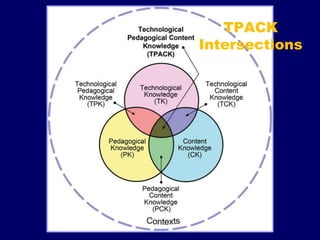
This document provides guidance for teachers on integrating technology into lesson planning and instruction. It discusses key concepts like curriculum, instruction, assessment, and Bloom's taxonomy. The document recommends that teachers use technology to improve existing tasks, do things not previously possible, and use it as a tool. It introduces the TPACK framework for planning technology-integrated lessons, considering the intersections between technology, pedagogy, and content knowledge. Teachers are advised to write measurable learning objectives and consider how technology can support knowledge building, expression and assessment of student understanding.