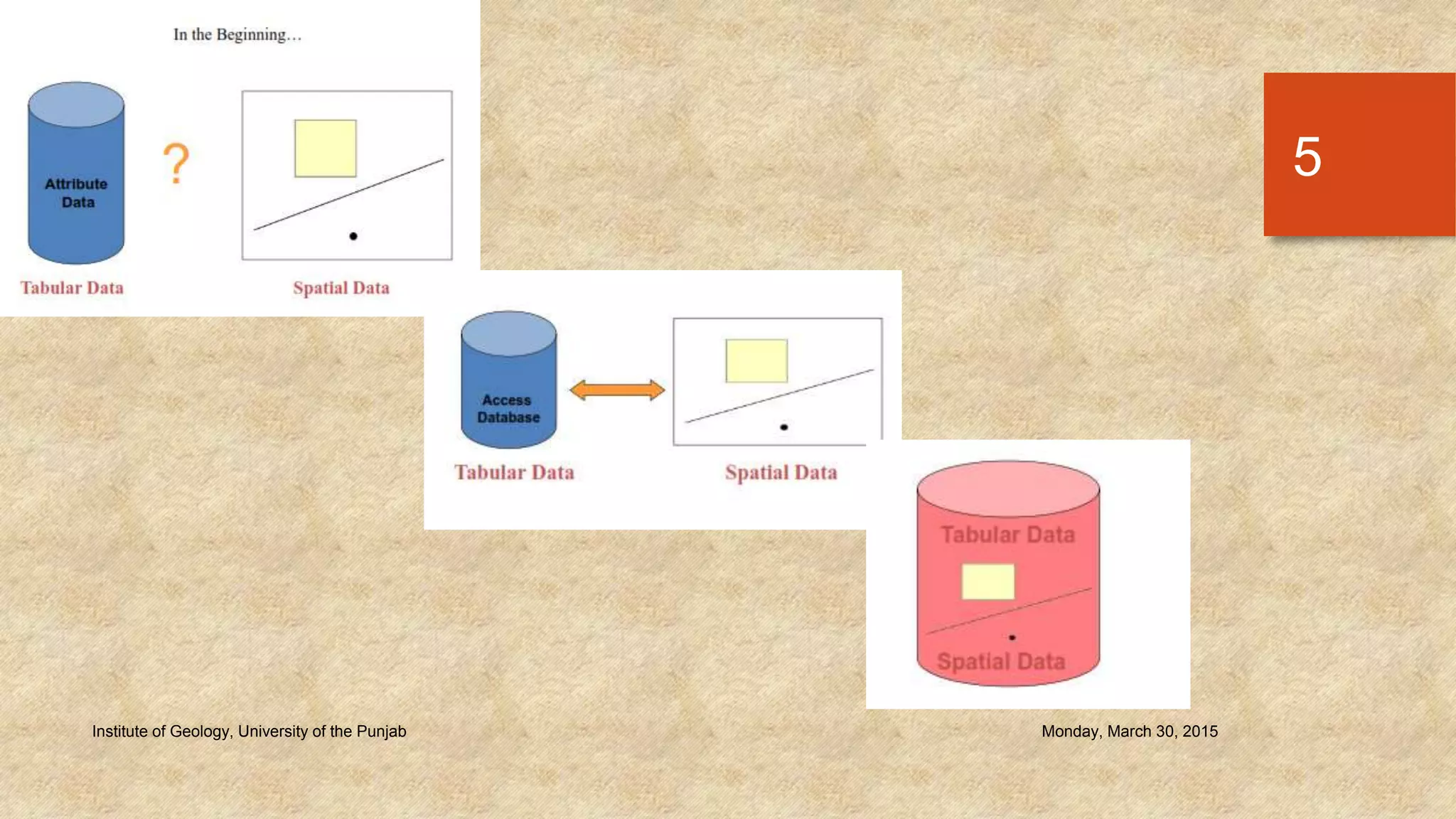
