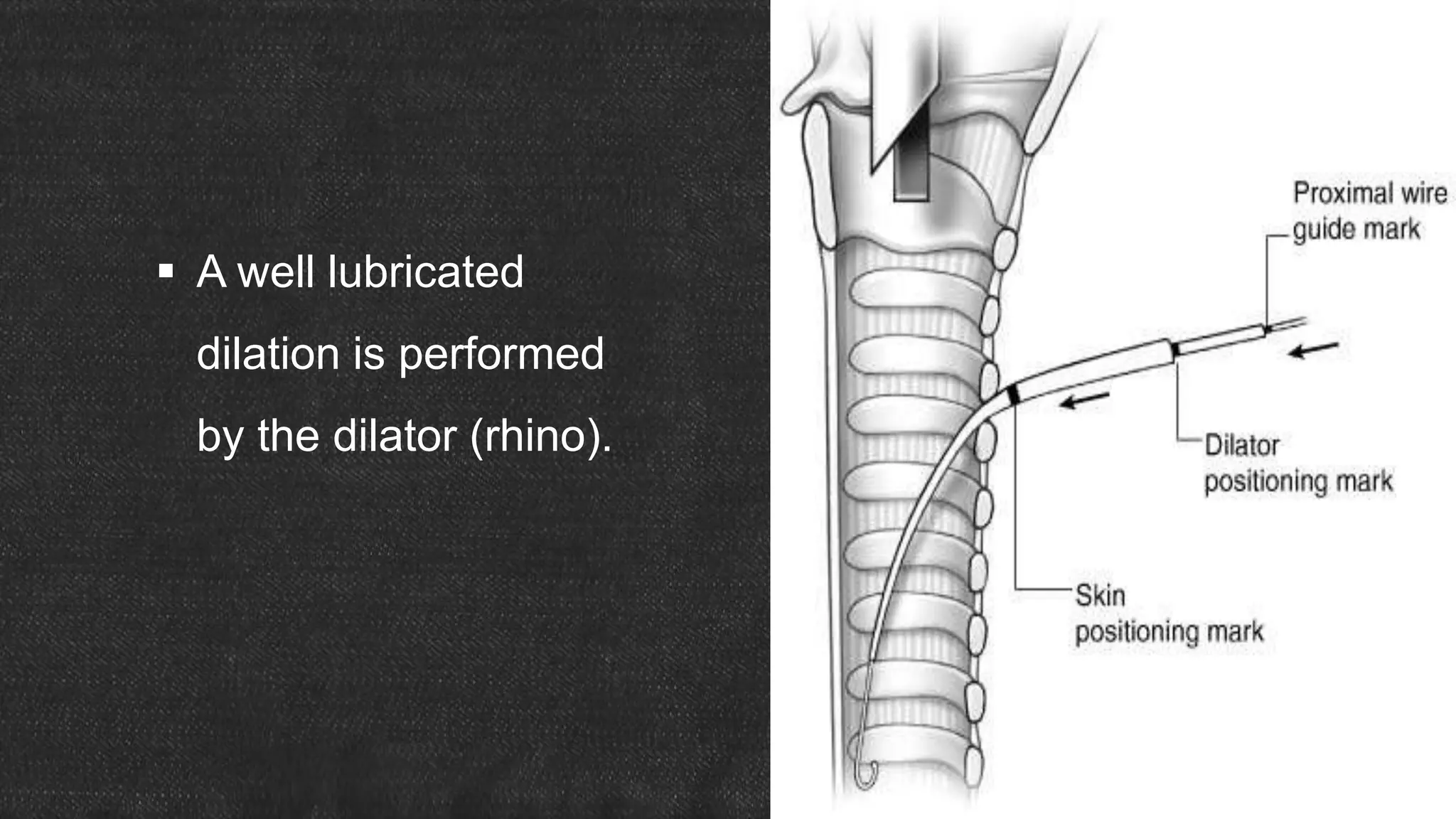
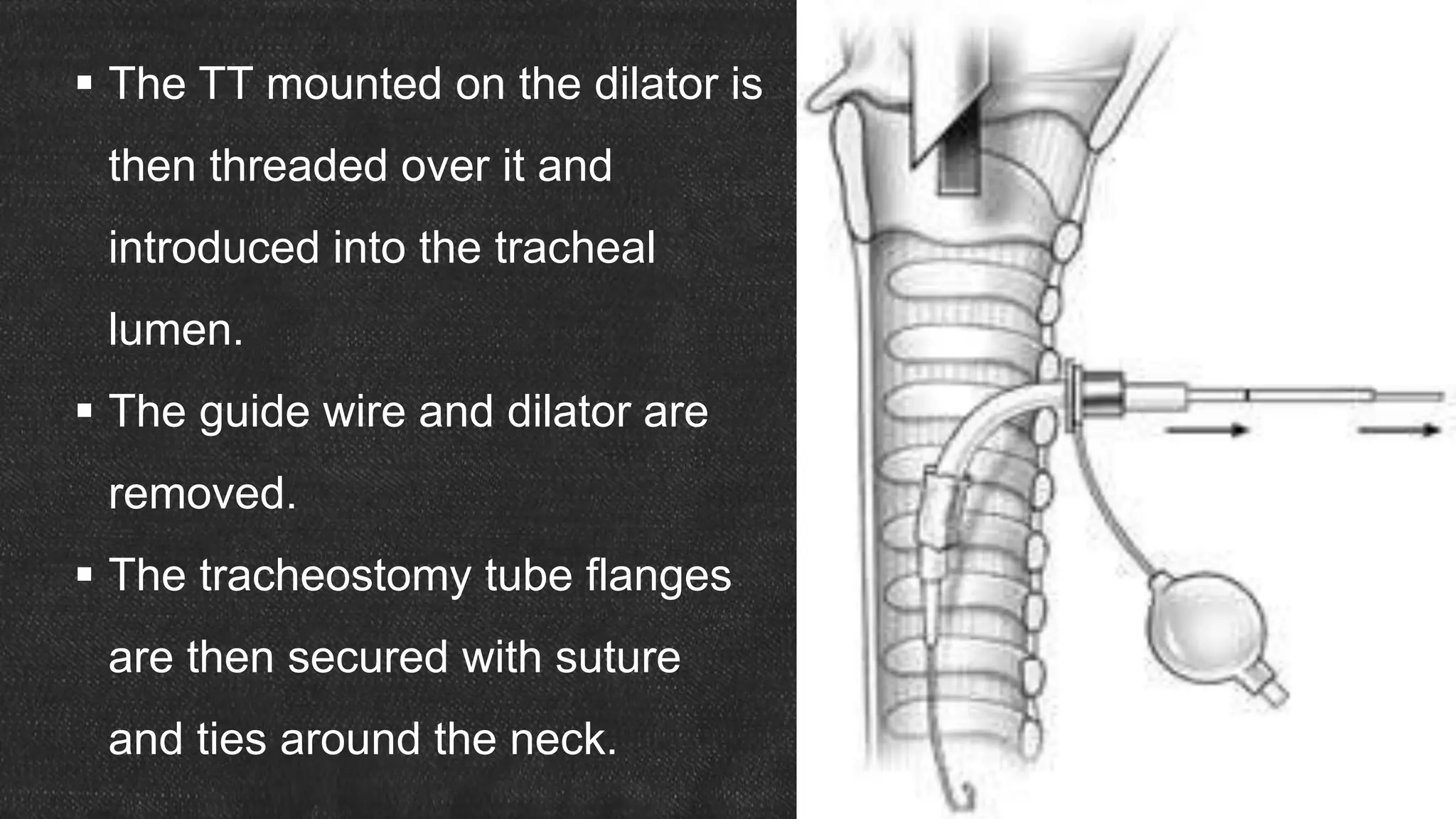
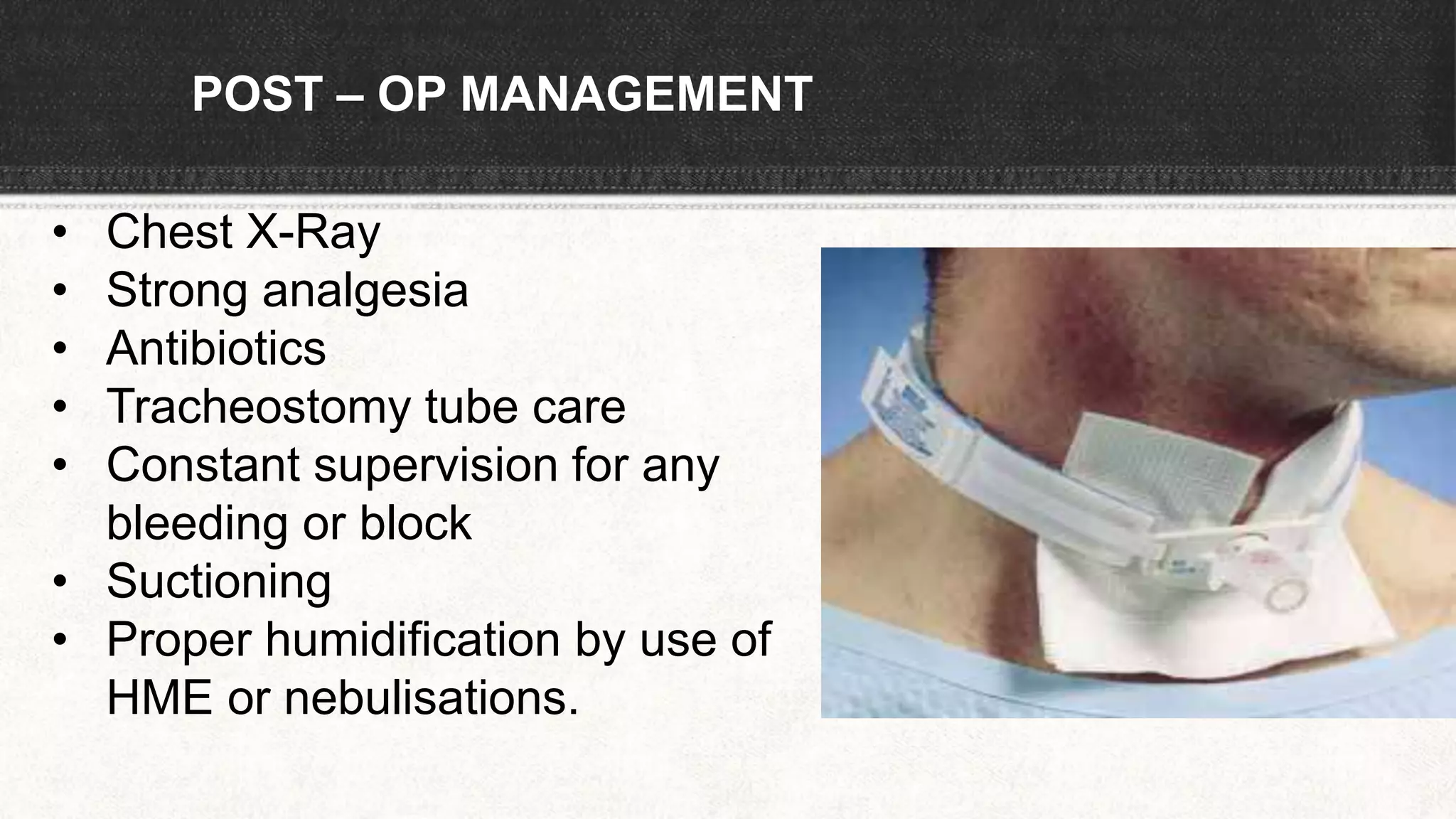
