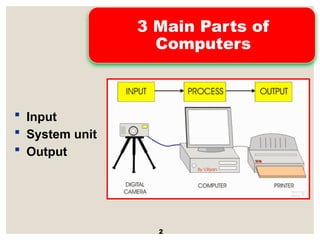
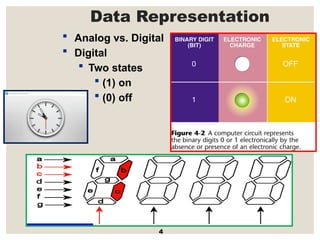
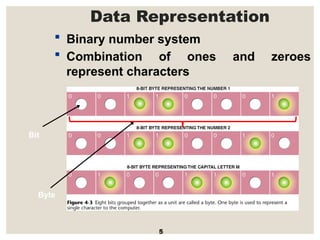
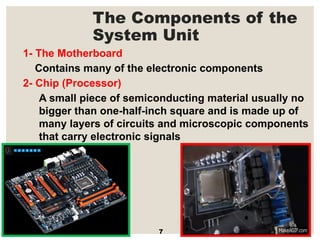
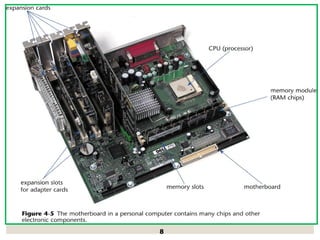
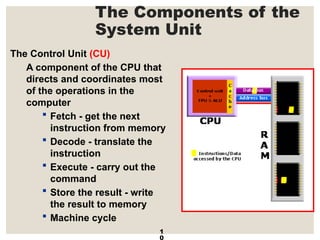
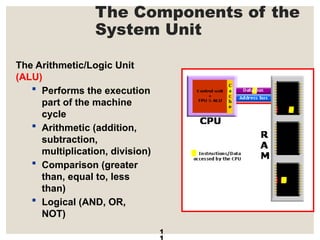
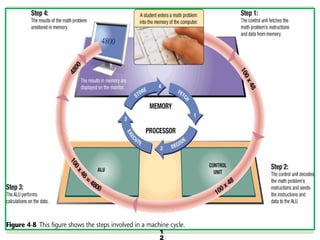
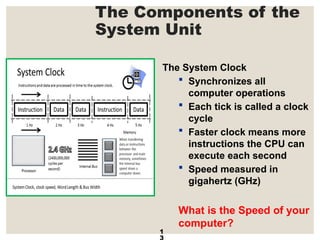
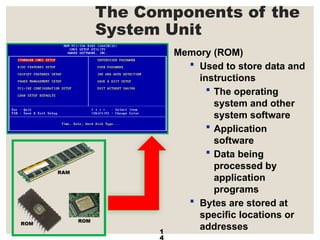
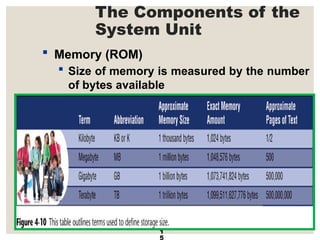
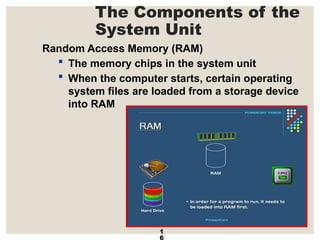
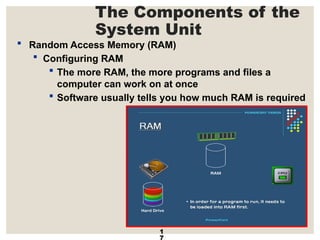
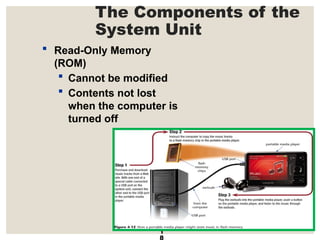
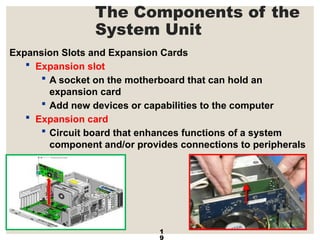
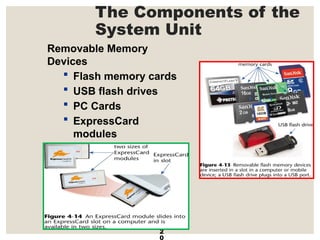
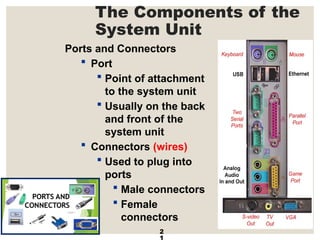
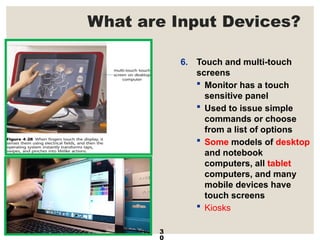
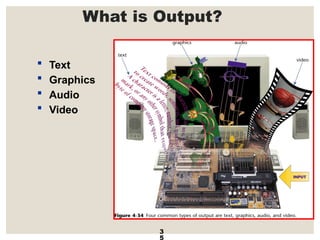
