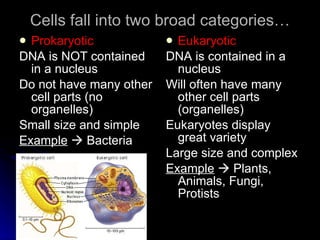
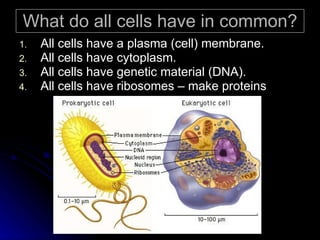
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life. In the 17th-18th centuries, advances in microscope technology allowed scientists like Hooke and van Leeuwenhoek to observe cells. In 1838, Schleiden and Schwann proposed the Cell Theory - that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function, and new cells are produced from existing cells. The Cell Theory was a major unifying concept in biology and changed views of life by introducing a more materialistic, reductionist perspective.