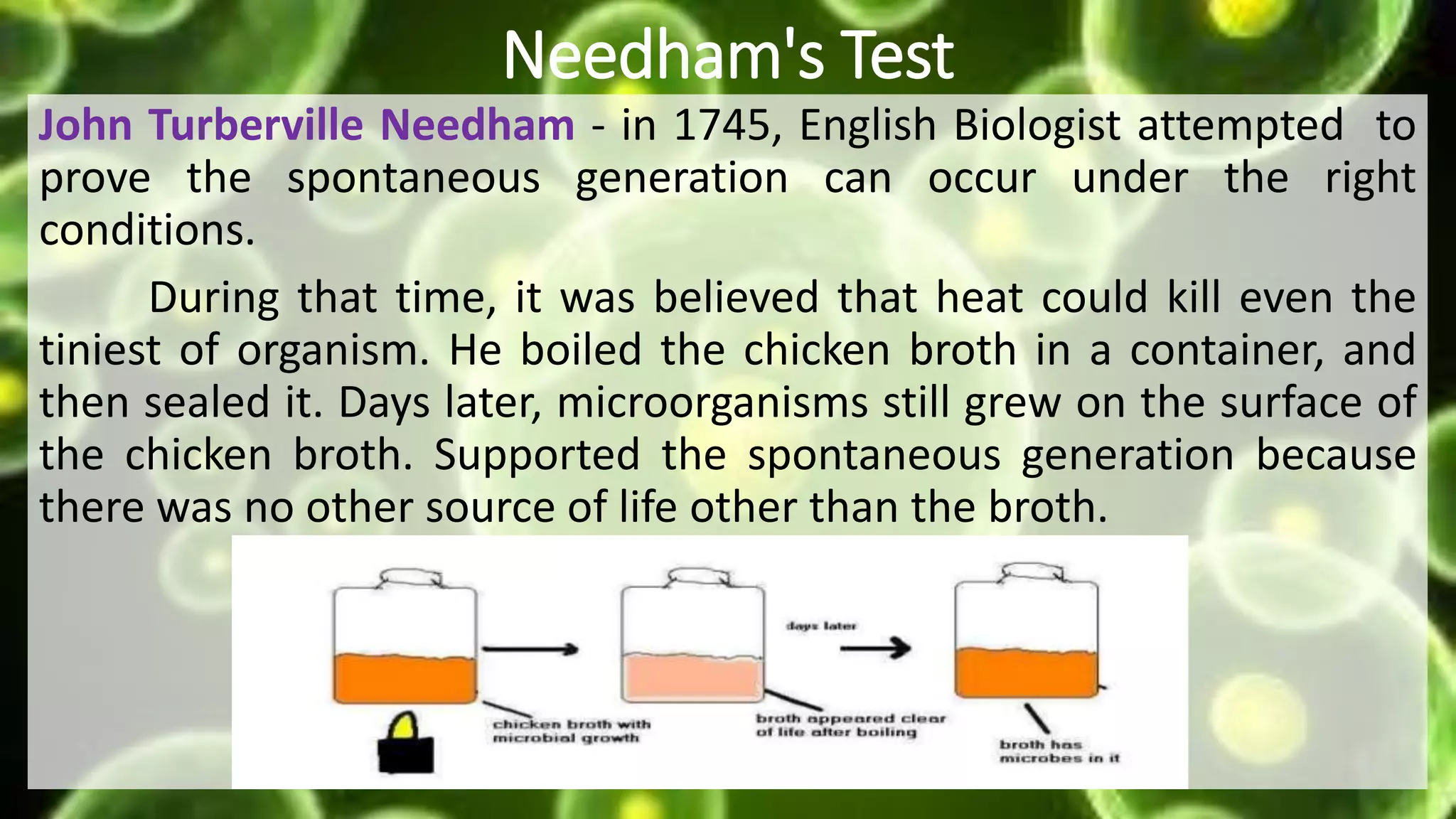
The document outlines the essential concepts and historical developments related to cell theory, including key postulates and notable scientists' contributions. It covers the understanding of cell types, structures, functions, and the distinctions between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Additionally, it discusses experiments that disproved spontaneous generation and laid the foundation for microbiology.