This document discusses network topology and modeling of internet structure. It begins by explaining why network topology is important for tasks like routing, simulation, and analysis. It then covers models for representing internet topology at the router and domain level. Common models discussed include Waxman, Barabasi-Albert, and transit-stub models. The document also addresses concepts of complex networks, scale-free networks, and power laws observed in real-world networks like the web. It provides an example of search in peer-to-peer networks like Gnutella and how their power law structure can be leveraged. Finally, it outlines the hierarchical structure of the internet and components within an ISP like points of presence.



![Modeling Internet Topology [1]:
Graph representation
Router-level modeling
- vertices are routers
-edges are one-hop IP connectivity
Domain- (AS-) level model (high degree of abstraction)
- vertices are domains (ASes)
- edges are peering relationships
Nodes can be assigned numbers rep. e.g. buffer
capacity
Edges migth have weights rep. e.g. – prop. delay,
bandwidth capacity.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologyppt-140220112807-phpapp01/85/Topology-ppt-4-320.jpg)
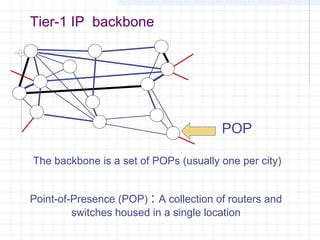
![Modeling Internet Topology [1]:
transit domains
domains/autonomous systems
exchange point
border routers
peering
hosts/endsystems
routers
stub domains
access networks
lowly worm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologyppt-140220112807-phpapp01/85/Topology-ppt-5-320.jpg)

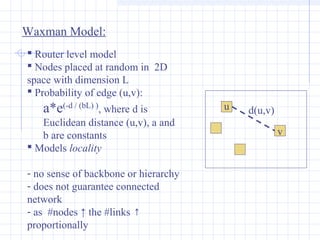
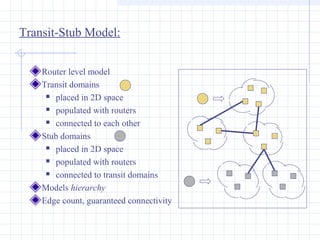

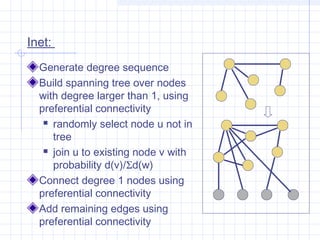
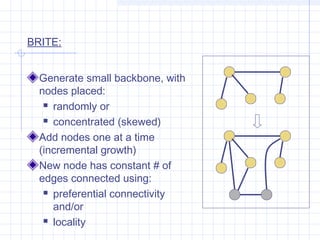
![Complex Networks:
Two limiting-case topologies have been extensively considered in
the literature [4],[5].:
regular network (lattice), the chosen topology of innumerable
physical models such as the Ising model or percolation.
random graph, studied in mathematics and used both in
natural and social sciences. Properties studied in detail by Pal
Erdos.
Most of Erdos’ work concentrated on the case in which the
number of vertices is kept constant but the total number of links
between vertices increases: the Erdös-Rényi result states that for
many important quantities there is a percolation-like transition
at a specific value of the average number of links per vertex.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologyppt-140220112807-phpapp01/85/Topology-ppt-12-320.jpg)


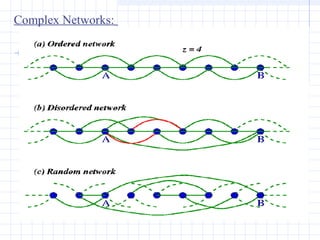
![Complex Networks:
The Watts-Strogatz model [5]. :
To bridge the two limiting cases, Watts and Strogatz
[Nature 393, 440 (1998)] have introduced a new type of
network which is obtained by randomizing a fraction p of
the links of the regular network.
Initial structure (p=0) is the one-dimensional regular
network where each vertex is connected to its z nearest
neighbors.
For 0 < p < 1, we denote these networks disordered.
for the case p=1, we have a completely random
network.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologyppt-140220112807-phpapp01/85/Topology-ppt-16-320.jpg)









