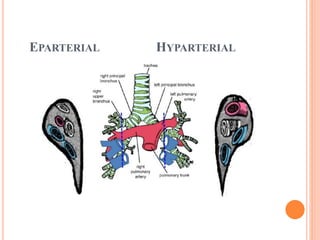
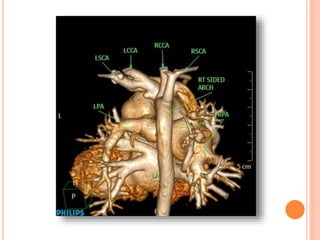
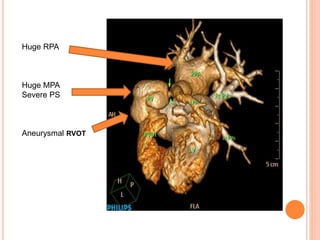
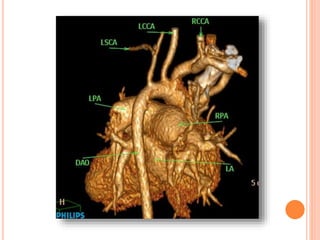
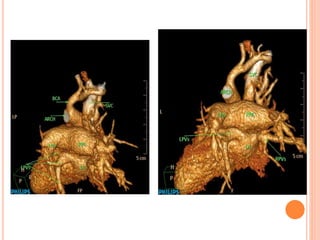
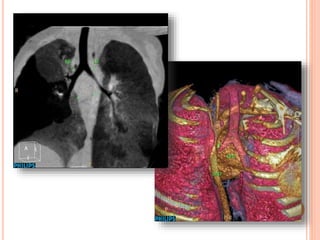
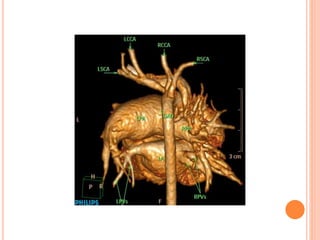
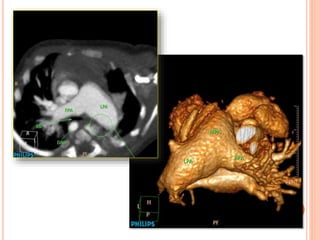
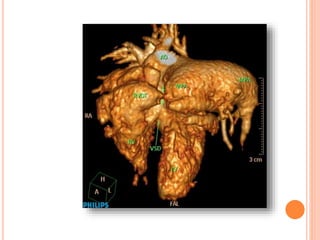
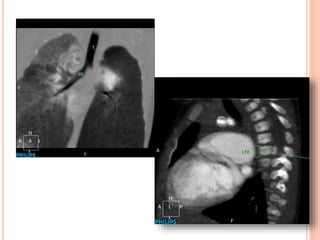
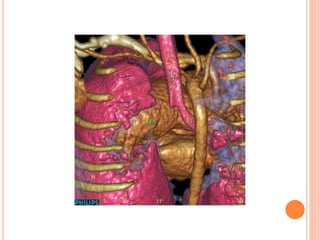
Absent pulmonary valve syndrome is a rare congenital heart defect where the pulmonary valve is either completely absent or has rudimentary tissue. This causes the pulmonary arteries to dilate massively and compress the trachea during fetal development. After birth, affected infants often experience respiratory distress or complications like pneumonia. Surgical repair is needed to close the ventricular septal defect and restore competence to the pulmonary valve to address both the cardiac issues and pulmonary complications.