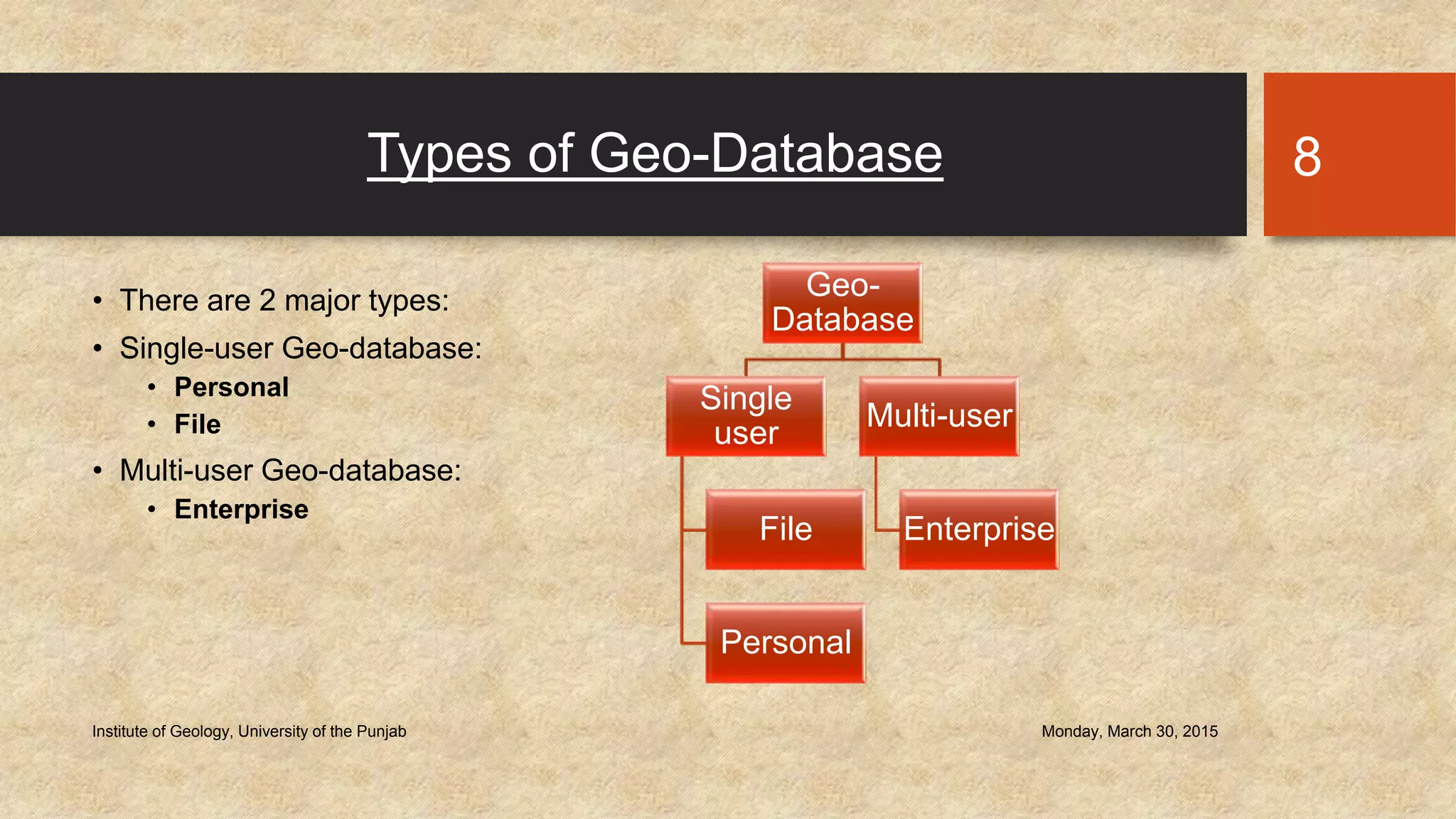
