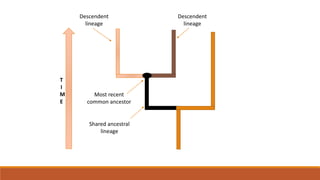
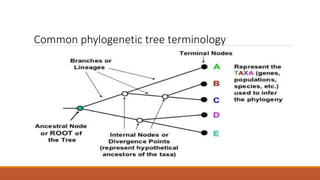
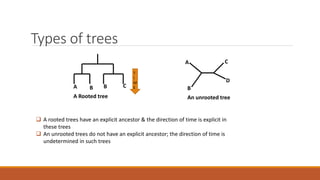
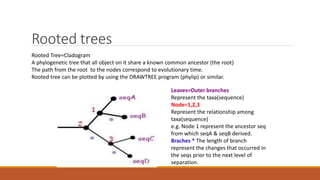
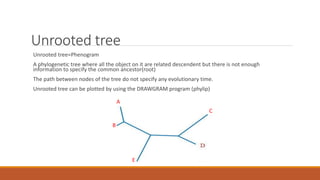
The document explains phylogenetics, detailing the evolutionary relationships between organisms through concepts like phylogenetic trees, cladograms, and rooted/unrooted trees. It describes various methods for constructing these trees, such as distance-based and character-based methods, emphasizing the importance of sequence selection and analysis software. The document also highlights the differences between coding and non-coding regions in terms of mutation rates and presents commonly used phylogenetic analysis programs.