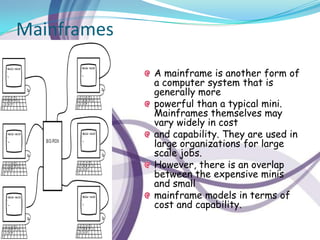
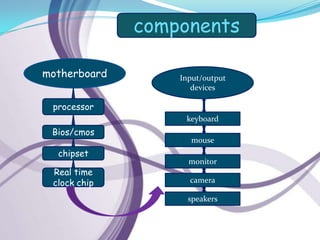
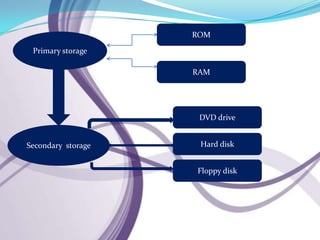
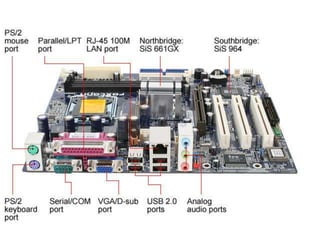
Computers can be categorized by size and performance. Personal computers like desktops and laptops are microcomputers commonly used by individuals. Larger systems include minicomputers and mainframes used by large organizations. A computer contains a processor, memory, storage, input/output devices, and software. It executes programs to perform tasks like banking, weather forecasting, and medical diagnosis. Hardware components communicate via the motherboard and work together under the instruction of software.