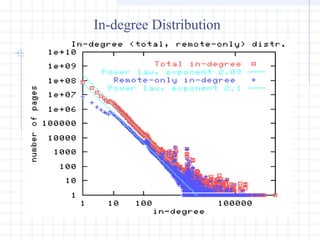
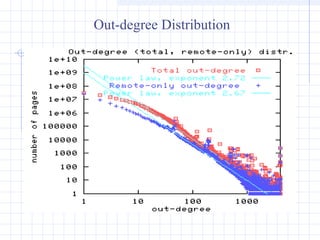
![Power-laws of the Web [2].:
•How many links on a page (outdegree)?
• How many links to a page (indegree)?
•Probability that a random page has k other pages
pointing to it is ~k
-2.1
(Power law)
• Probability that a random page points to k other pages is
~k
-2.7
(Power law)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologyppt-140220112807-phpapp01/85/Topology-ppt-27-320.jpg)
![Search in power-law networks: GNUTELLA [3].
Most of the P2P networks display a power-law
distribution in their node degree. This distribution
reflects the existence of a few nodes with very high
degree and many with low degree.
In P2P networks, the name of the target file may be
known, but due to the network’s ad hoc nature, the node
holding the file may not be known until a real-time
search is performed.
A simple strategy to locate files, implemented by
NAPSTER, is to use a central server that contains an
index of all the files every node is sharing as they join
the network.
GNUTELLA and FREENET do not use a central
server.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologyppt-140220112807-phpapp01/85/Topology-ppt-30-320.jpg)
![Search in power-law networks: GNUTELLA [3].
GNUTELLA is a peer-to-peer file-sharing system that treats
all client nodes as functionally equivalent and lacks a central
server that can store file location information. This is advantageous
because it presents no central point of failure.
The obvious disadvantage is that the location of files is unknown.
When a user wants to download a file, he sends a query to
all the nodes within a neighborhood of size ttl, the time to
live assigned to the query. Every node passes on the query to
all of its neighbors and decrements the ttl by one. In this
way, all nodes within a given radius of the requesting node
will be queried for the file, and those who have matching
files will send back positive answers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologyppt-140220112807-phpapp01/85/Topology-ppt-31-320.jpg)
![Search in power-law networks: GNUTELLA [3].
This broadcast method will find the target file quickly,
given that it is located within a radius of ttl. However, broadcasting
is extremely costly in terms of bandwidth.
Such a search strategy does not scale well. As query traffic
increases linearly with the size of GNUTELLA graph, nodes
become overloaded.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologyppt-140220112807-phpapp01/85/Topology-ppt-32-320.jpg)
![Search in power-law networks: GNUTELLA [3].
Typically, a GNUTELLA client wishing to join the network
must find the IP address of an initial node to connect to.
Currently, ad hoc lists of ‘‘good’’ GNUTELLA clients exist.
It is reasonable to suppose that this ad hoc method of
growth would bias new nodes to connect preferentially to
nodes that are already fairly well connected, since these
nodes are more likely to be ‘‘well known.’’
Based on models of graph growth where the ‘‘rich get richer,’’
the power-law connectivity of ad hoc peer-to-peer networks may
be a fairly general topological feature.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologyppt-140220112807-phpapp01/85/Topology-ppt-33-320.jpg)
![Search in power-law networks: GNUTELLA [3].
By passing the query to every single node in the network,
the GNUTELLA algorithm fails to take advantage of the
connectivity distribution [3].
To take advantage of the power-law distribution, we can modify
each node to keep lists of files stored in first and second neighbor.
Instead of passing the query to every node, now we can pass it
only to the nodes with highest connectivity.
High degree nodes are presumably high bandwidth node that can
handle the query traffic.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologyppt-140220112807-phpapp01/85/Topology-ppt-34-320.jpg)
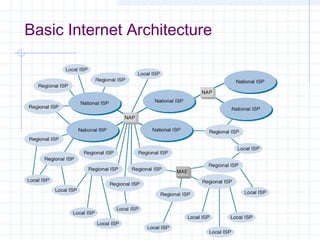
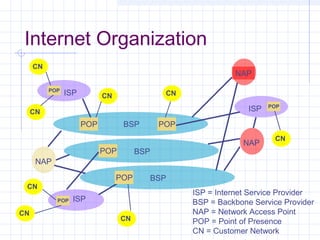
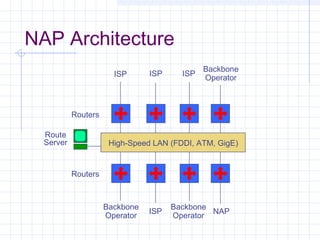
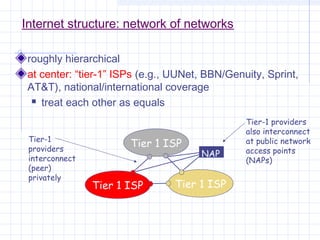
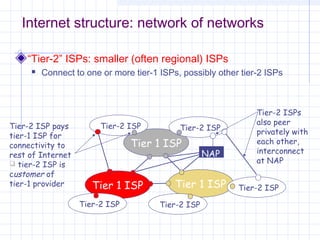
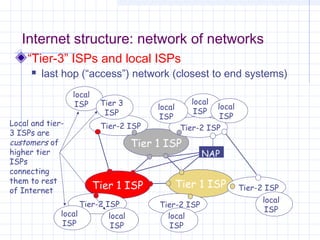
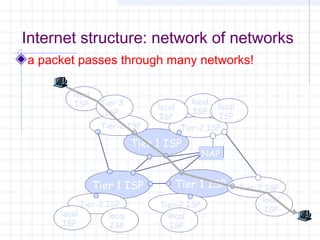
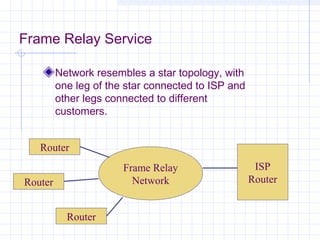
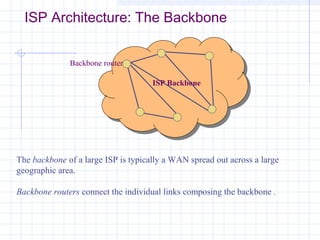
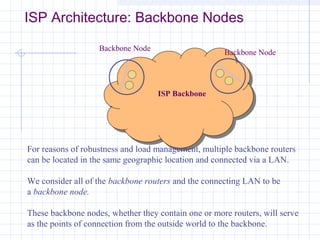
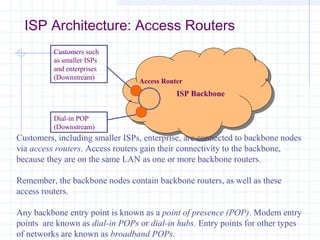
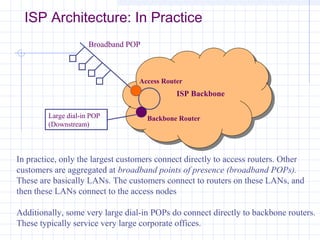
![Outline:
Internet Structure
&Organization
Internet Hierarchical Structure
ISPs, interconnection and organization [ref. 7].
POP Architecture and Load Balancing
ISP Architecture [ref. 7]. in detail
Topology Mapping Tool: Rocketfuel[ref. 8]
Discussion
ELEG 667-013 Spring 2003](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologyppt-140220112807-phpapp01/85/Topology-ppt-35-320.jpg)


