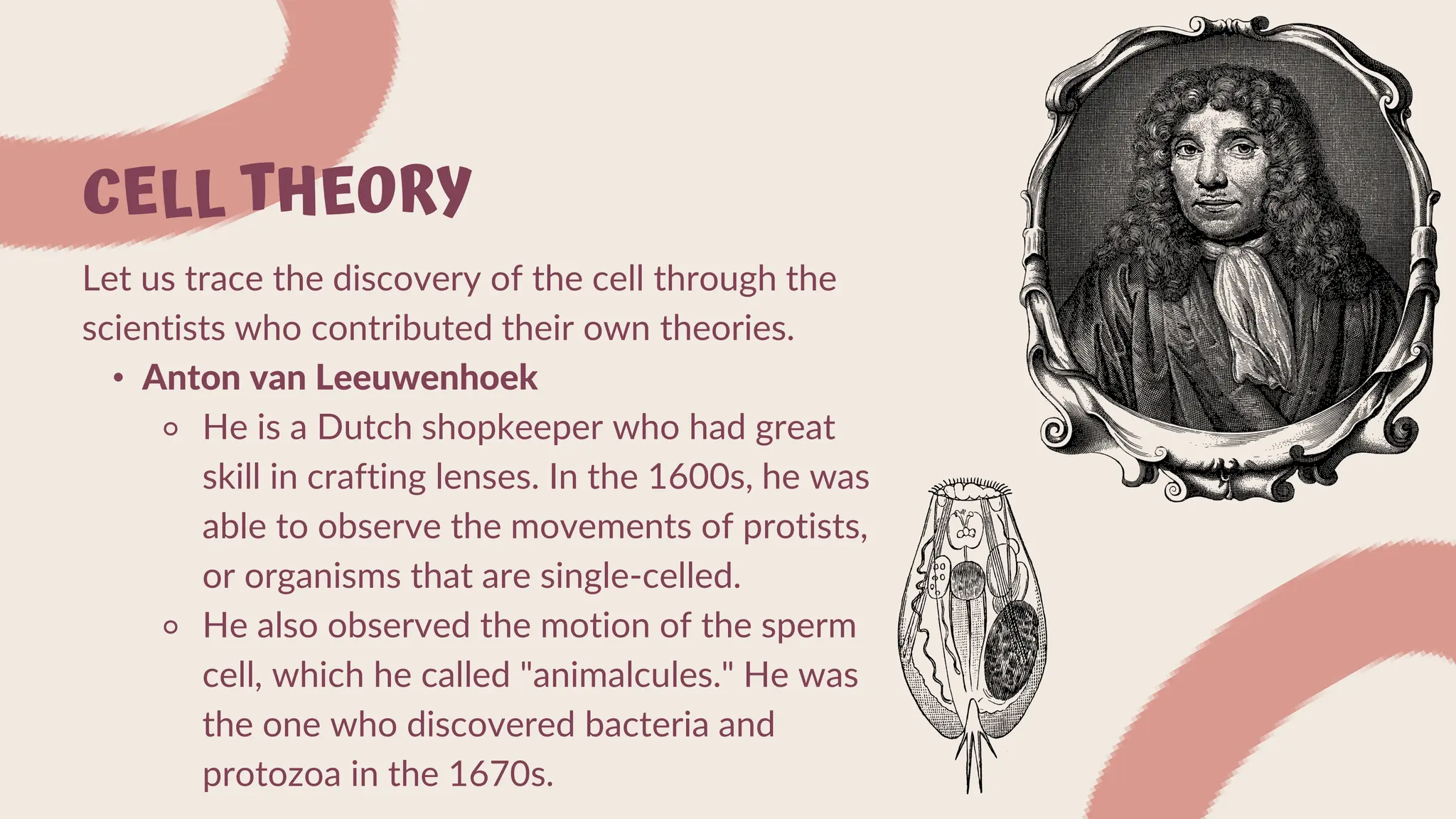
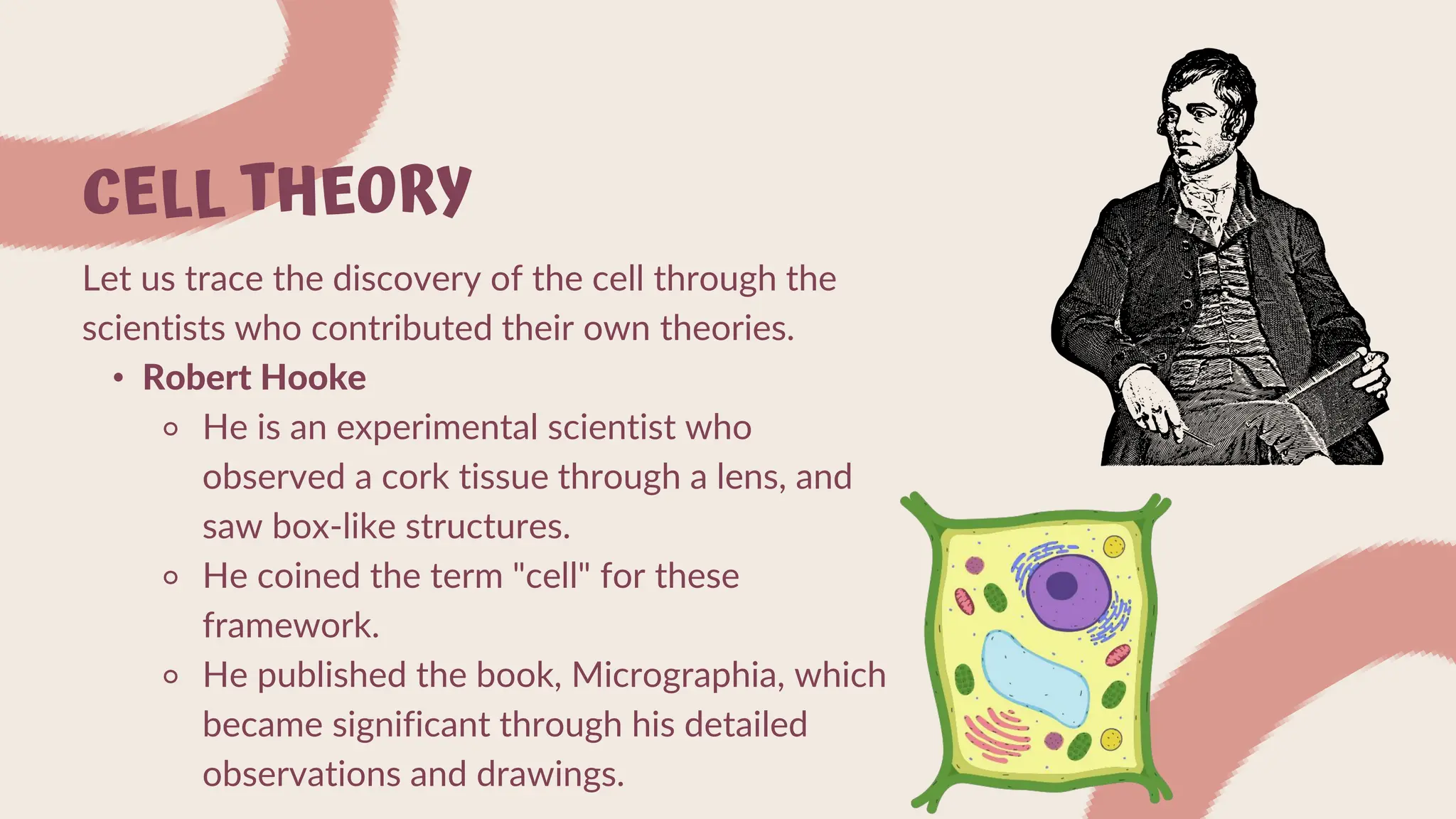
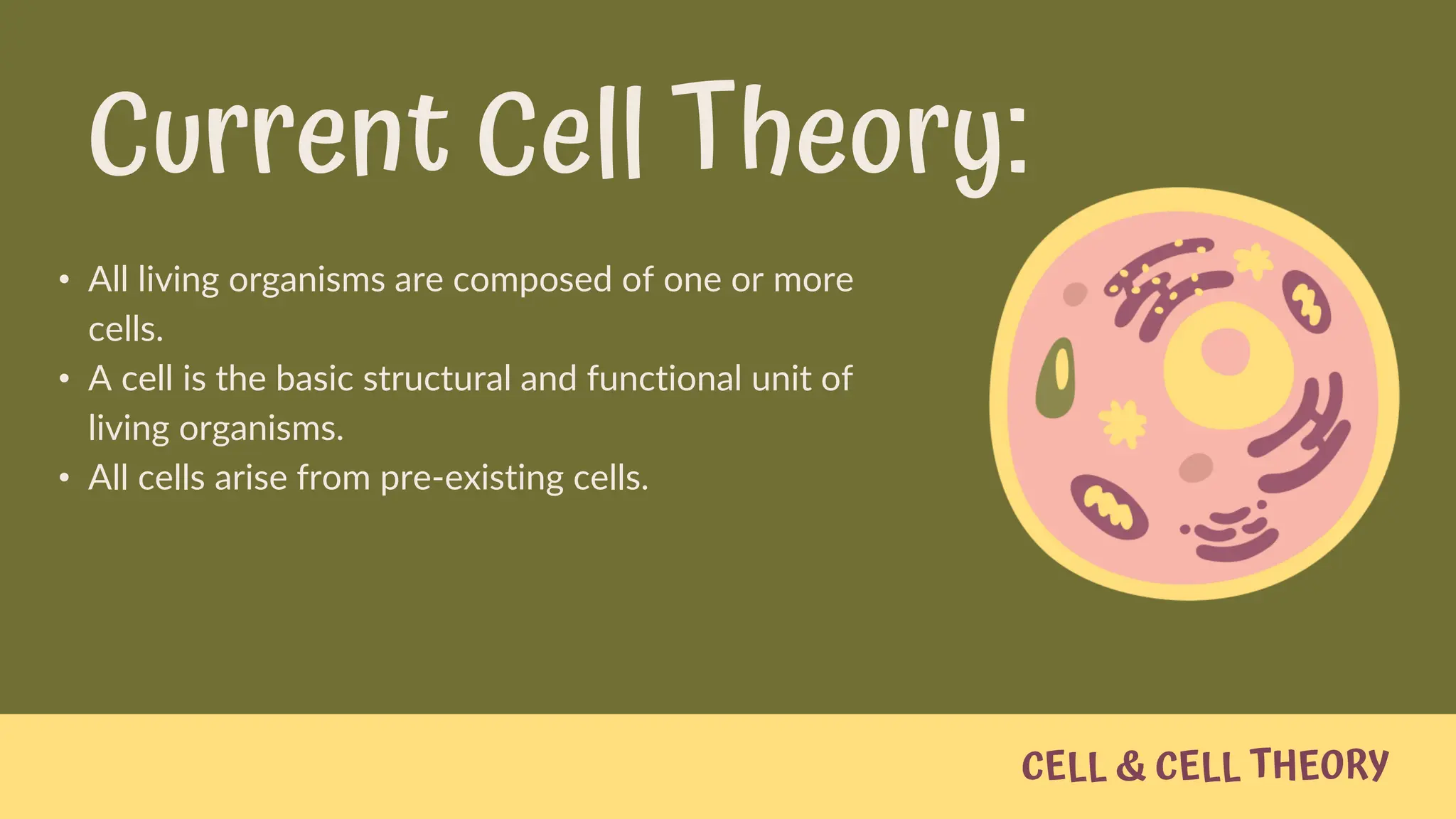
The document summarizes cell theory and the history of cell discovery. It discusses how early scientists like Anton van Leeuwenhoek, Robert Hooke, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow contributed to our understanding of cells. The cell theory states that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function, and all cells come from pre-existing cells. Current cell theory is that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, the cell is the basic unit of life, and cells only arise from other cells.