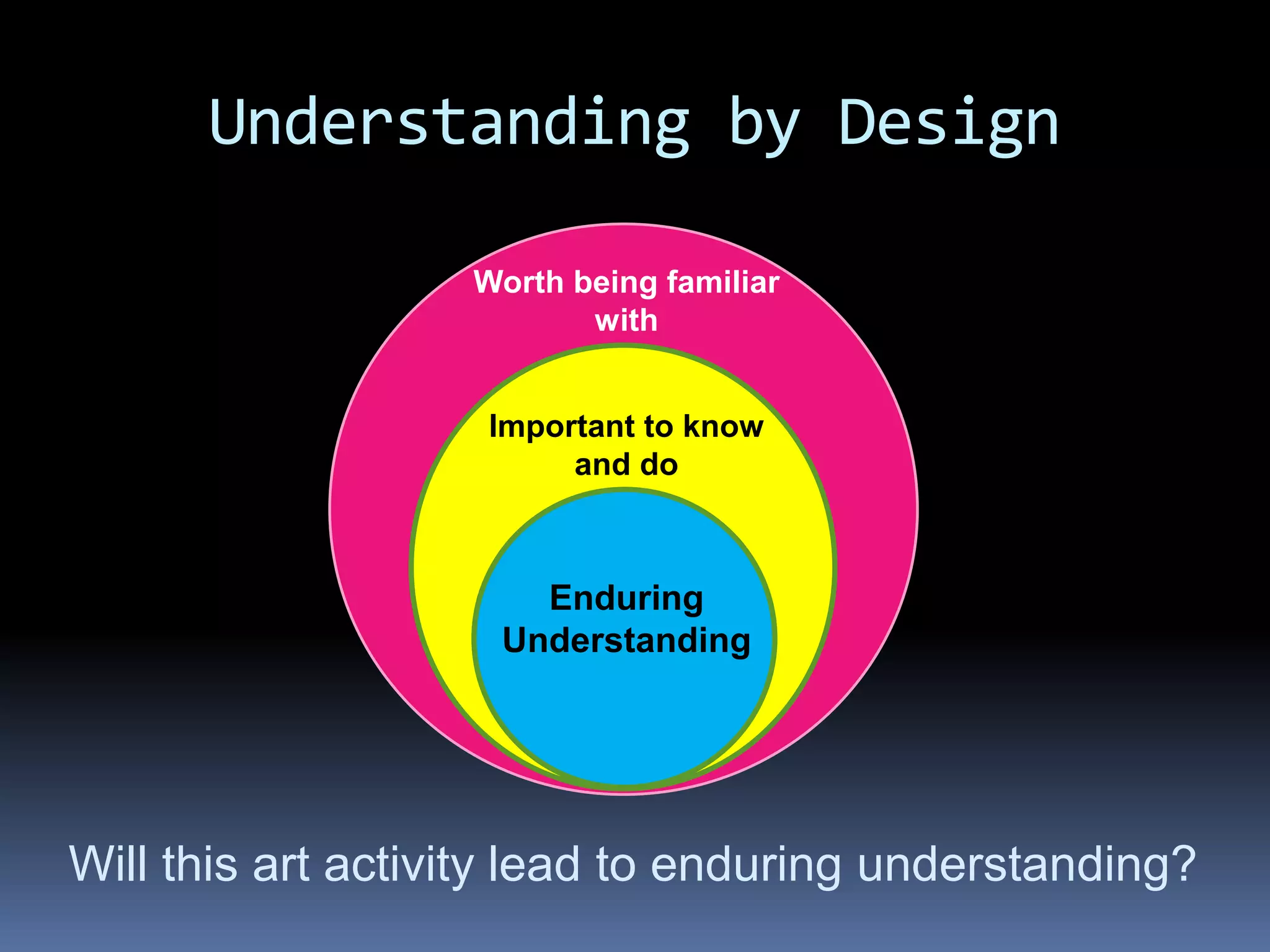
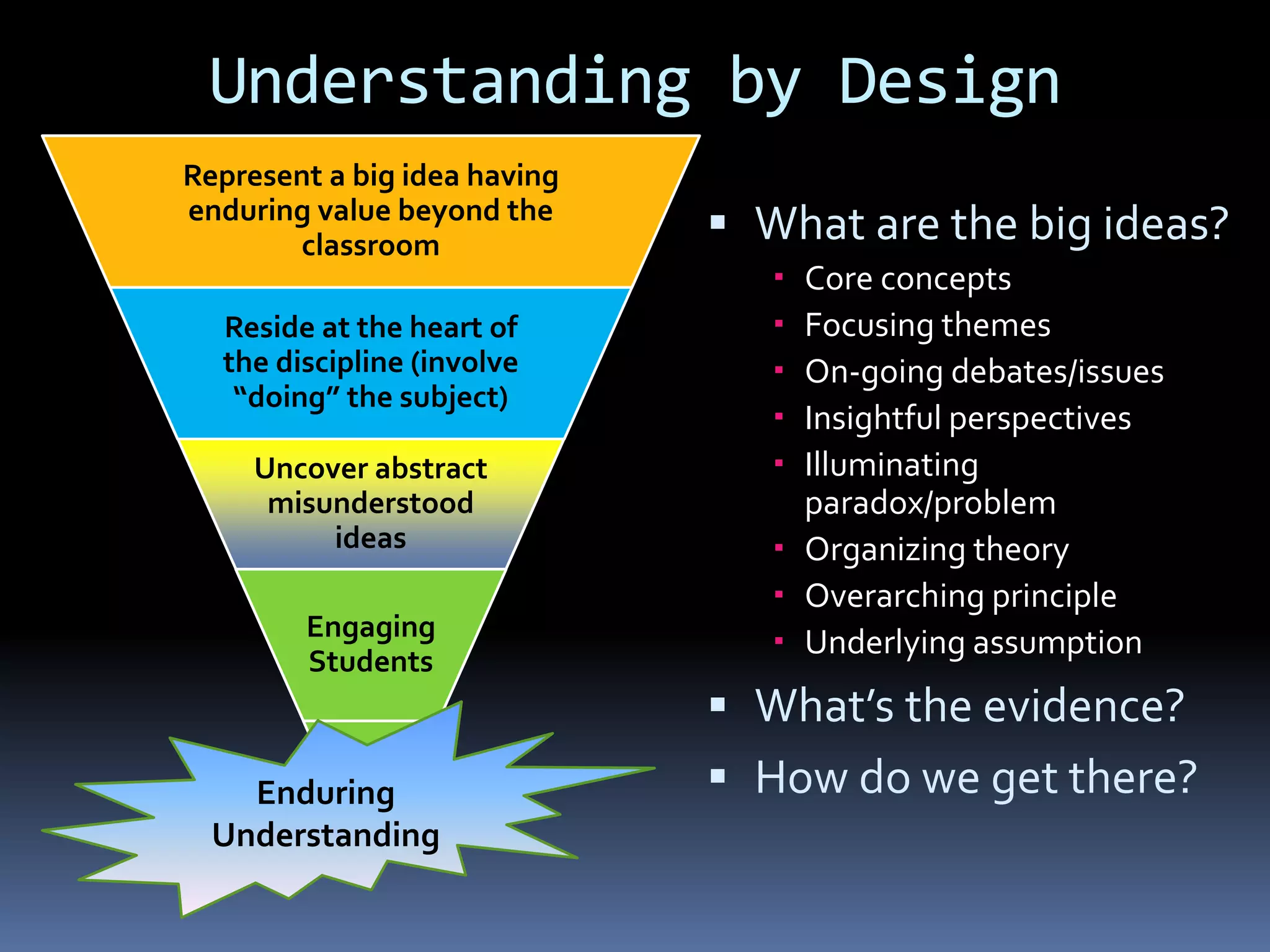
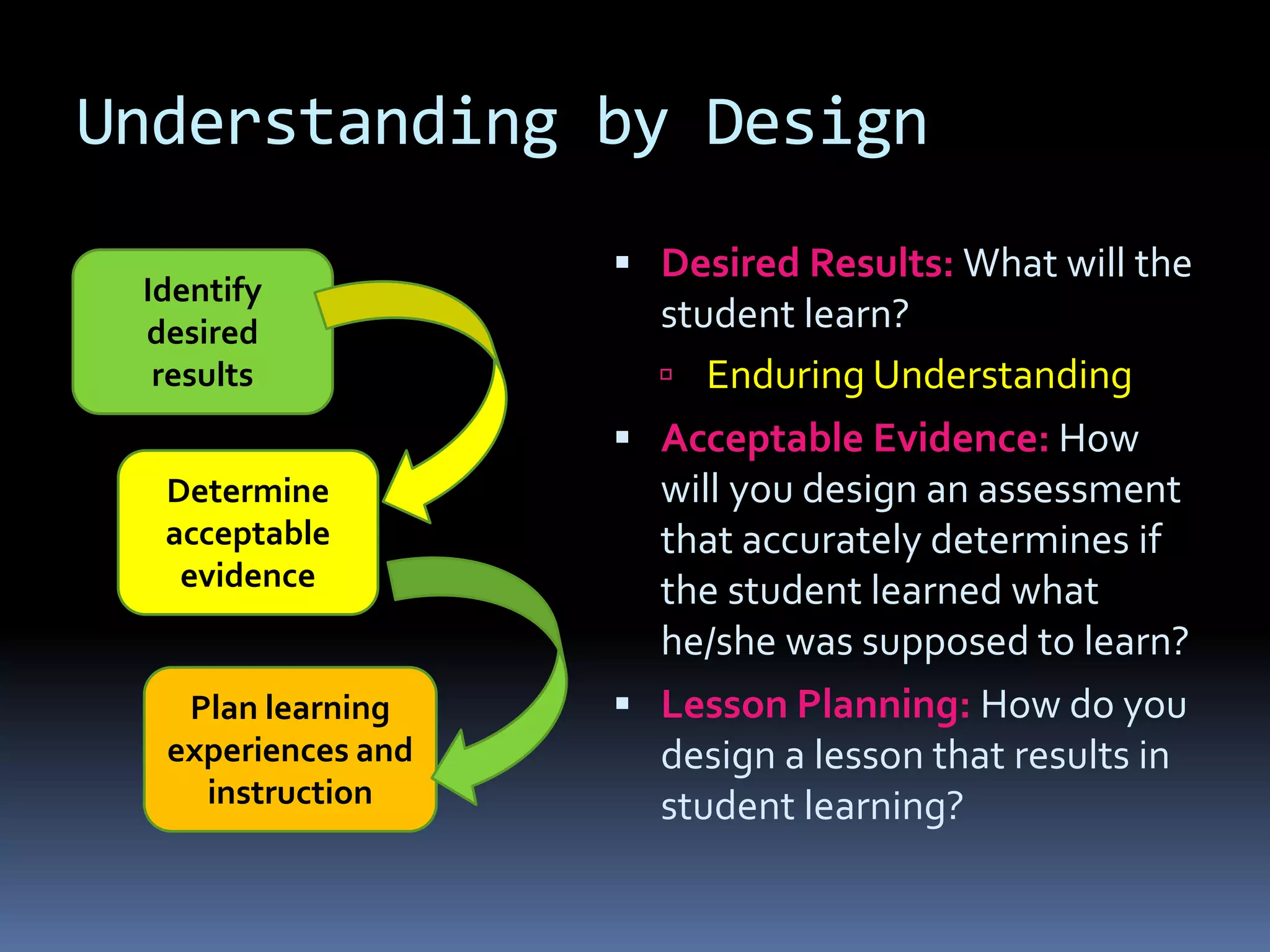
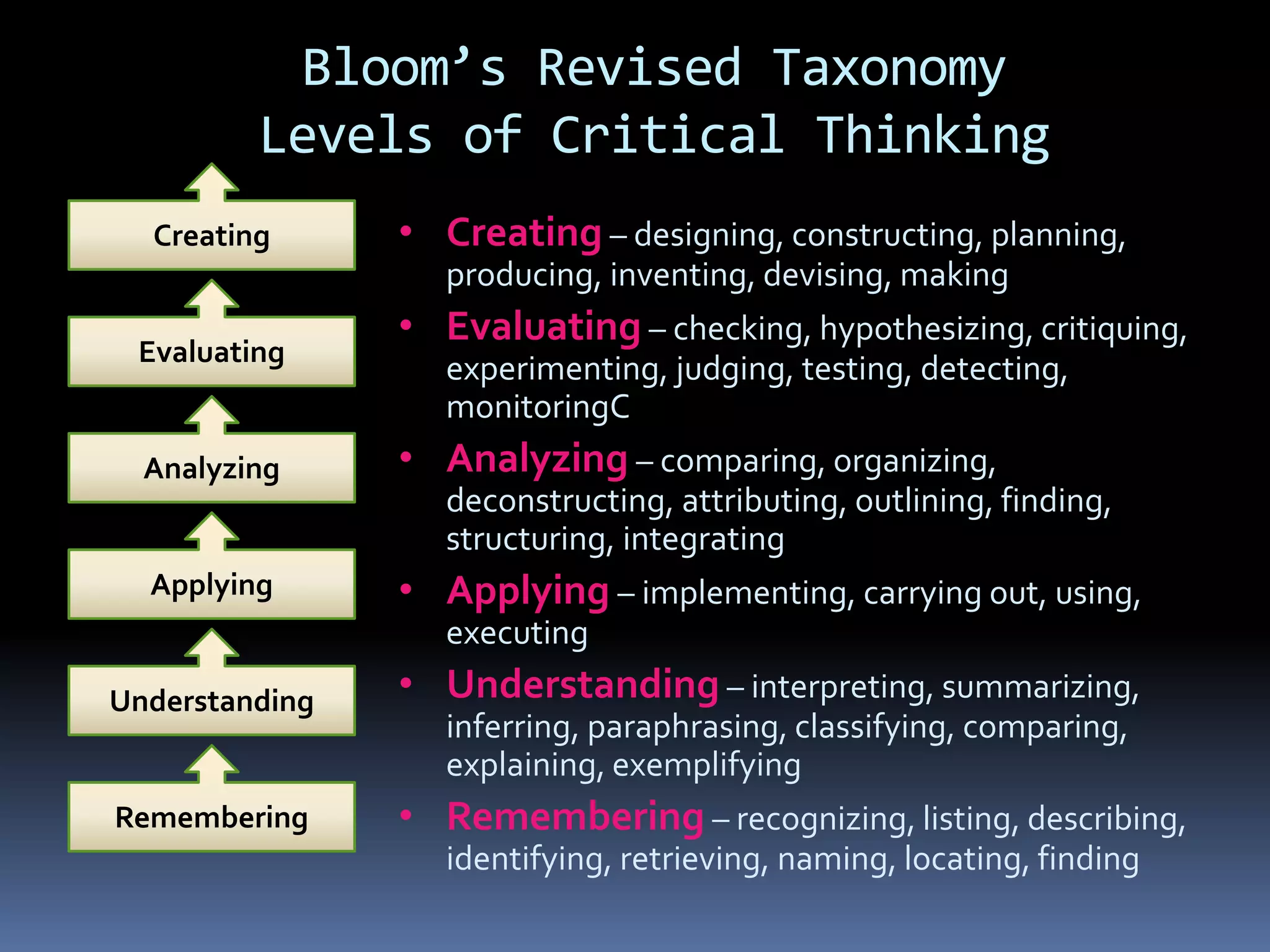
