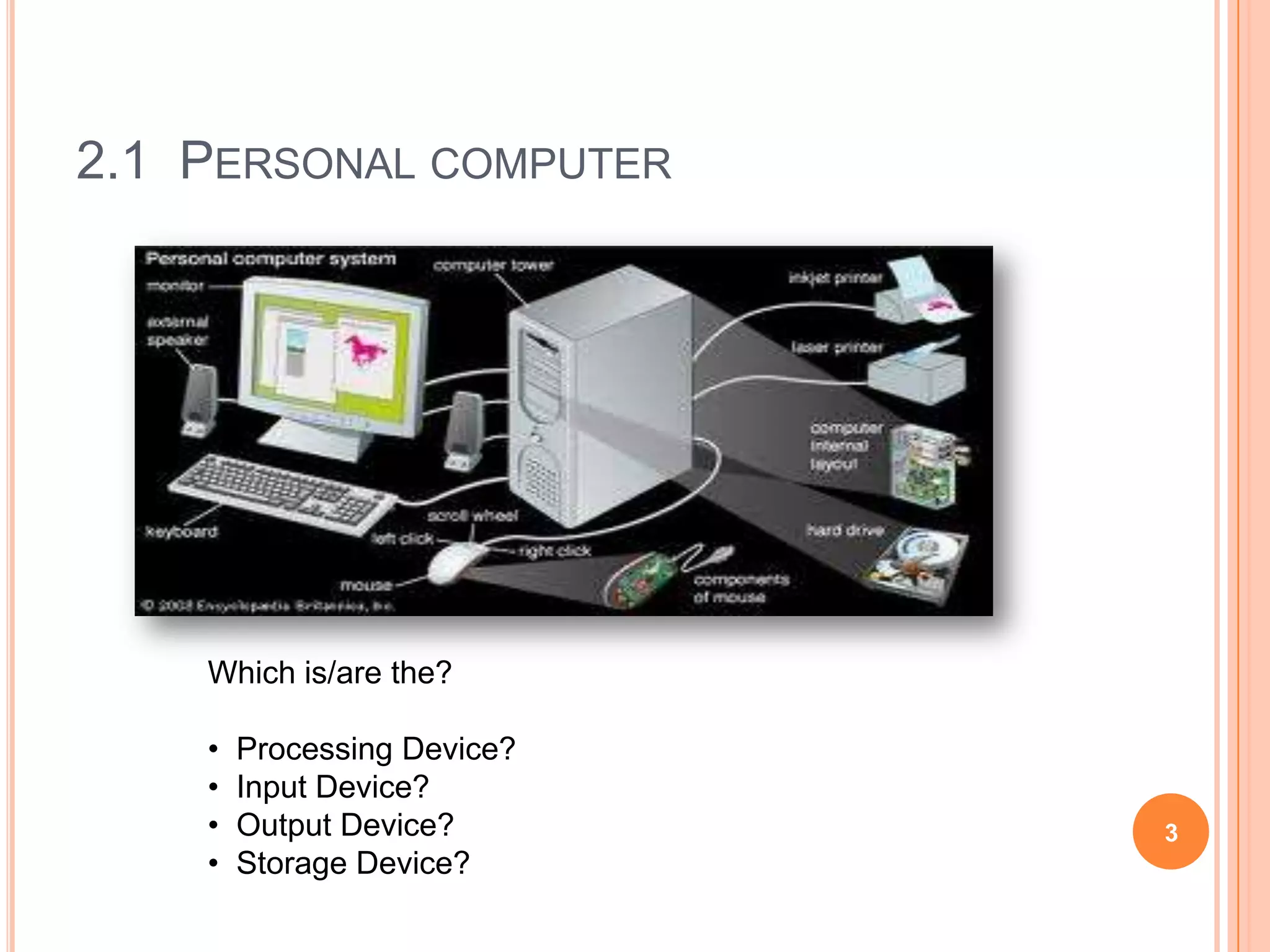
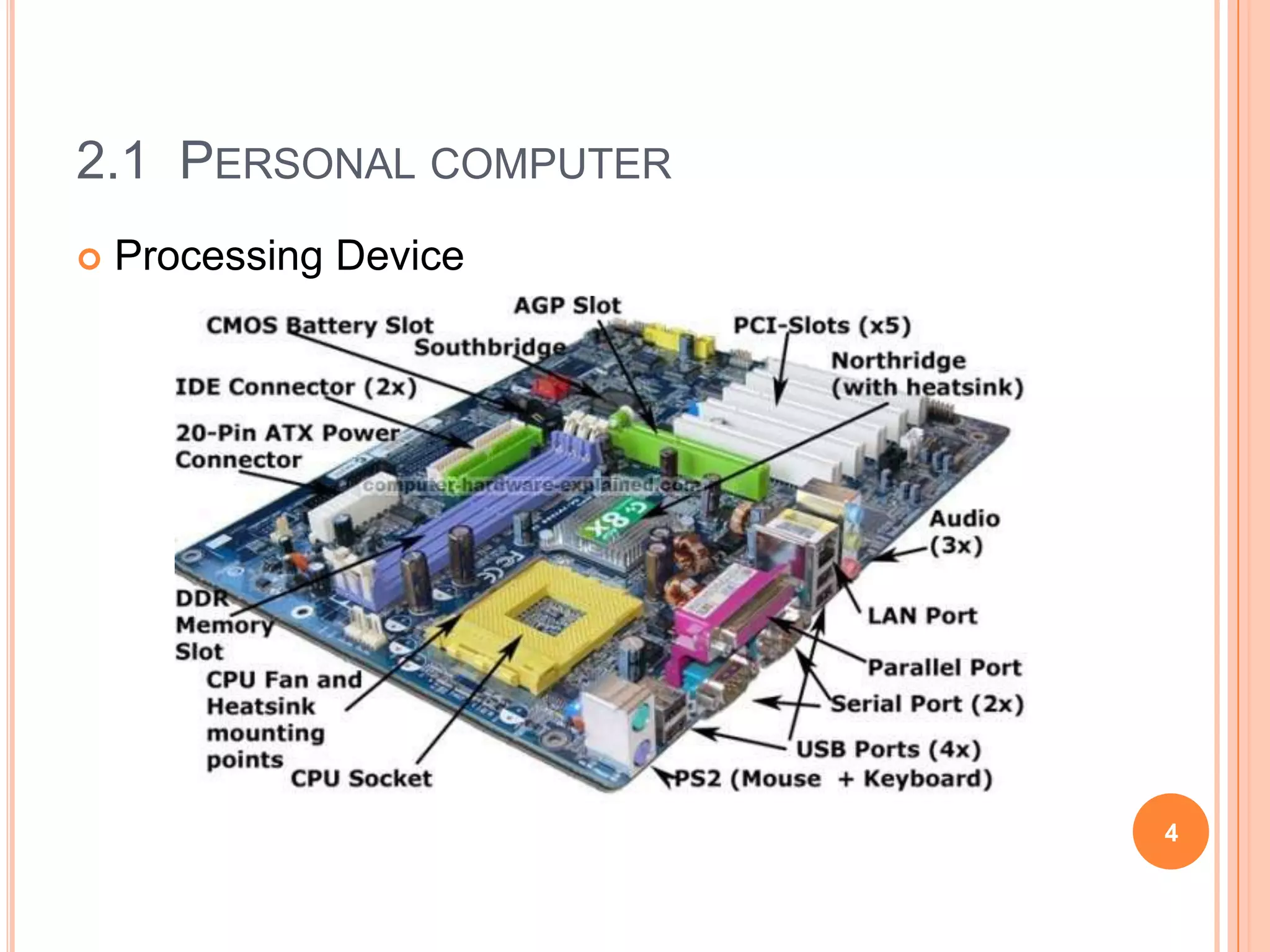
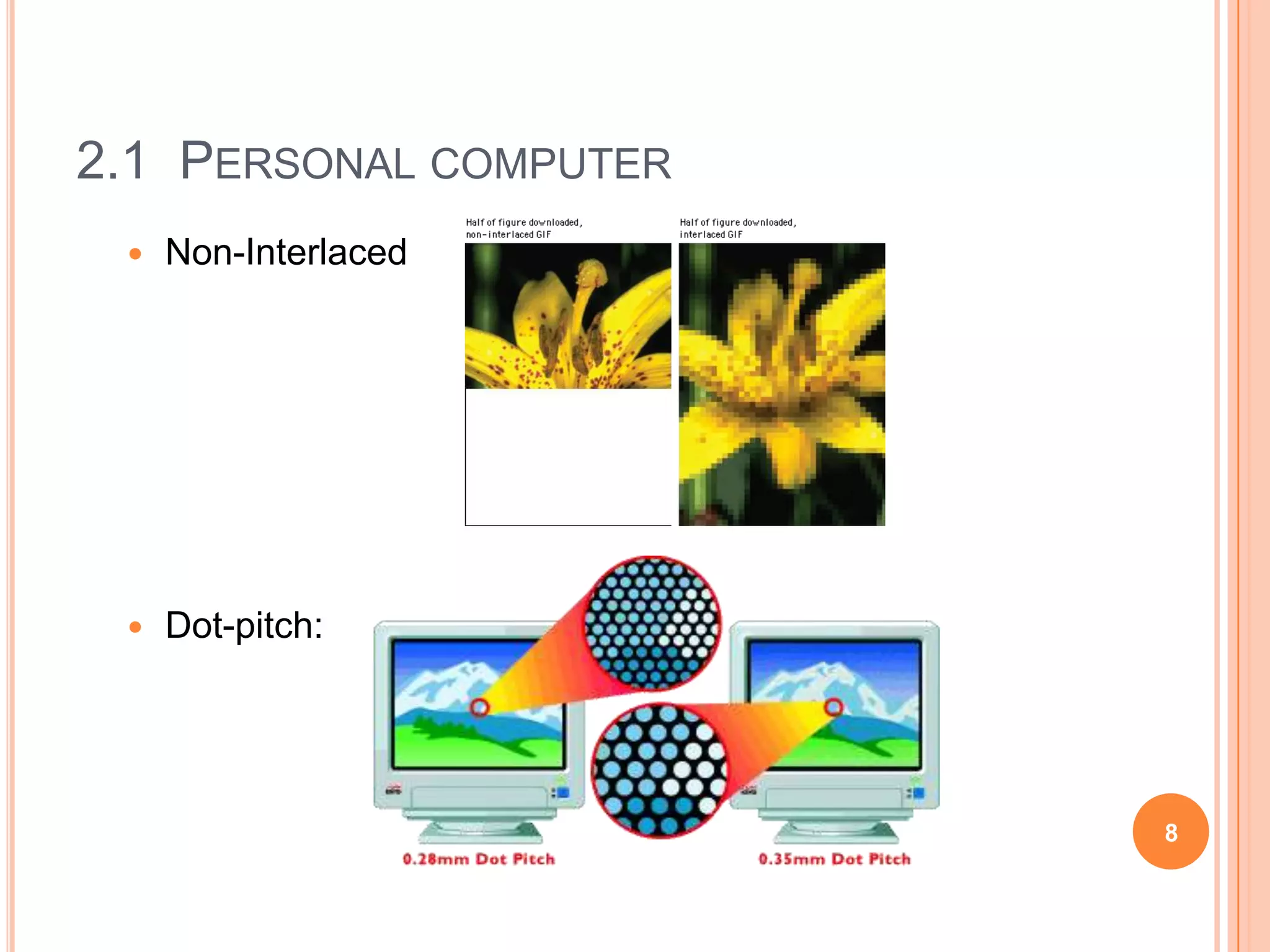
This document discusses hardware components for integrative media systems. It describes personal computer components including desktops, laptops and tablets as processing devices. Input devices include pointing devices, scanners, audio recorders and network cards. Monitors are described as output devices, with factors like resolution, screen size and refresh rate discussed. Storage devices include primary storage (RAM) and secondary storage like hard disks, USB drives, CDs and optical disks. Playback and development systems must have sufficient processing speed, memory, storage and display capabilities to smoothly run media applications and content creation.