This document discusses phylogenetic analysis, which is used to determine evolutionary relationships among genes and organisms. There are two main categories of phylogenetic analysis methods - distance methods and character methods. Distance methods determine genetic distance between sequences and use these distances to predict evolutionary relationships. Character methods, like maximum parsimony and maximum likelihood, examine changes in sequence alignments to determine the most probable evolutionary tree. Proper tree evaluation is also important to ensure the generated tree is meaningful.


![PHYLOGENETIC ANALYSIS
Placing the sequences as outer branches on a tree represents the evolutionary
relationships.
Two sequences that are much alike will be located as neighbouring outside
branches and would be joined to a common branch beneath them.
Phylogenetic tree is a 2- dimensional graph showing the evolutionary relationship
among the organisms. The tree is composed of nodes [ where branches bifurcate]
representing the taxa and branches representing the relationships among the taxa.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phylogenetictreeconstruction-231104051923-7dc75014/85/PHYLOGENETIC-TREE-CONSTRUCTION-pptx-3-320.jpg)

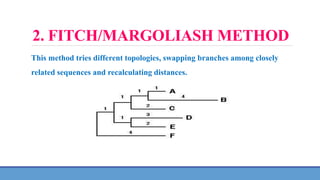
![1. NJ METHOD [NEIGHBOUR JOINING METHOD]
The NJ method is one of the simplest distance methods.
It begins by choosing the two most closely related sequences and then
adding the next most distant sequence as a third branch to the tree.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phylogenetictreeconstruction-231104051923-7dc75014/85/PHYLOGENETIC-TREE-CONSTRUCTION-pptx-7-320.jpg)
![1. NJ METHOD [NEIGHBOUR JOINING METHOD]
ADVANTAGES :
1. Fastest tree building method.
2. Can use empirical substitution scoring methods.
DISADVANTAGES :
1. Tests only a single tree.
2. Does not consider intermediate ancestors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phylogenetictreeconstruction-231104051923-7dc75014/85/PHYLOGENETIC-TREE-CONSTRUCTION-pptx-8-320.jpg)
![1. NJ METHOD [NEIGHBOUR JOINING METHOD]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phylogenetictreeconstruction-231104051923-7dc75014/85/PHYLOGENETIC-TREE-CONSTRUCTION-pptx-9-320.jpg)