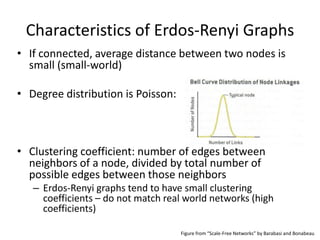
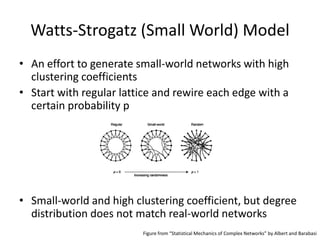
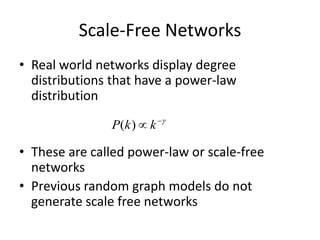
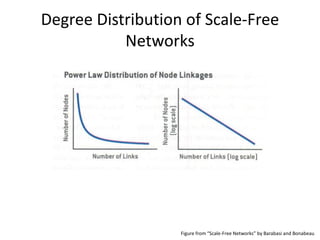
This document summarizes three common random graph models used to model complex real-world networks: Erdos-Renyi graphs, Watts-Strogatz small-world networks, and Barabasi-Albert scale-free networks. Erdos-Renyi graphs use a simple random edge placement process that can result in disconnected graphs or ones with small clustering. Watts-Strogatz networks address this by rewiring edges in a lattice, creating small-world properties but not realistic degree distributions. Barabasi-Albert networks use a preferential attachment mechanism where new nodes attach preferentially to higher degree nodes, producing power-law degree distributions seen in many real networks.