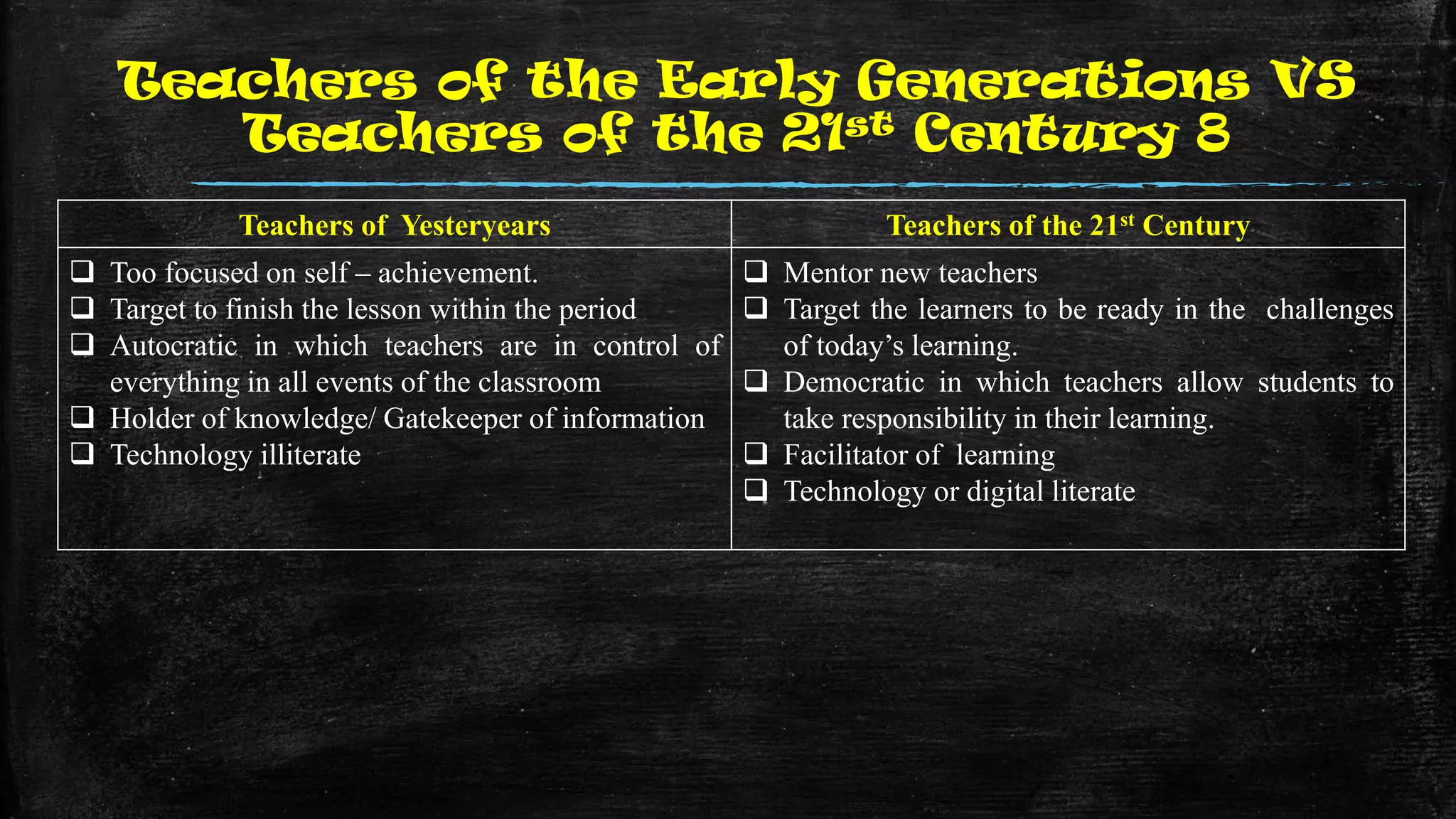
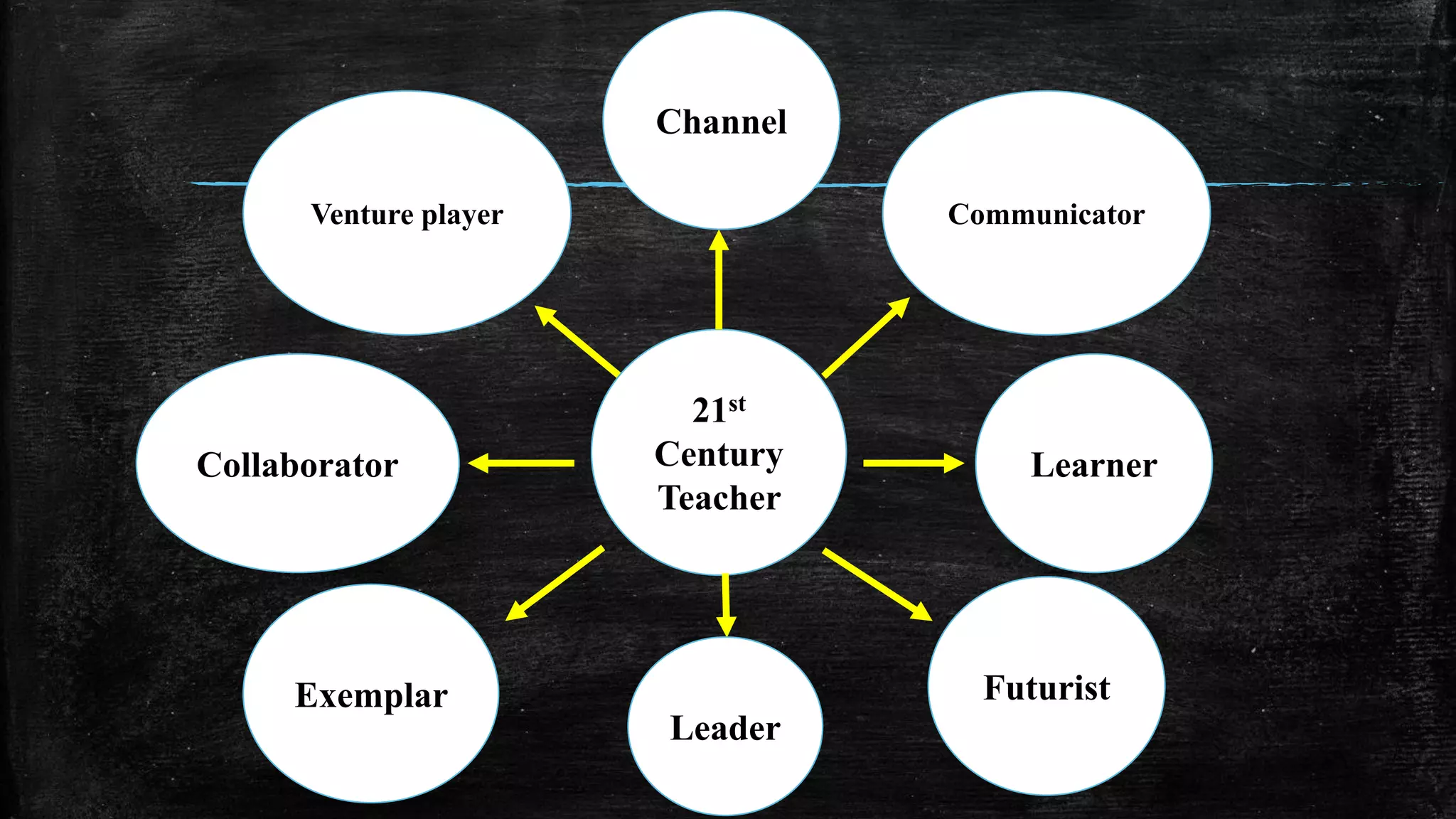
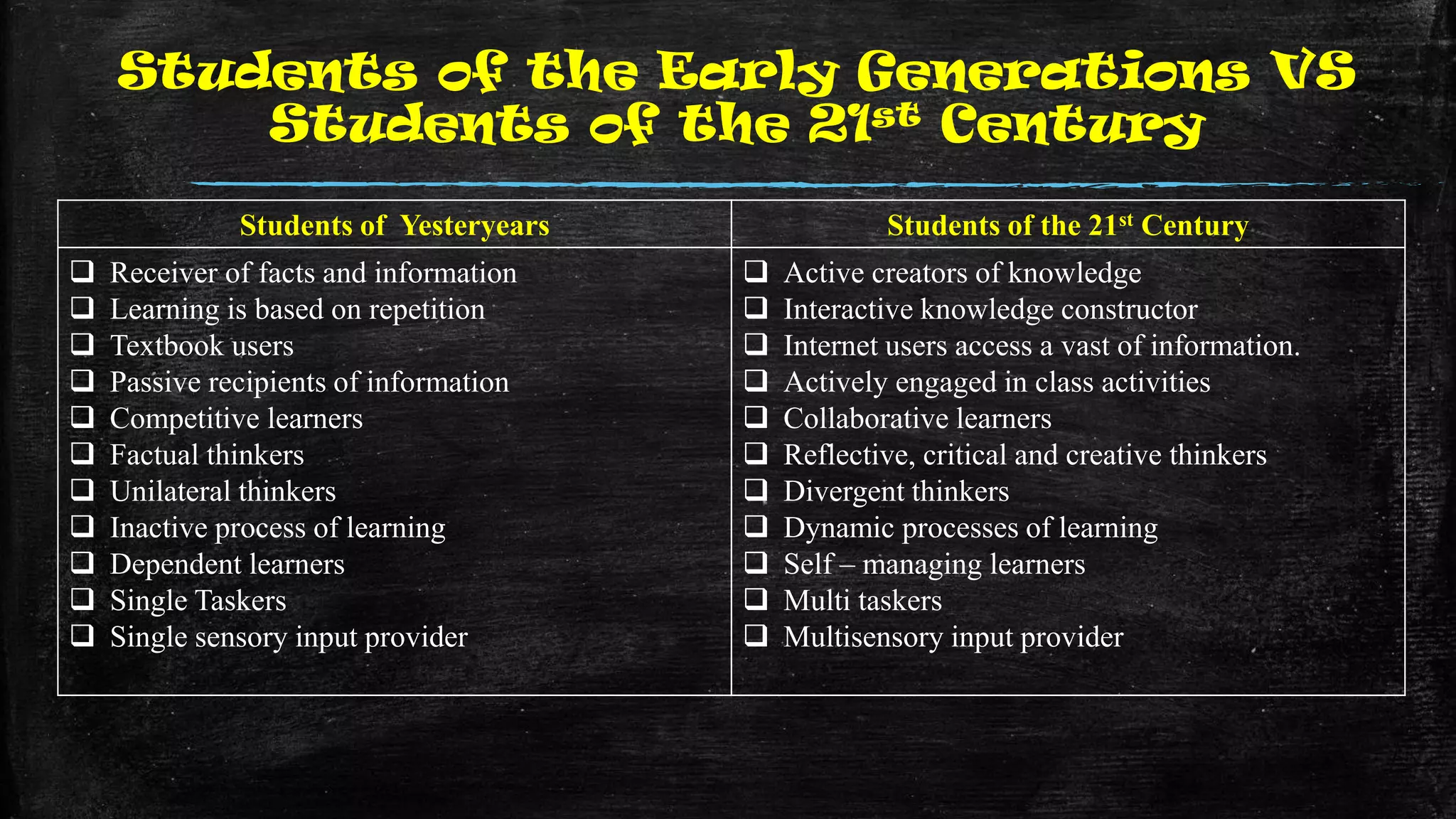
