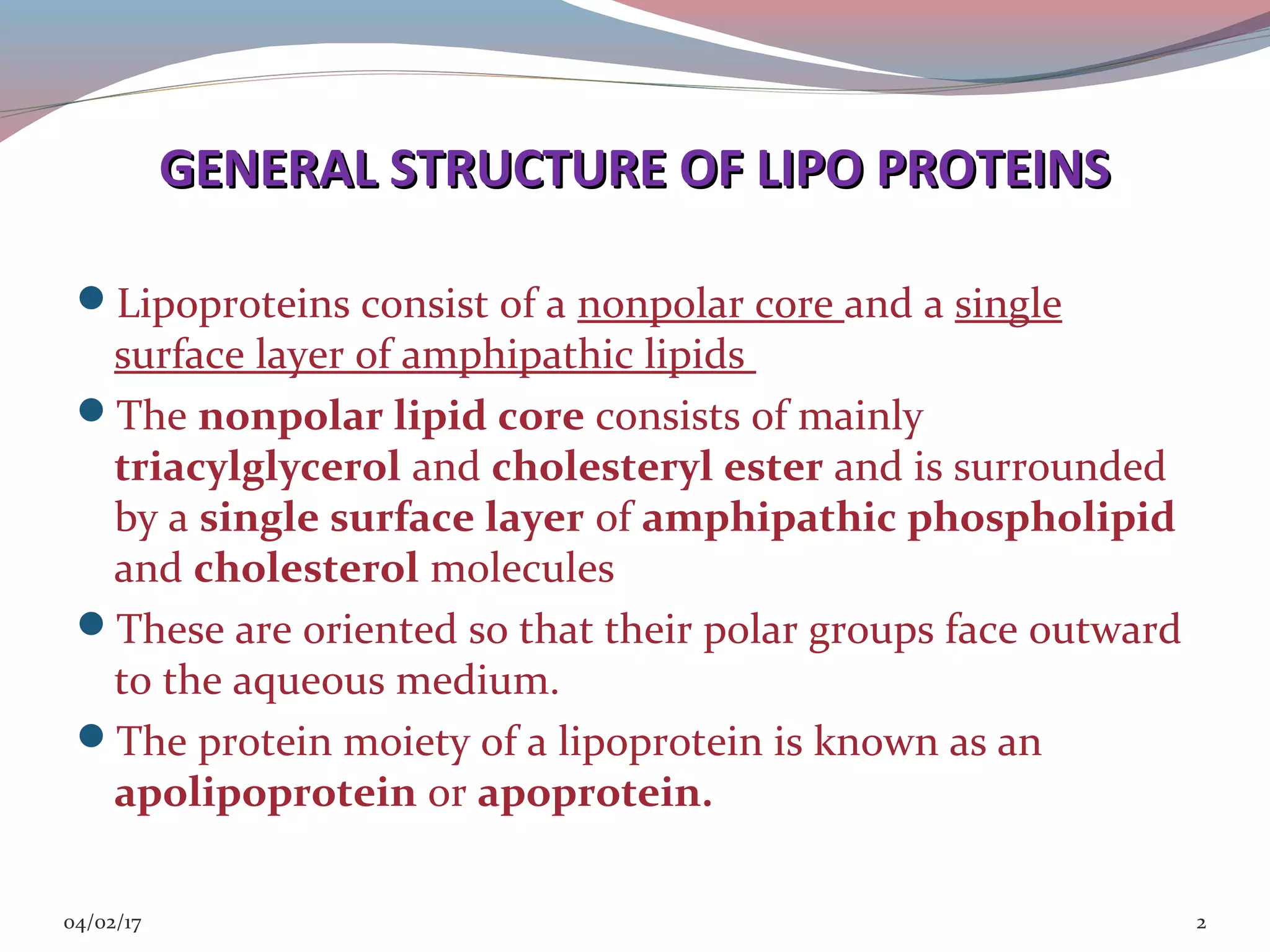
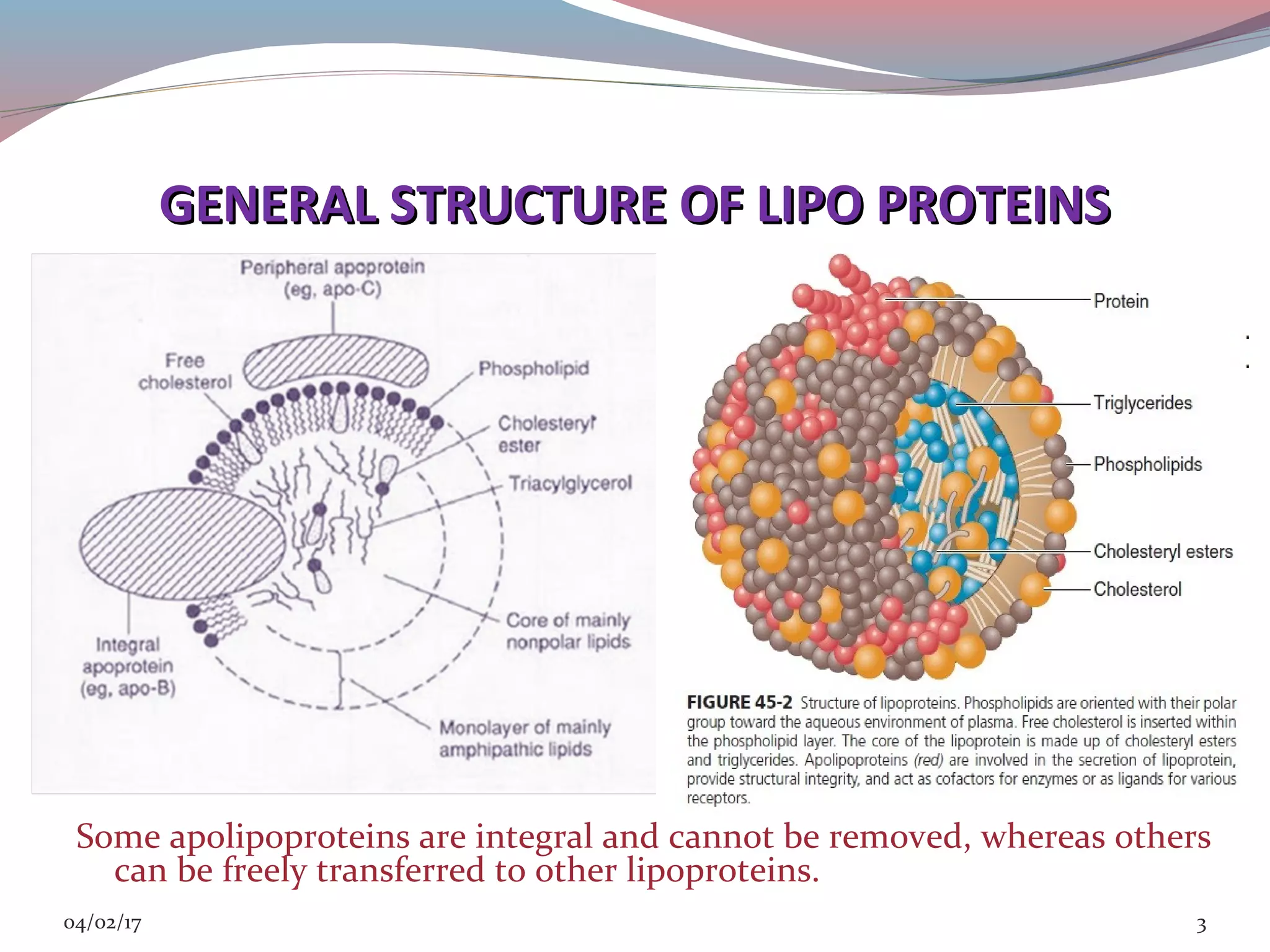
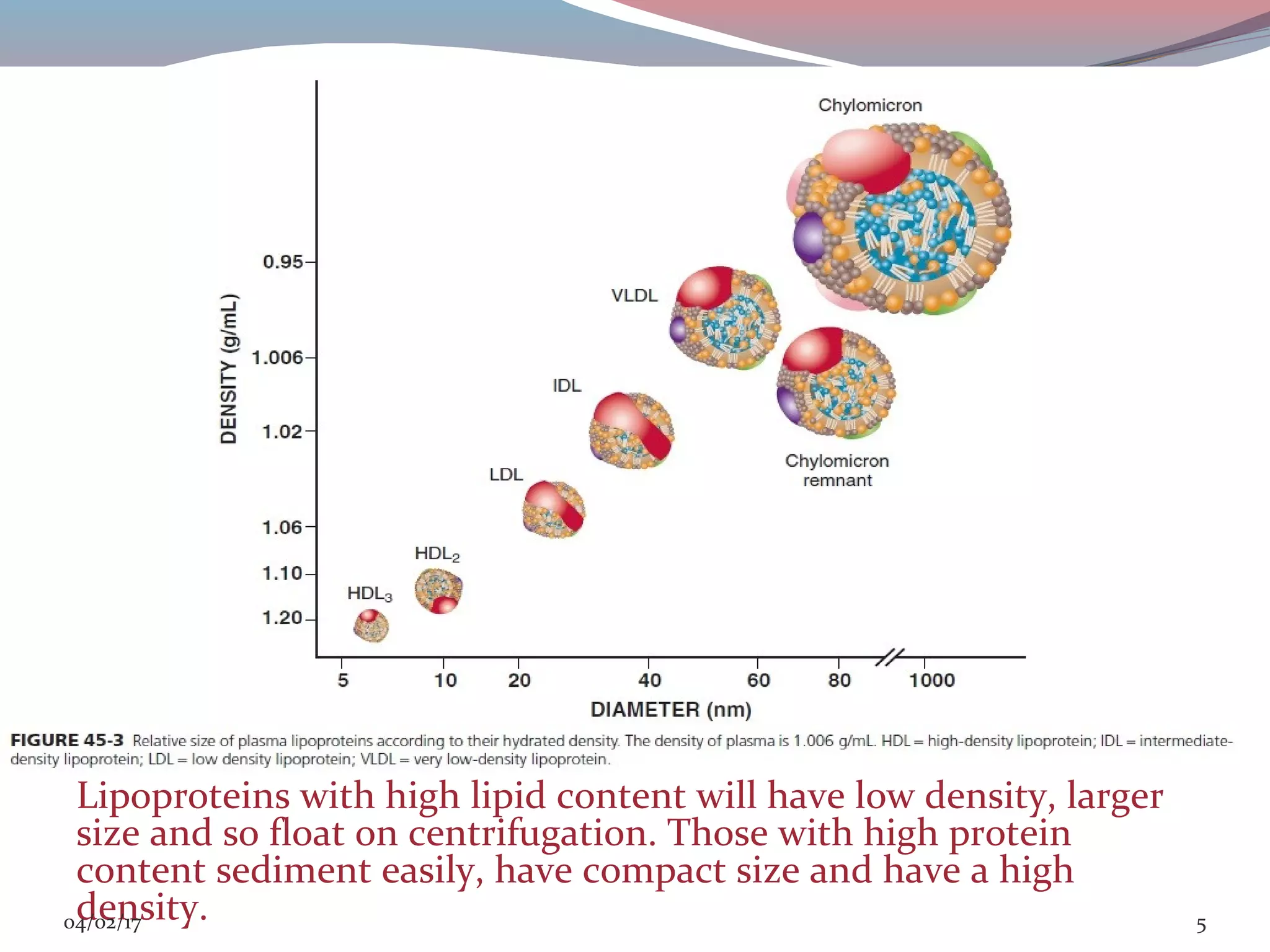
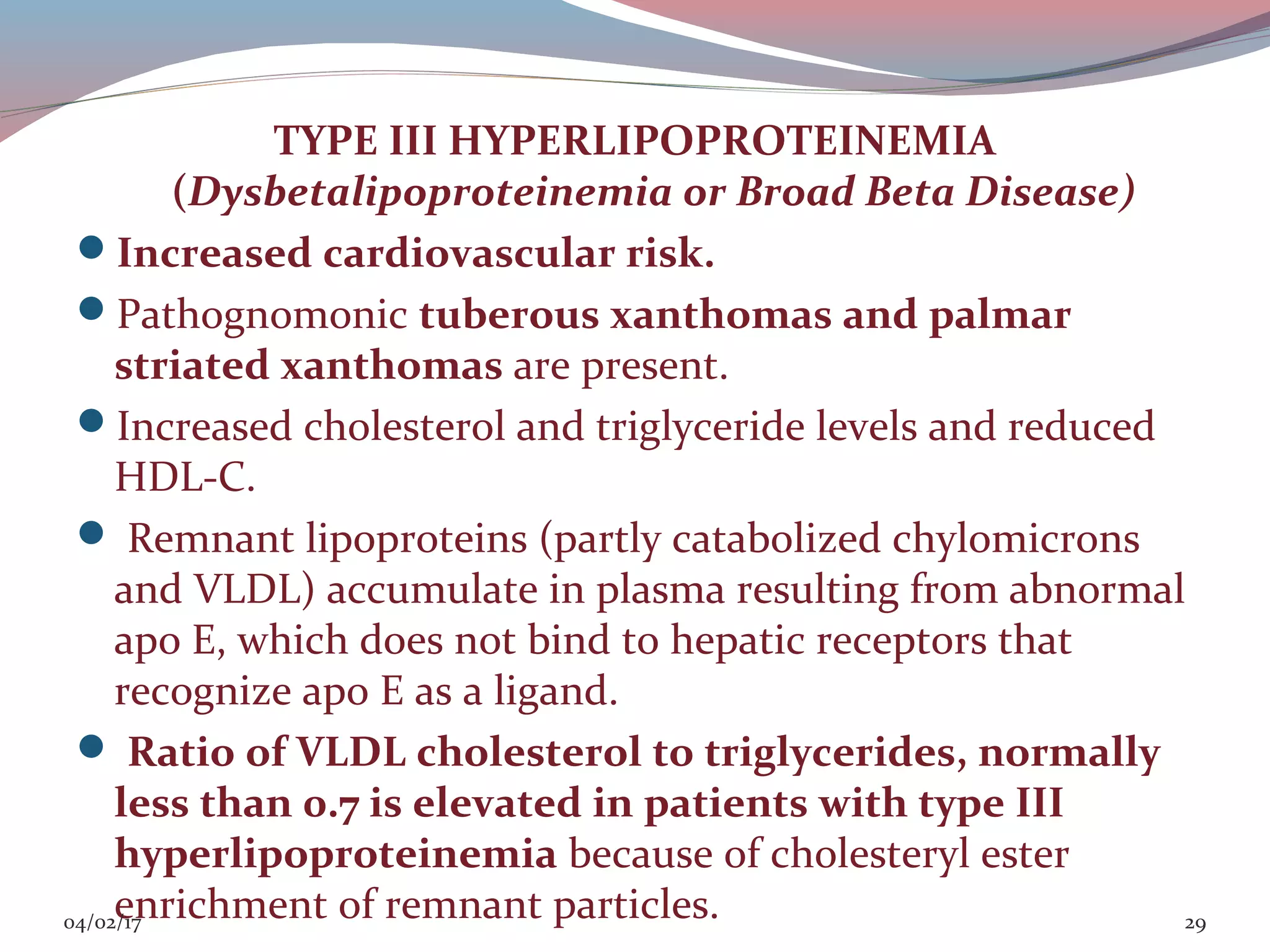
This document discusses lipoprotein disorders and their relationship to cardiovascular disease. It begins by describing the general structure of lipoproteins, which consist of a nonpolar lipid core surrounded by amphipathic proteins and lipids. It then covers the classification of lipoproteins based on density, describes various genetic lipoprotein disorders like familial hypercholesterolemia and their effects, and discusses specific disorders involving high-density lipoproteins, triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, and lipoprotein processing enzymes. The document provides an overview of the pathogenesis and clinical manifestations of major lipoprotein disorders and their implications for cardiovascular risk.




































![2013 ACC/AHA Guidelines:2013 ACC/AHA Guidelines:
Statins without any lipid “goals”Statins without any lipid “goals”
Circulation 2014; 129: S1-S45
• Clinical ASCVD*
• LDL-C ≥190 mg/dL, Age ≥21 years
• Primary prevention – Diabetes: Age 40-75 years, LDL-C
70-189 mg/dL
• Primary prevention - No Diabetes†: ≥7.5%‡ 10-year
ASCVD risk, Age 40-75 years, LDL-C 70-189 mg/dL
*Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
†
Requires risk discussion between clinician and patient before statin initiation
‡
Statin therapy may be considered if risk decision is uncertain after use of ASCVD risk calculator
Circulation. 2014;129[suppl 2]:S1-S45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lipidfinal-170402143650/75/Lipoprotein-disorders-41-2048.jpg)


