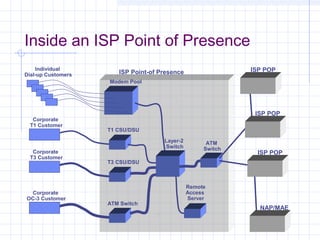
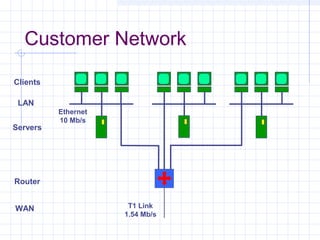
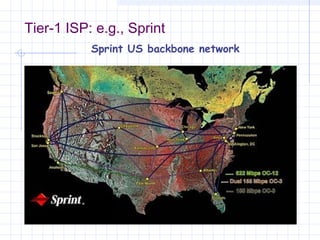
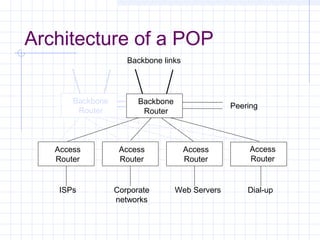
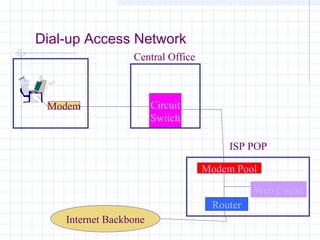
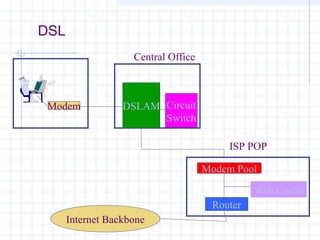
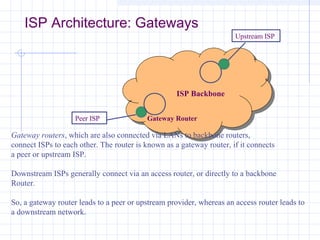
![Connecting to an ISP
ISPs provide access to the Internet through a Point of
Presence (POP).
Individual users access the POP through a dial-up
line using the PPP protocol.
The call connects the user to the ISP’s modem pool,
after which a remote access server (RAS) checks the
userid and password.
Once logged in, the user can send TCP/IP/[PPP]
packets over the telephone line which are then sent
out over the Internet through the ISP’s POP.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologyppt-140220112807-phpapp01/85/Topology-ppt-40-320.jpg)




