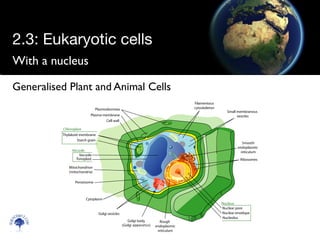
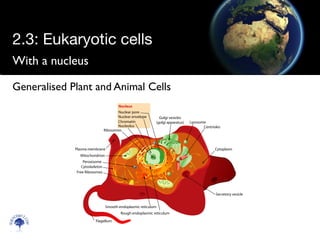
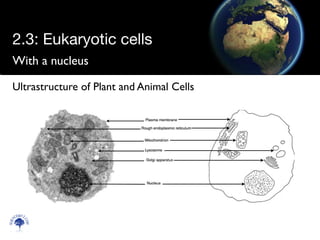
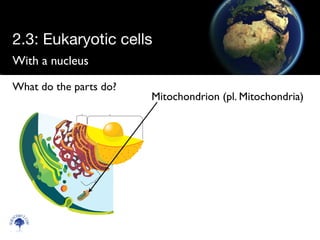
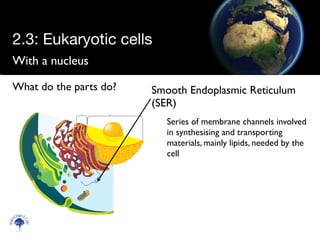
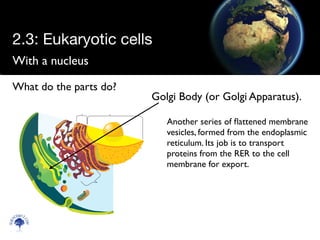
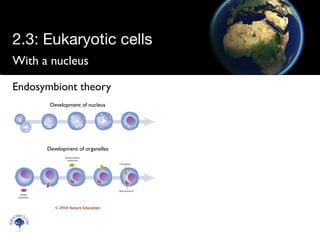
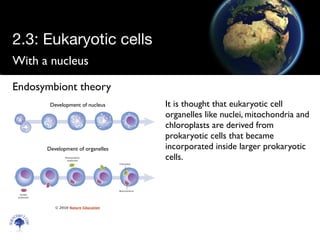
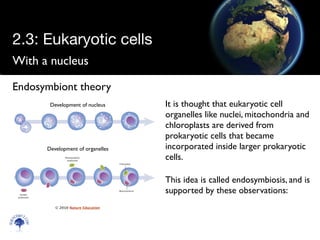
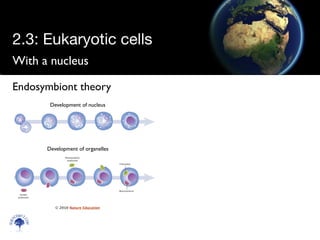
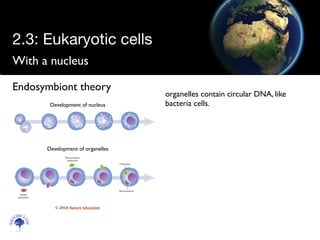
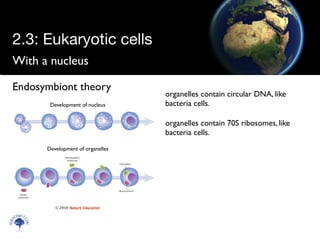
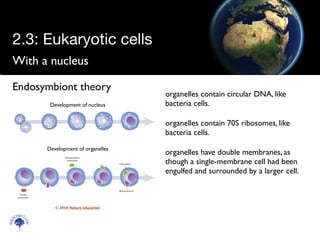
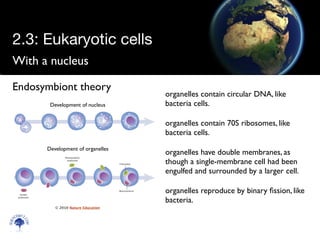
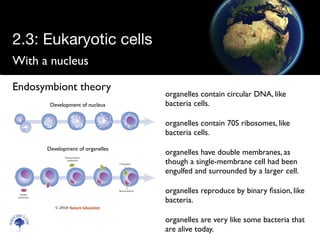
Eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles, unlike prokaryotic cells. Organelles include the mitochondria, which generates energy for the cell, and chloroplasts in plant cells, which perform photosynthesis. The endosymbiotic theory proposes that organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts originally came from prokaryotic cells engulfed by larger cells during evolution. Eukaryotic cells are generally larger than prokaryotic cells and have complex internal structures suited to multicellular life.