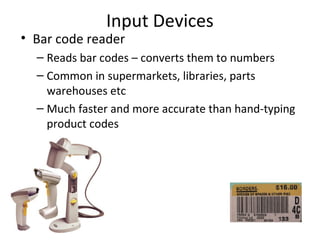
This power point presentation summarizes common hardware components used in information and communication technology systems. It describes input devices like keyboards, mice, scanners and touch screens. It also outlines various output devices such as monitors, printers, and data projectors. Finally, it discusses storage hardware including hard drives, solid state drives, CDs, DVDs, and USB flash drives. The presentation provides brief descriptions of each type of hardware component and notes their key features and uses.