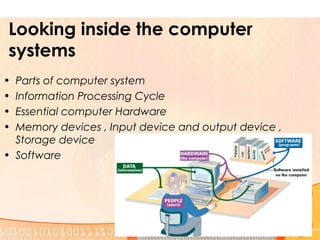
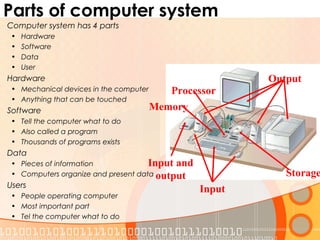
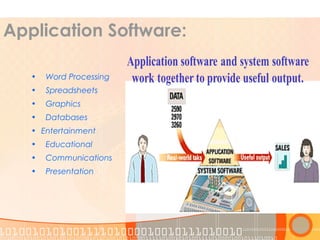
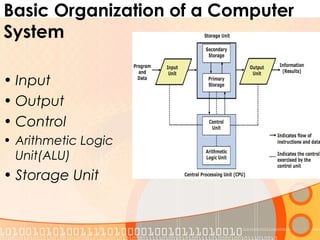
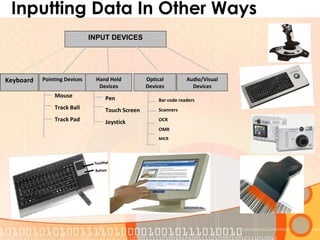
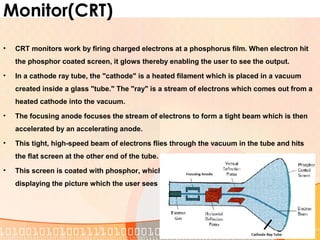
This document provides an overview of the course "Computer Fundamentals" taught by Taslima Ferdous Shova at Daffodil International University. The course covers topics such as introducing computer systems, hardware components, input/output devices, software, and using a keyboard and mouse. It describes the parts of a computer system including hardware, software, data, and users. It also discusses different types of computers used by individuals and organizations.