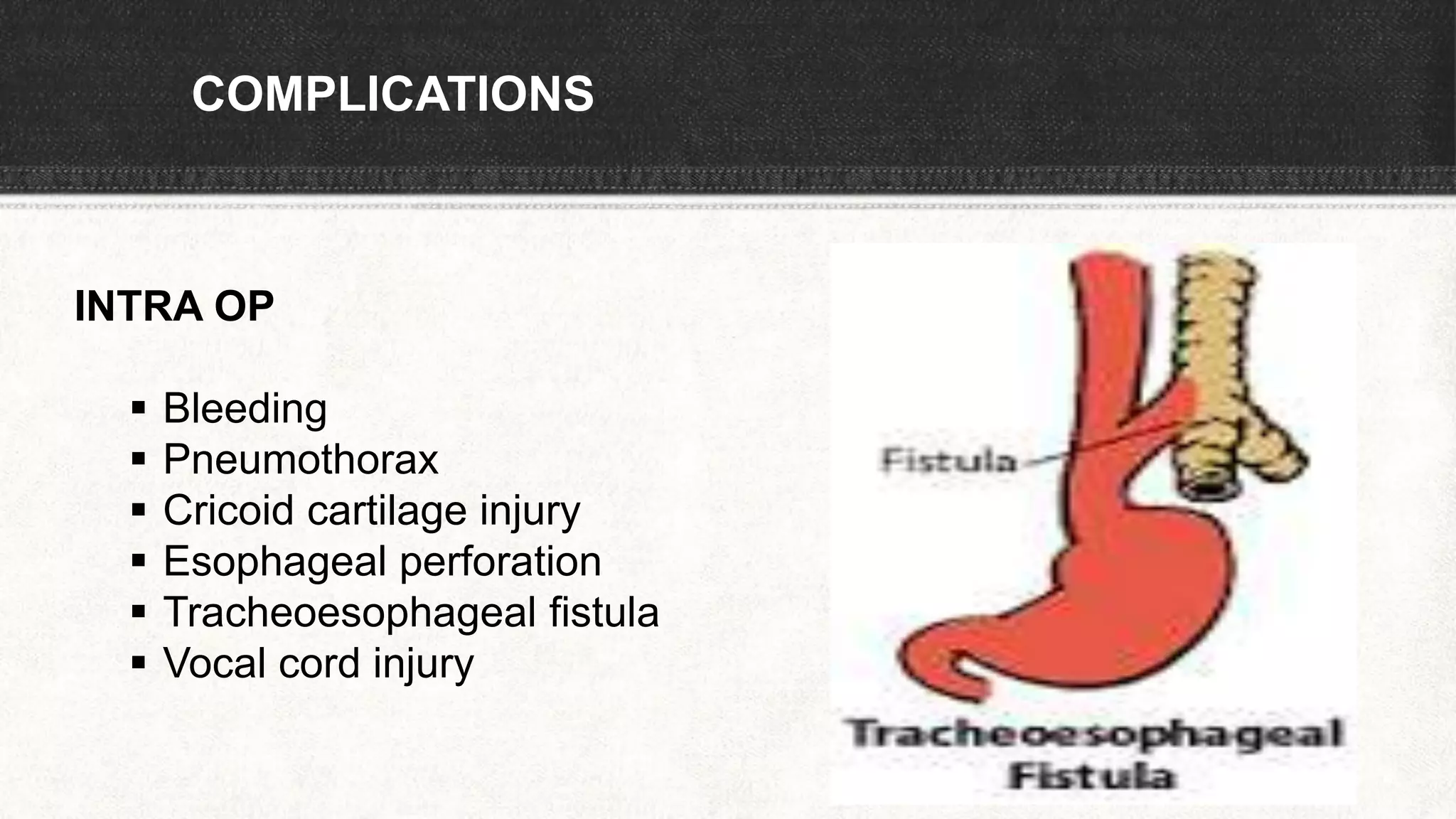
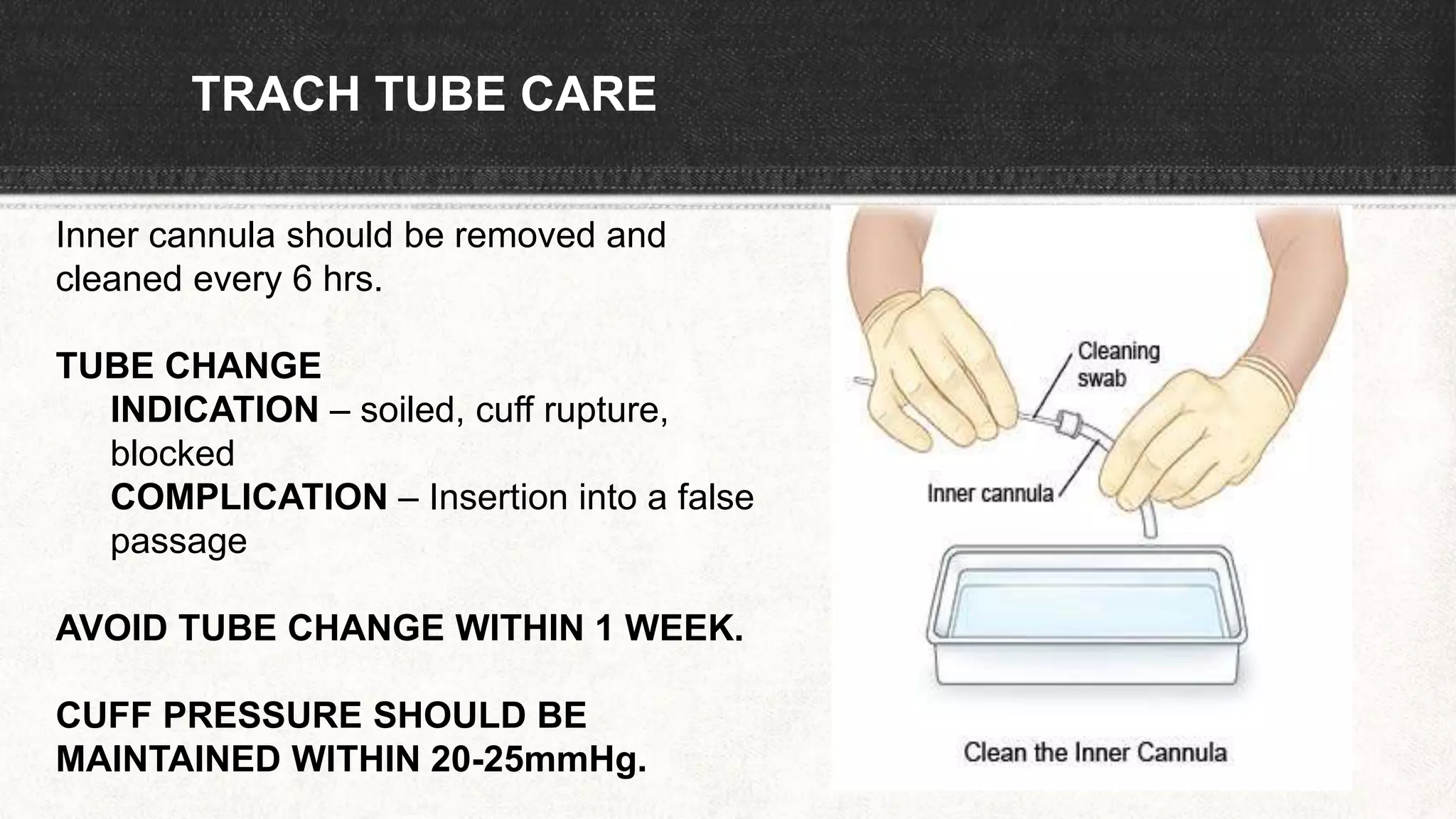
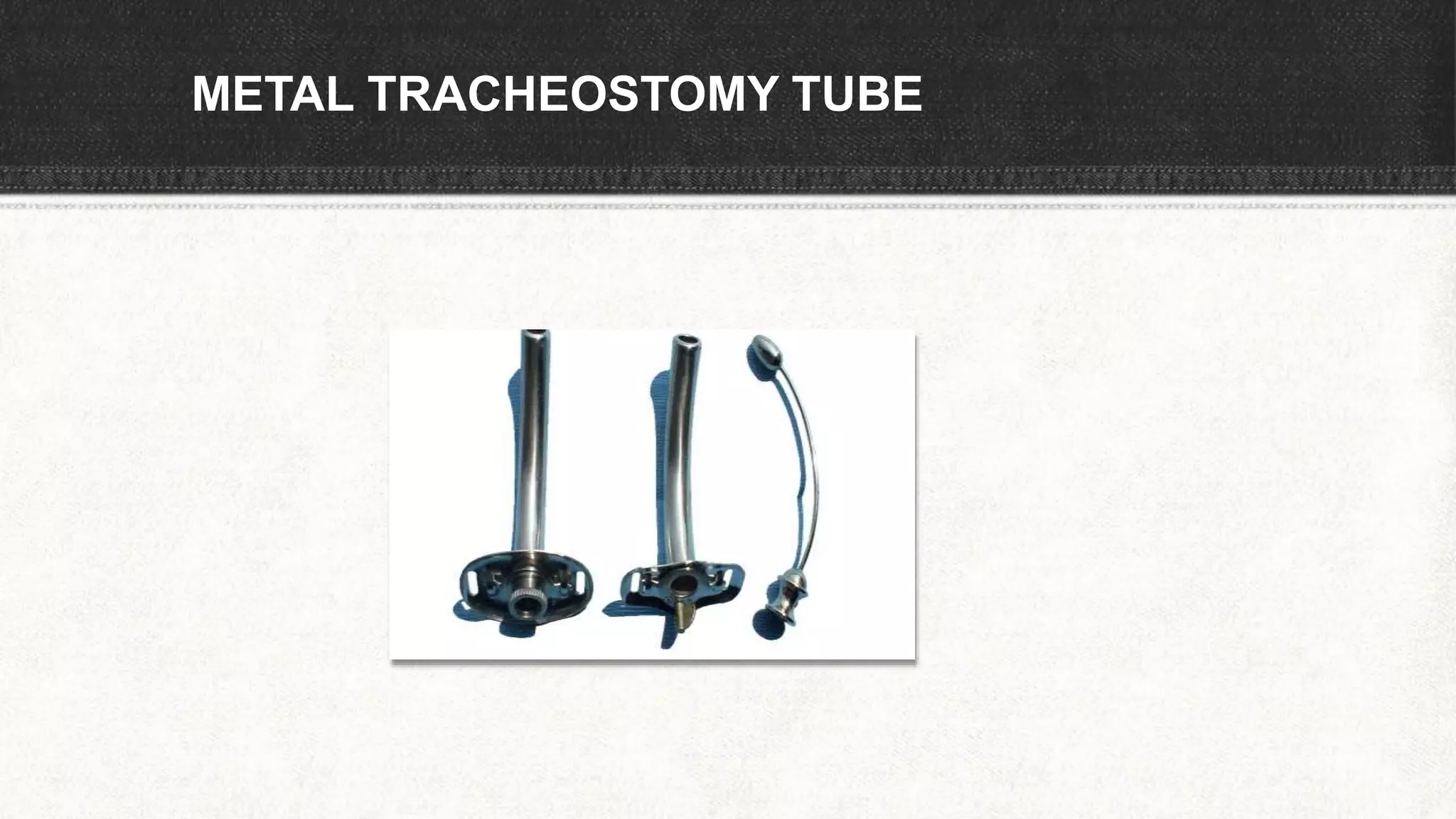
The document provides information about tracheostomy including anatomy, procedure, indications, complications and post-operative care. It describes the trachea's cartilaginous structure, relations, and layers. Surgical and percutaneous tracheostomy procedures are outlined in detail including positioning, incision, dilation, tube insertion and securing. Indications include airway bypass, bronchial toilet and ventilation. Complications can be intraoperative or postoperative. Tracheostomy tube care and decannulation criteria and process are also summarized.