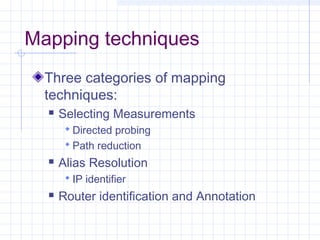
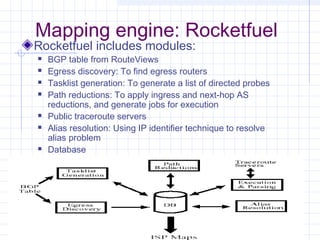
![Measuring ISP Topologies with Rocketfuel[8]:
Rocketfule – internet topology mapping engine
The goal is to obtain realistic, router-level maps of ISP networks.
Important influence on:
- The dynamics of routing protocols
- The scalability of multicast
- The efficacy of proposals for denial-of-service tracing and
response
- Other aspects of protocol performance (Internet path
selection)
Real topologies are not publicly available
- Confidential](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologyppt-140220112807-phpapp01/85/Topology-ppt-65-320.jpg)
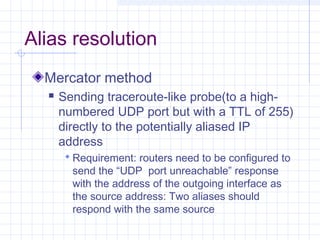



![References:
[1] Kenneth Calvert, Matthew Doar, Ellen Zegura, “Modeling Internet
Topology”.
[2]. Michalis Faloudsos, Petros Faloudsos, Christos Faloudsos, “On
Power-law Relationships of the Internet Topology”
[3]. Lada A. Adamic,1, Rajan M. Lukose,1, Amit R. Puniyani,2, and
Bernardo A. Huberman1,” Search in power-law networks”.
[4]. L. A. N. Amaral, A. Scala, M. Barthélémy, & H. E. Stanley, 1997,
“Classes of small-world networks.”
http://polymer.bu.edu/~amaral/Content_network.html
[5]. Ellen Zegura, Kenneth Calvert, “How to model an Internetwork”
[6]. Stefan Bornholdt, Holger Ebel, “World Wide Web scaling
exponent from Simon’s 1955 model”
[7]. S. Halabi and D. McPherson, Internet Routing Architectures, 2nd
ed., Cisco Press, Indianapolis, 2000.
[8]. Neil Spring Ratul Mahajan David Wetherall, Measuring ISP
Topologies with Rocketfuel](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topologyppt-140220112807-phpapp01/85/Topology-ppt-74-320.jpg)