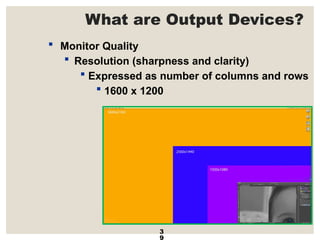
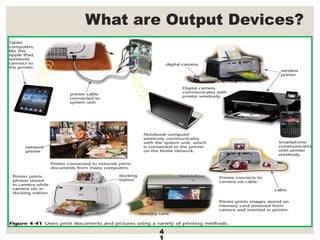
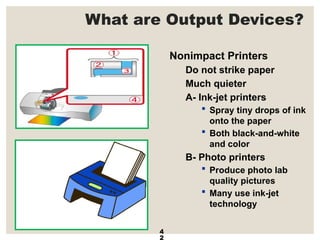
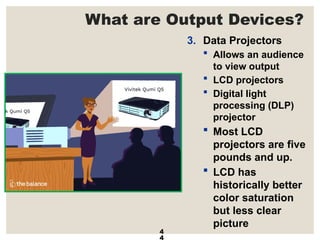
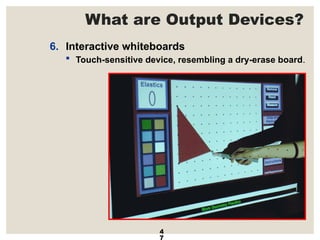
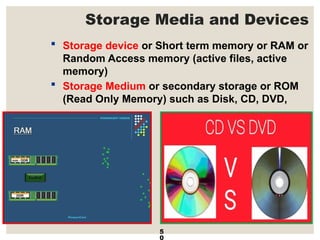
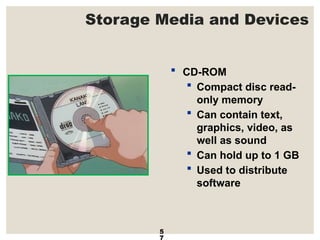
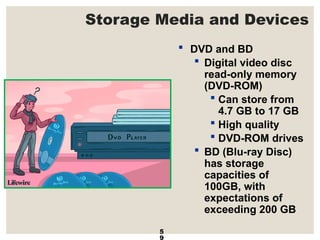
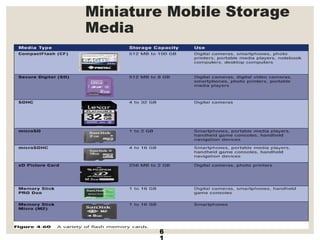
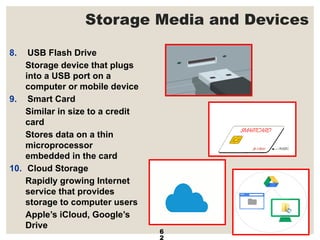
The document provides a comprehensive overview of computer systems, detailing the main components: input, system unit, and output. It explains the functions of the system unit's parts, including the CPU, memory, and various input and output devices. Additionally, it covers storage media types and their functionalities, highlighting advancements in memory technology.