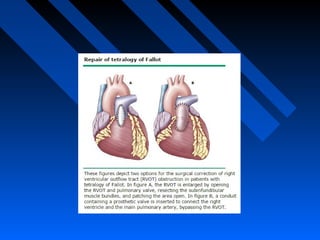
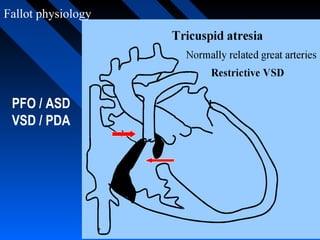
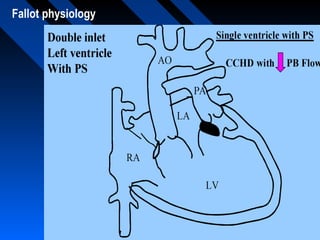
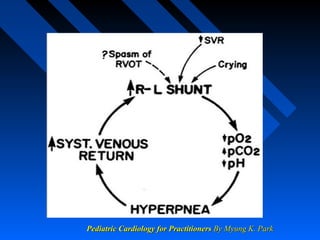
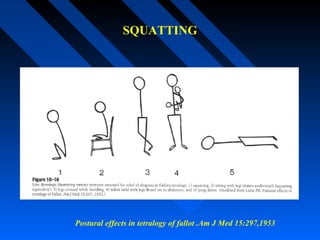
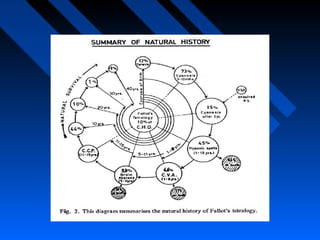
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a congenital heart defect characterized by four anatomical abnormalities - ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy, and overriding aorta. It was first described in detail in 1888. The physiology involves deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle being shunted away from the lungs due to pulmonary stenosis. Severity of cyanosis and murmurs depends on degree of pulmonary stenosis. Management involves treating spells and definitive surgical repair is usually done in early childhood.








![GENETIC FACTORS
Genetic causes of TOF are heterogeneous:
a)Monogenic or polygenic mode of inheritance.
b)Autosomal dominant mode of inheritance with reduced
penetrance,
c)An autosomal recessive mode of inheritance.
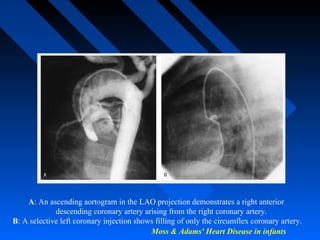
Moss & Adams' Heart Disease in infants
Environmental factors:
Maternal diabetes [threefold increased risk], Retinoic
acids,Maternal phenylketonuria (PKU), and Trimethadione
Edward J et al .Edward J et al .N Engl J Med 1985; 313:837-841N Engl J Med 1985; 313:837-841](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tofphysiology-160518094724/85/Tof-physiology-10-320.jpg)











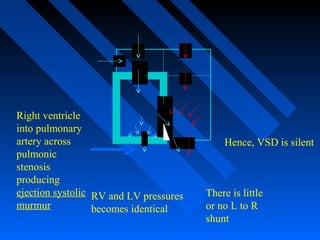



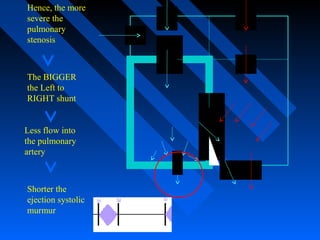
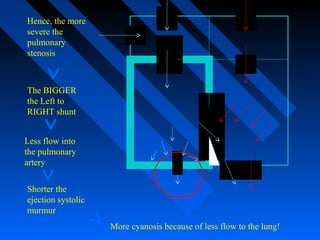







![ Systolic murmur - crescendo-decrescendo at LUSB.
The intensity of the murmur inversely parallels the degree
of pulmonic obstruction.
Diastolic murmurs are unusual.
TOF with PA- no harsh, obstructive precordial murmurs
TOF and APV syndrome - A harsh diastolic murmur, with
a harsh murmur of PS. [Harsh sawing, to-and-fro murmur]
Continuous murmurs - PDA, aortopulmonary collaterals,
may be best heard in the back.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tofphysiology-160518094724/85/Tof-physiology-43-320.jpg)

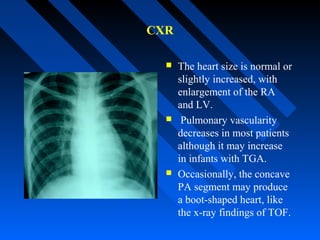
![CXR
Normal sized heart; [may be large in
PA]
Upturned apex; attenuated & concave
left heart border (infundibular and PA
hypoplasia)….boot-shaped heart, or
coeur en sabot
Diminished pulmonary vascularity in
proportion to the degree of cyanosis.
Right atrial enlargement
Right-sided aortic arch (20-25% of
patients) with indentation of leftward-
positioned tracheobronchial shadow.
Absent thymic shadow in the newborn
may indicate associated chromosome
22q11.2 microdeletion (DiGeorge
syndrome).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tofphysiology-160518094724/85/Tof-physiology-46-320.jpg)








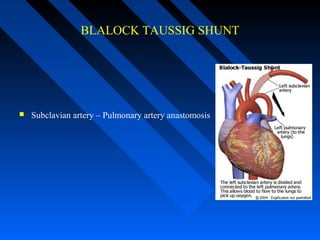
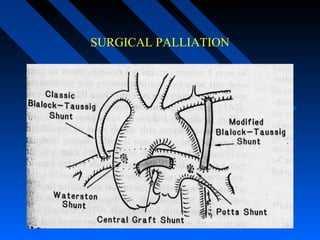
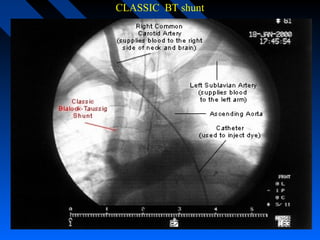
![PALLIATIVE PROCEDURES
Classic BT shunt[1945]…SCAPA on side opposite AA
Modified BT… esp in small infants <6 months…side to side anastomosis
with interposition graft of PTFE or Gore-Tex b/w SCA & PA [on the same
side of AA]
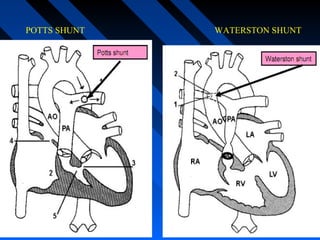
Waterston shunt : Side-side anastomosis of RPA to AA
Potts : Side - side anastomosis of LPA to DA
Waterston/Potts shunts : complications
Excessive PBF HF [20%] & PHTN
Difficulty taking shunt down at time of correction
Distortion of Rt/Lt PA ; Right/Left PA aneurysm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tofphysiology-160518094724/85/Tof-physiology-59-320.jpg)