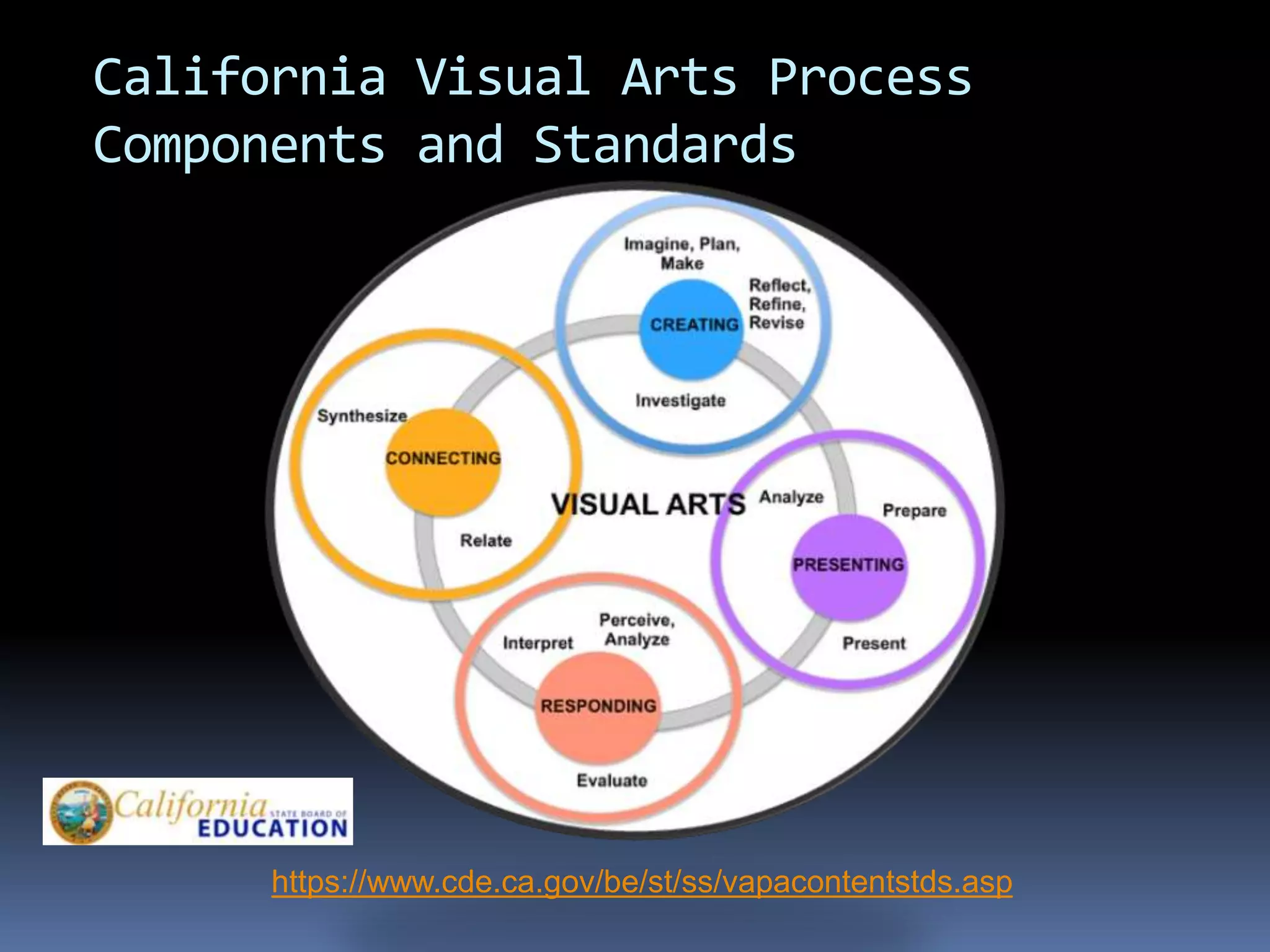
This document provides information on essential questions and enduring understandings for visual arts education. It discusses how essential questions spark curiosity about important ideas that have no single answer. Enduring understandings represent big ideas in a discipline that have value beyond the classroom. The document provides examples of essential questions for visual arts and discusses how to plan arts lessons to result in enduring understandings. It also outlines the California Visual Arts Standards and includes enduring understandings and essential questions for each standard.