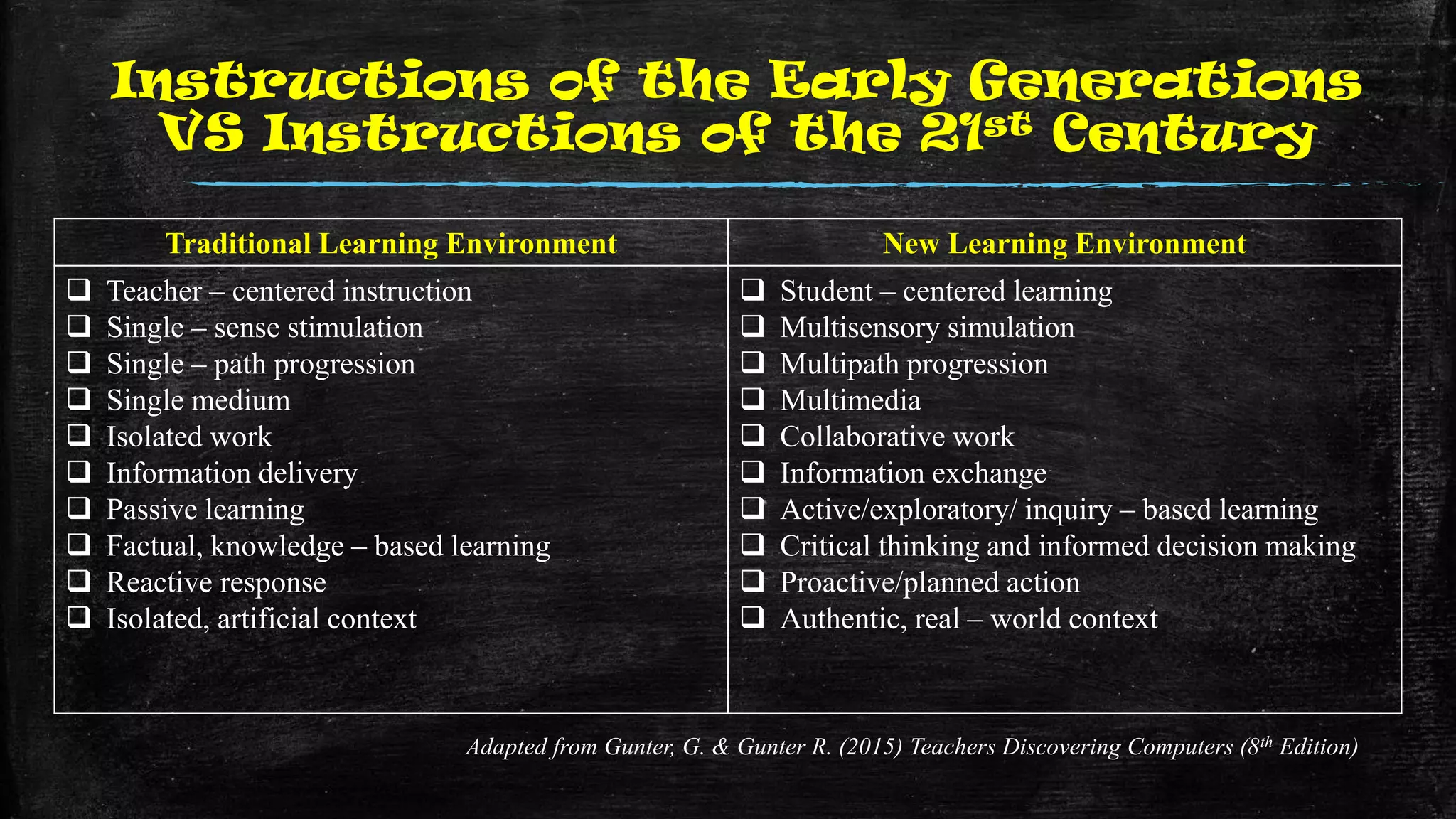
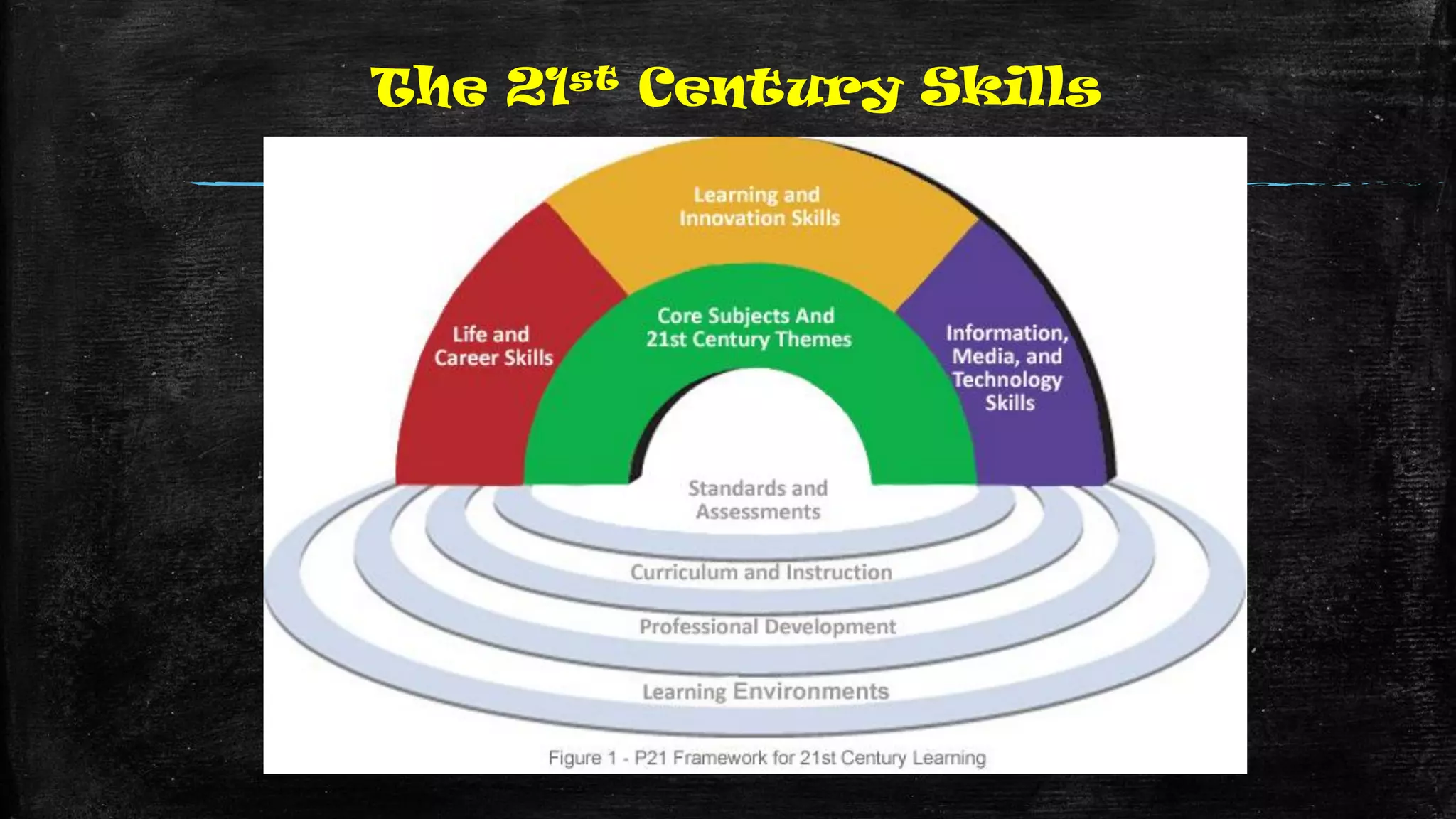
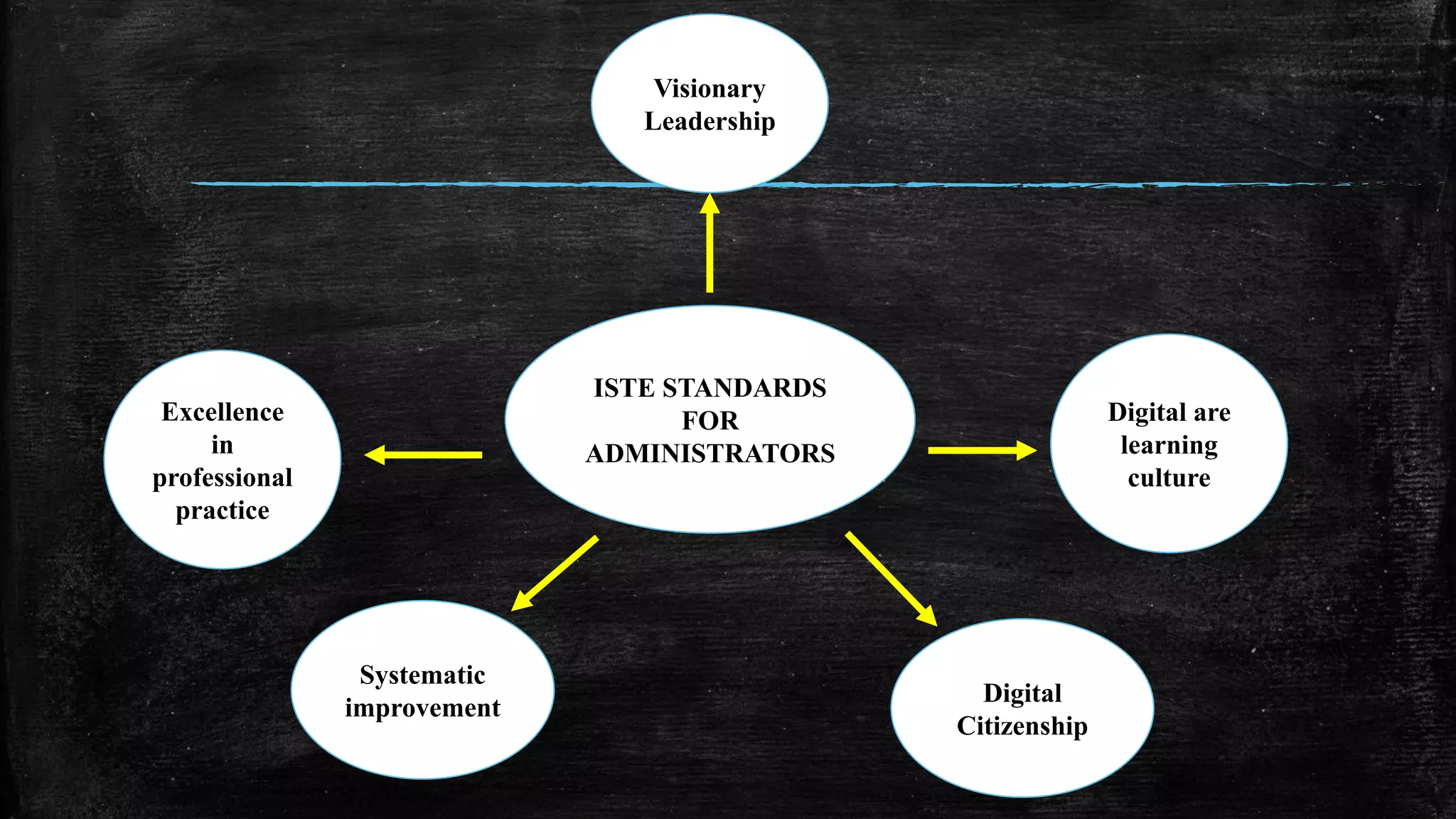
