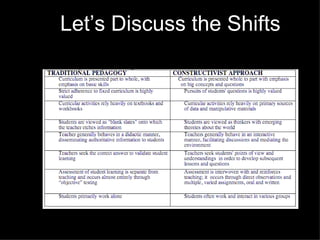
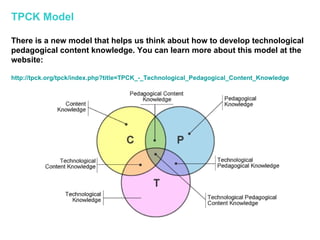
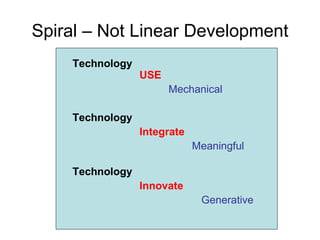
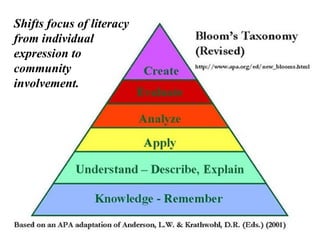
The document discusses several concepts related to shifting education to better prepare students for the 21st century, including:
- Learning as a participatory and collaborative process rather than a passive, individual one
- The need to "unlearn" outdated assumptions about learning only happening in the classroom or being a linear process
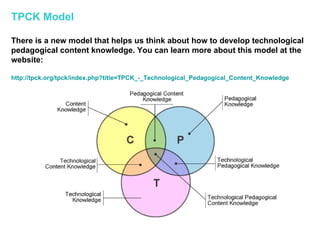
- Models for integrating technology, such as the TPCK model, to develop technological pedagogical content knowledge
- Strategies for making lesson plans more focused on 21st century skills like problem-finding, justification, curiosity and community