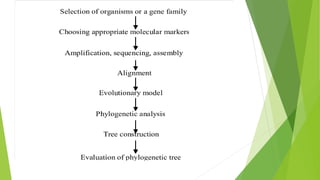
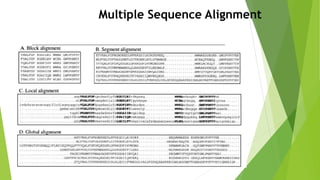
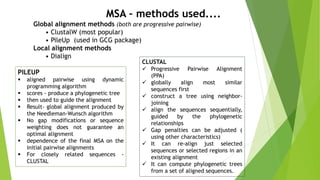
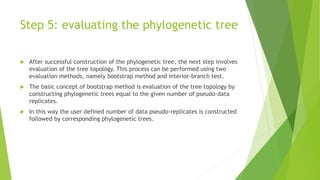
The document outlines the basic steps in constructing a phylogenetic tree:
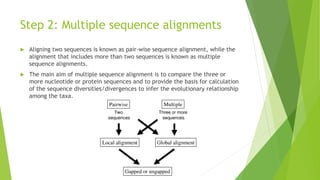
1) Assembling and aligning a dataset of DNA or protein sequences of interest.
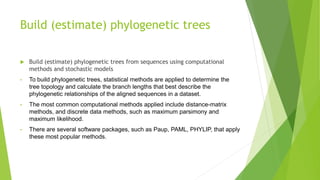
2) Using computational methods and evolutionary models to build phylogenetic trees from the sequence alignments.
3) Statistically testing and assessing the estimated trees to evaluate which tree topologies best describe the phylogenetic relationships between the sequences.
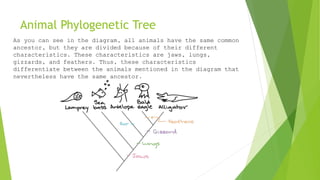
The process aims to provide a visual representation of how organisms have evolved from a common ancestor over time based on analyses of genetic similarities and differences in their molecular sequences.