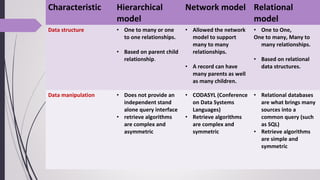
This document discusses different types of data models, including hierarchical, network, relational, and object-oriented models. It focuses on explaining the relational model. The relational model organizes data into tables with rows and columns and handles relationships using keys. It allows for simple and symmetric data retrieval and integrity through mechanisms like normalization. The relational model is well-suited for the database assignment scenario because it supports linking data across multiple tables using primary and foreign keys, and provides query capabilities through SQL.