Embed presentation
Downloaded 14 times



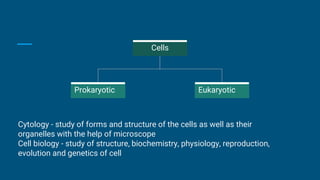
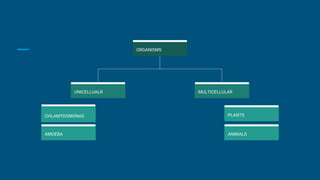

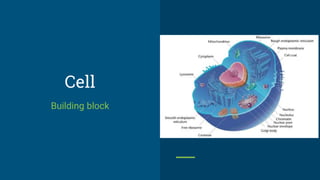




Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life. They were first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 when observing cells in a piece of cork under a microscope. Cells come in two main types - prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Cells can be either unicellular or multicellular. In humans, there are over 200 types of cells and the total number of cells is around 100 trillion. Cells are the building blocks that make up tissues, organs, organ systems and entire organisms.