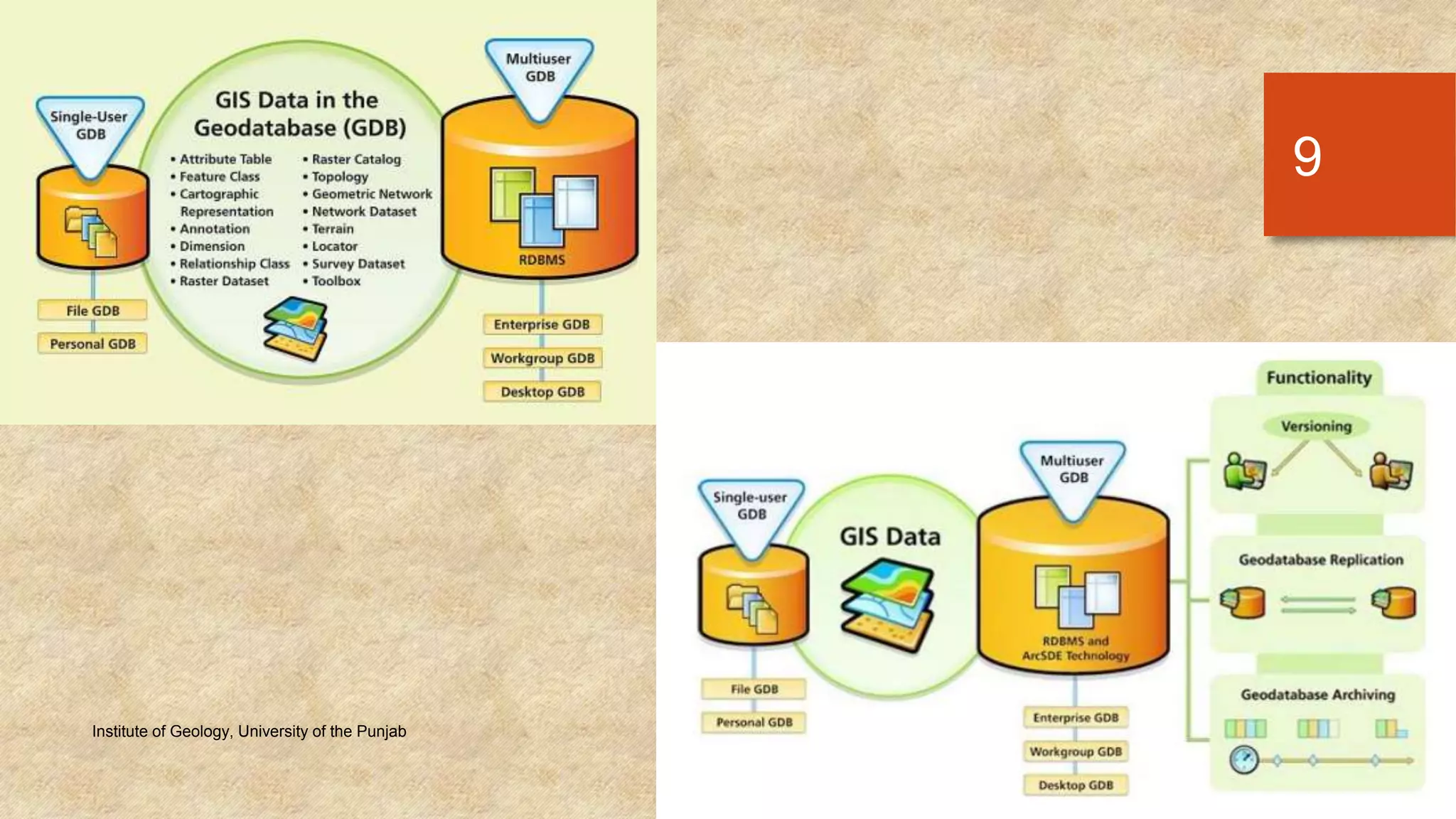