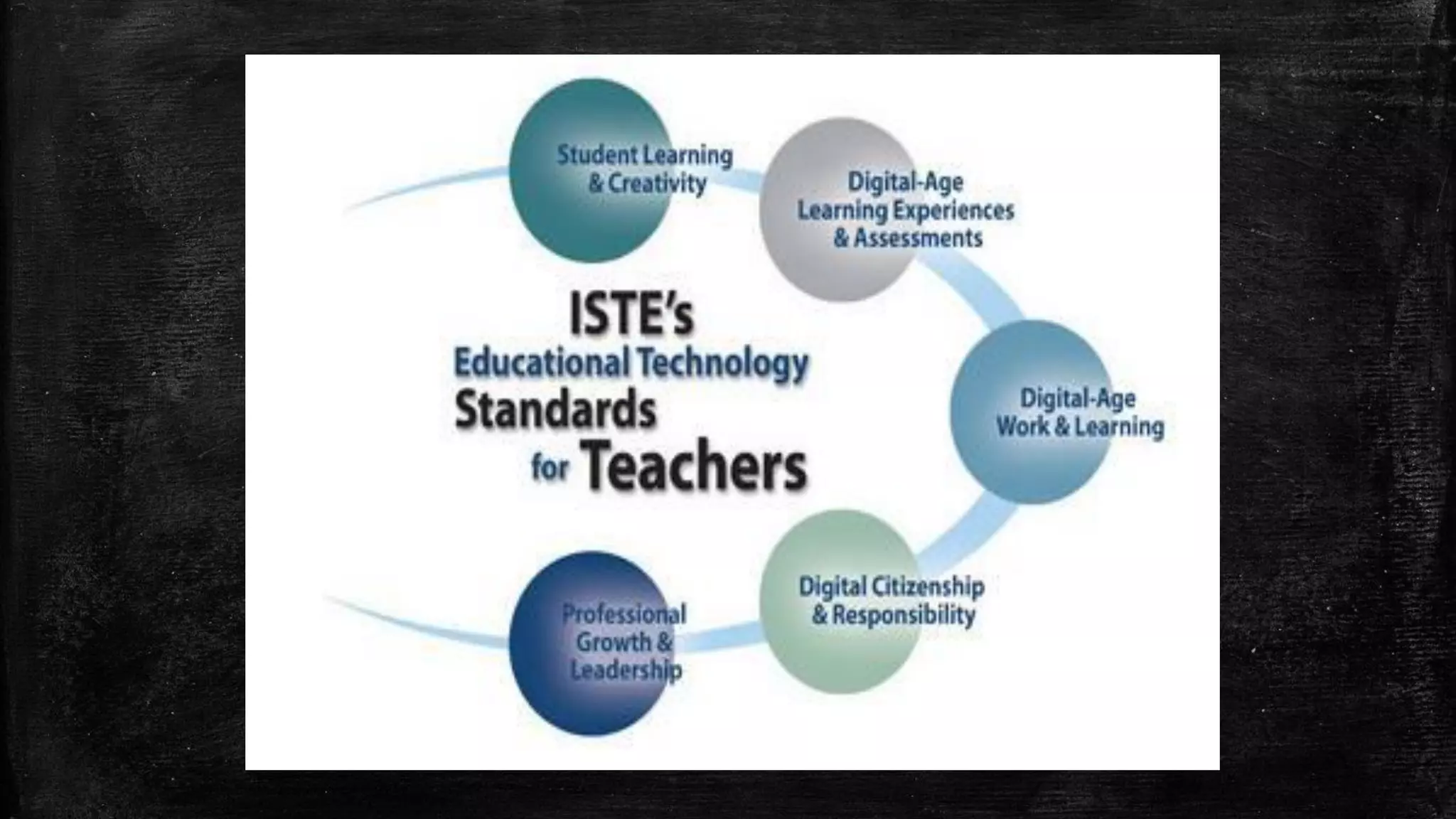
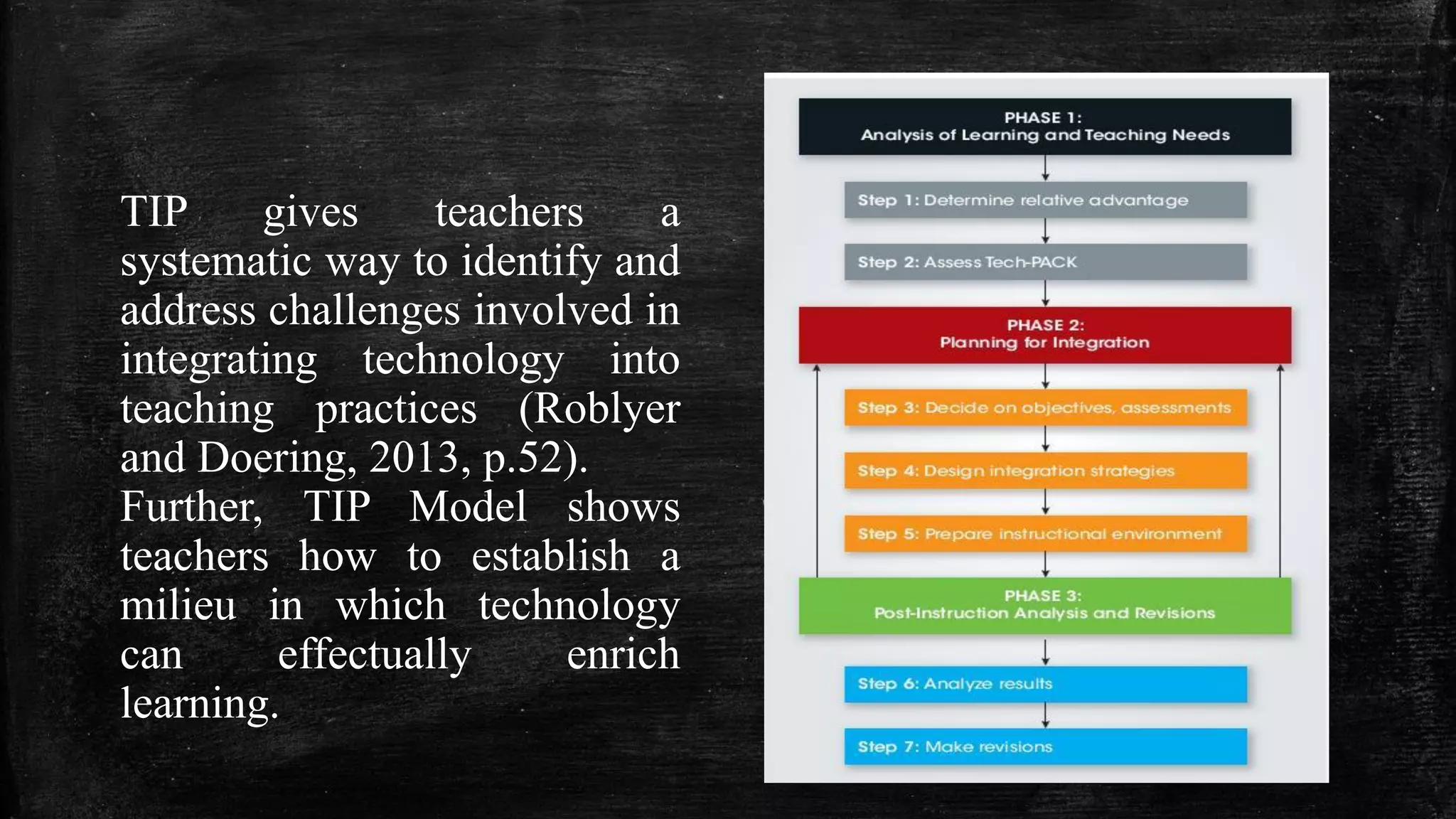
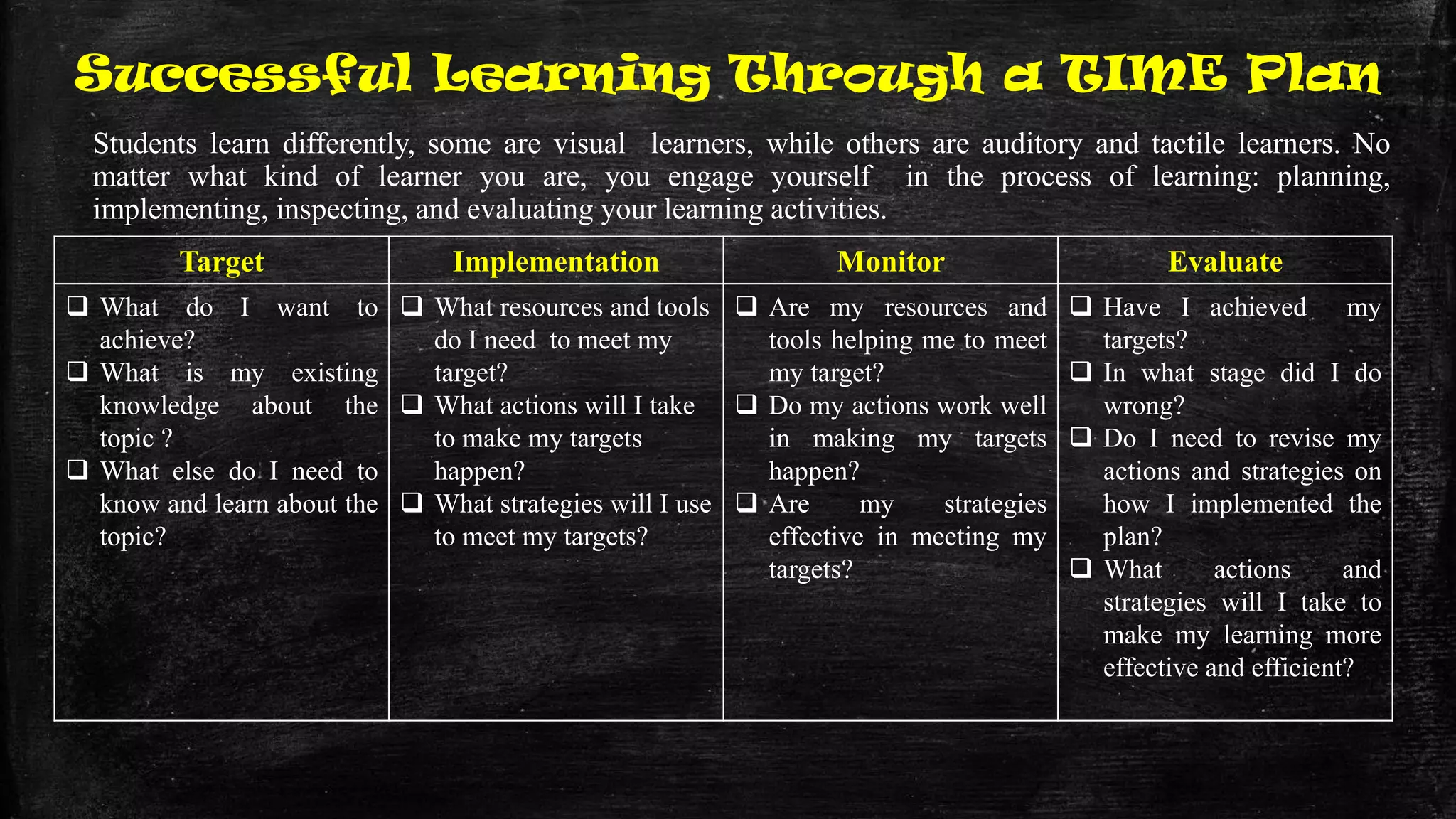
