This document provides an overview of tracheostomy, including:
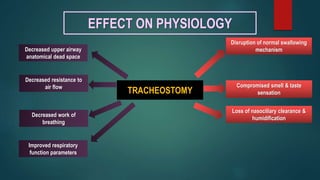
- Definitions of tracheostomy and the effect on physiology including disruption of swallowing and improved respiratory function.
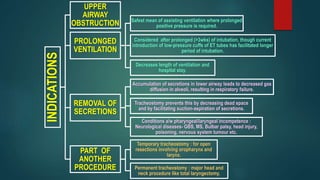
- Indications such as upper airway obstruction, prolonged ventilation, removal of secretions, and as part of another procedure.
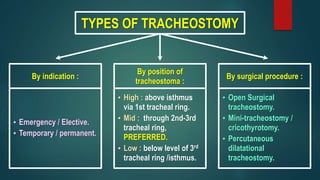
- Types including by indication, position, and surgical procedure.
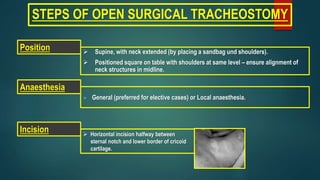
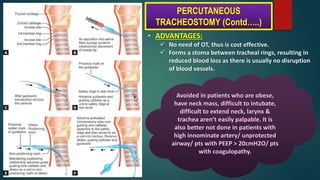
- Steps for open surgical tracheostomy and post-operative care.
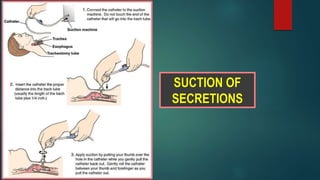
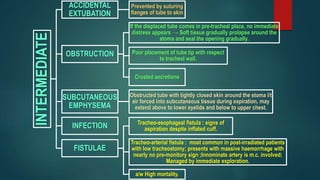
- Potential complications including immediate issues like hemorrhage and injuries, and later issues like tracheo-cutaneous fistula and stenosis.
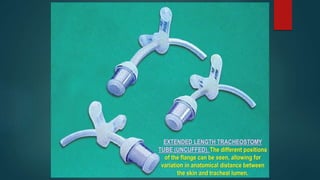
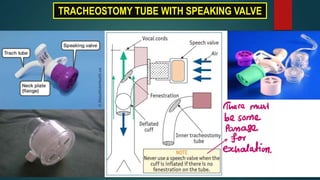
- Considerations for decannulation and tracheostomy tubes including fullers bivalve metallic and jacksons metallic