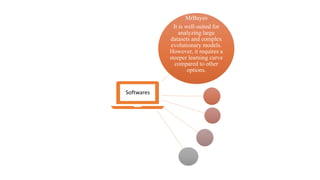
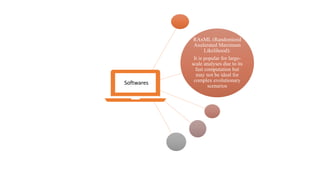
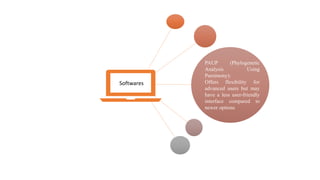
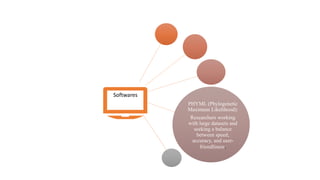
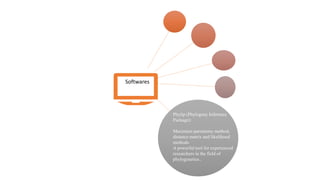
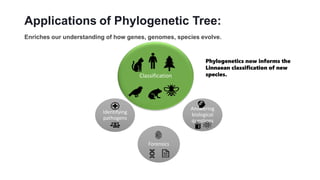
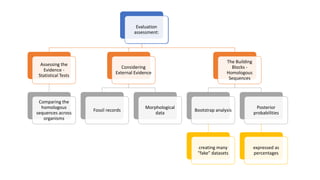
Phylogenetic trees depict the evolutionary relationships between organisms and are constructed through a four-step process: 1) gathering homologous DNA/protein sequences from different organisms, 2) aligning the sequences, 3) choosing a tree inference method like distance-based or character-based, and 4) visualizing the tree. Software tools can generate phylogenetic trees, with popular programs including RAxML, MrBayes, and PHYML. Phylogenetic analysis helps with classification, answering biological questions, forensics, pathogen identification, and other applications, but presents challenges with large datasets like data assembly and visualization.