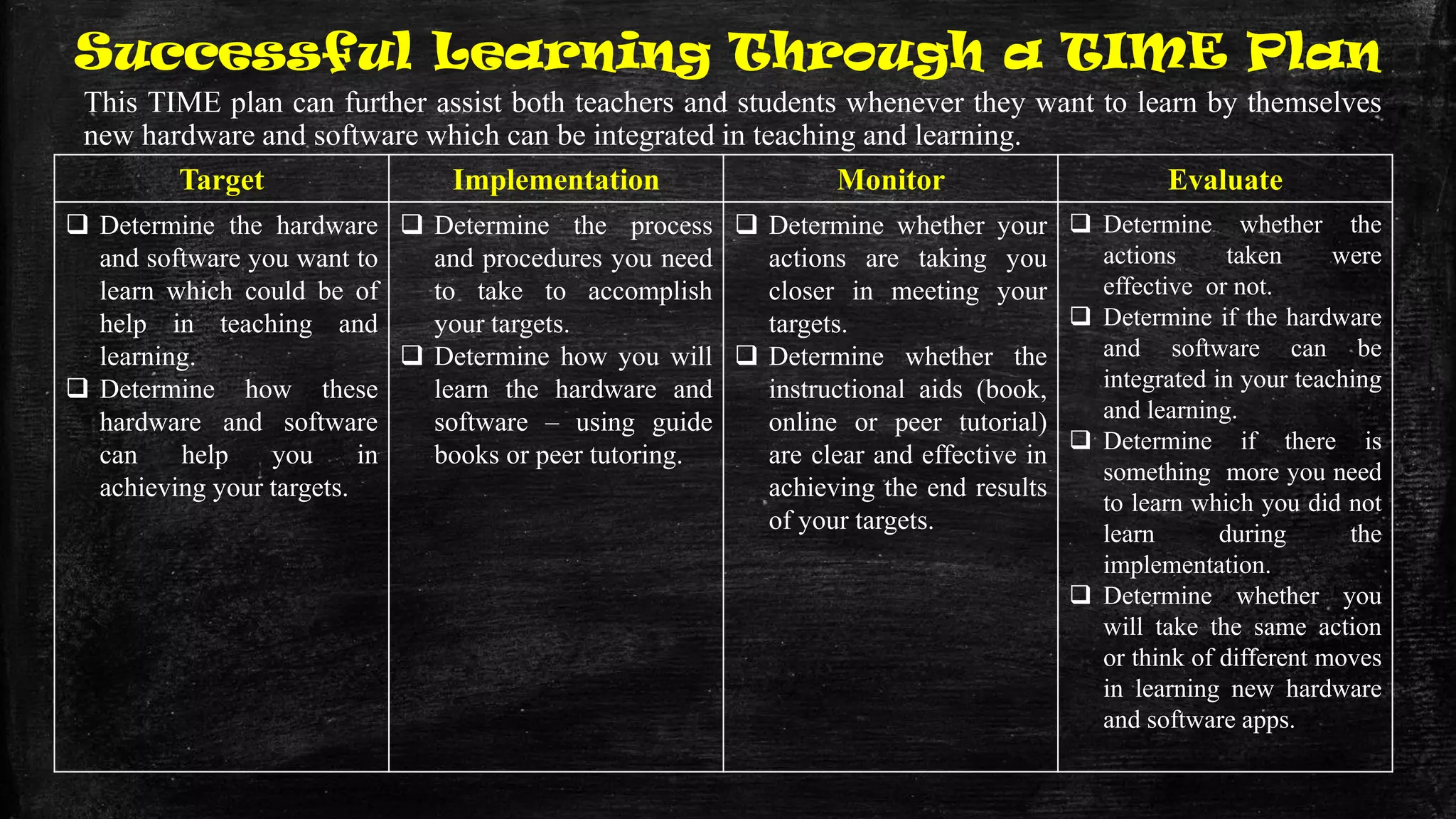
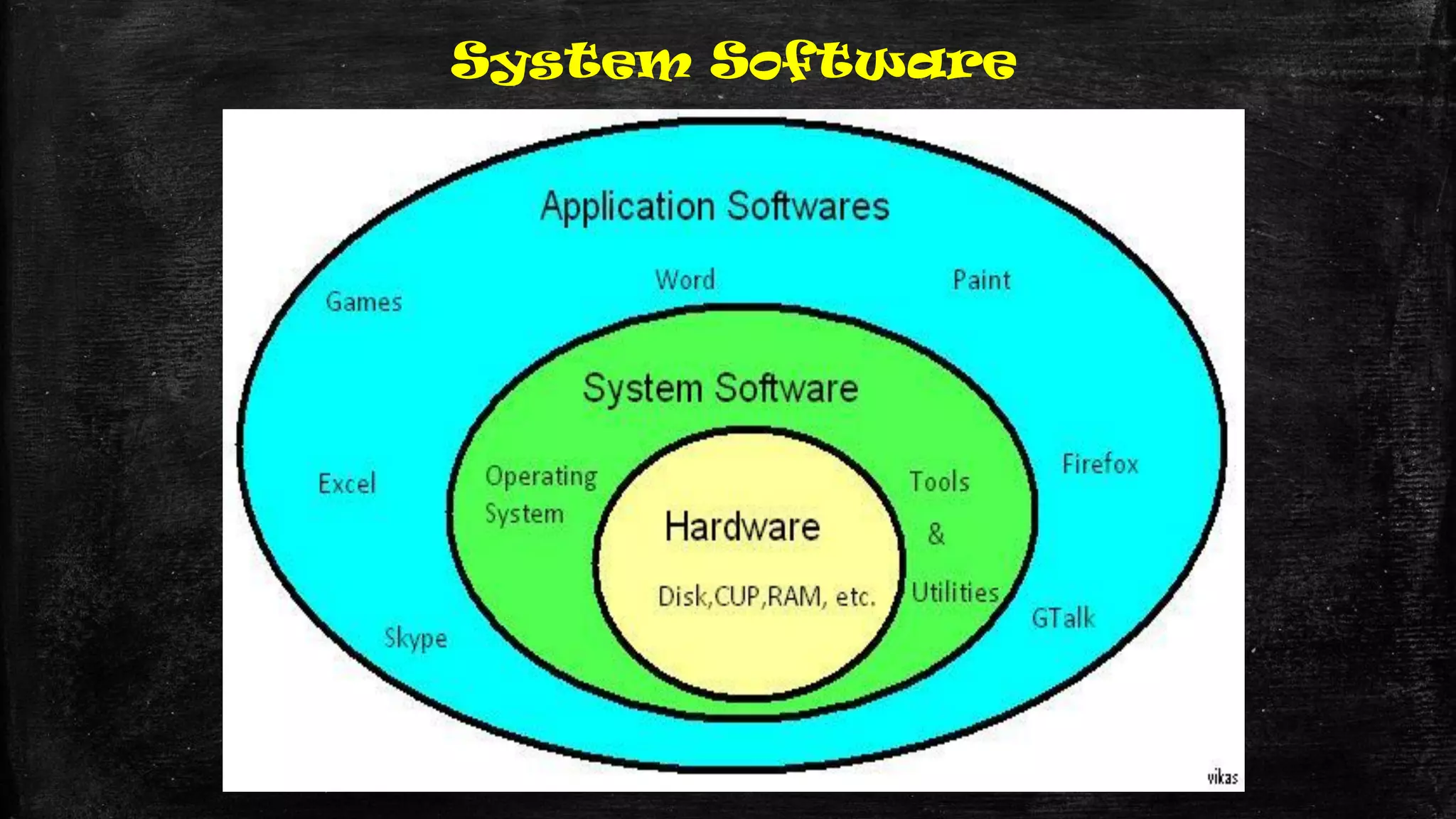
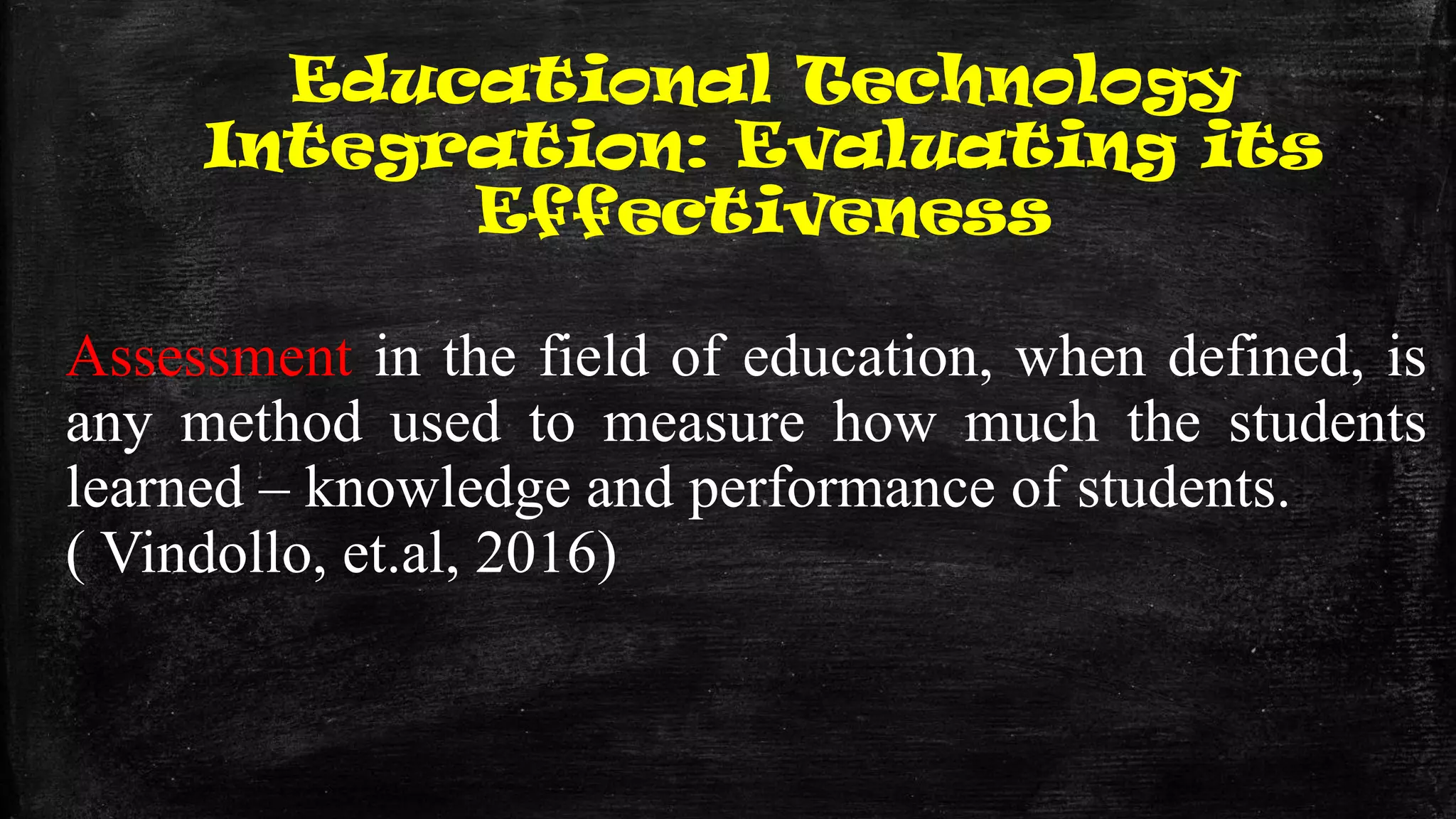
The document discusses the evolution of educational practices from traditional to 21st-century teaching, highlighting differences in student and teacher roles, methods of instruction, and technology integration. It emphasizes the importance of adapting to new learning environments that promote active, collaborative, and critical thinking skills among students. Additionally, it raises awareness of ethical considerations in technology use in education, advocating for responsible practices among educators and learners.