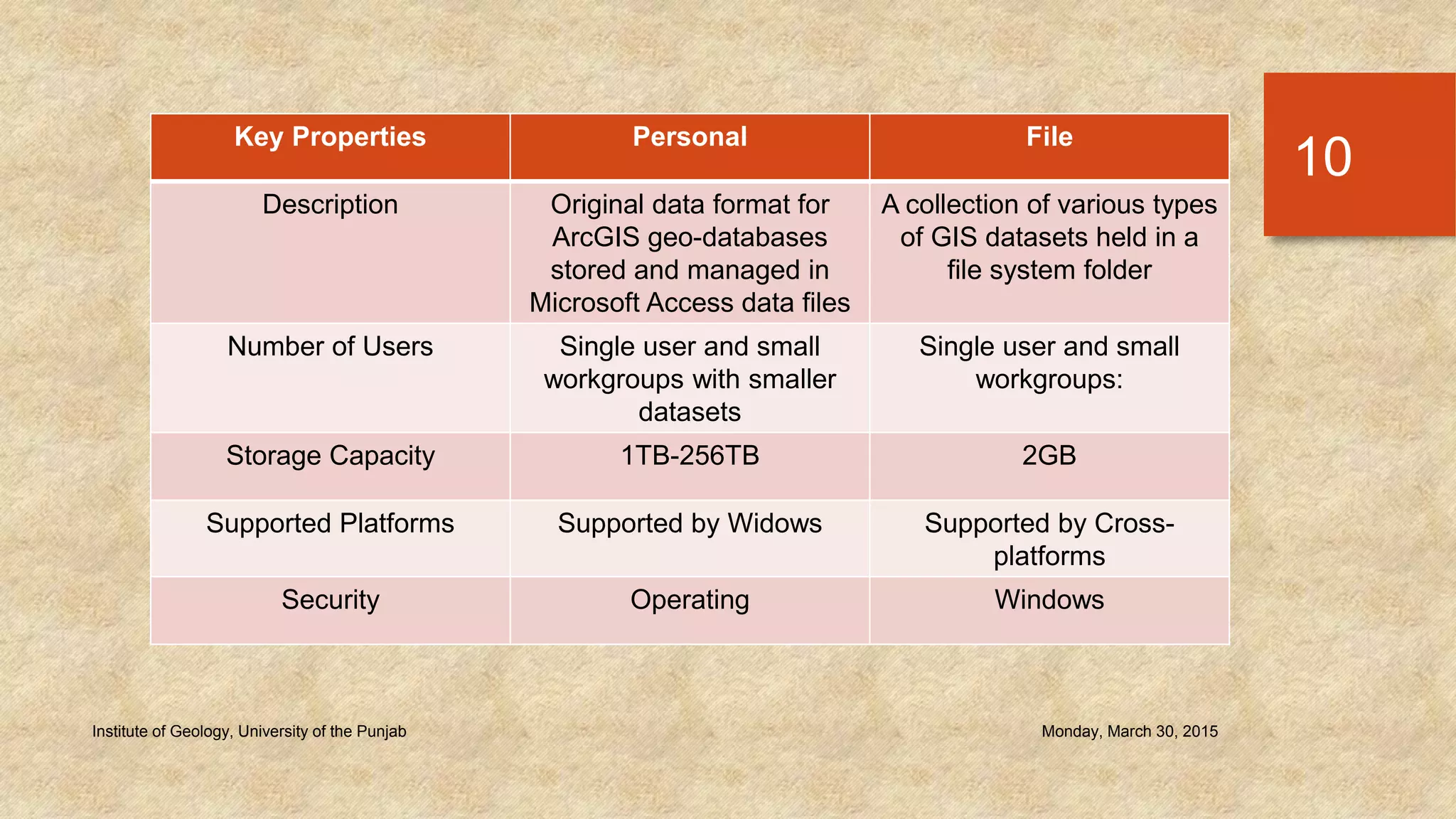
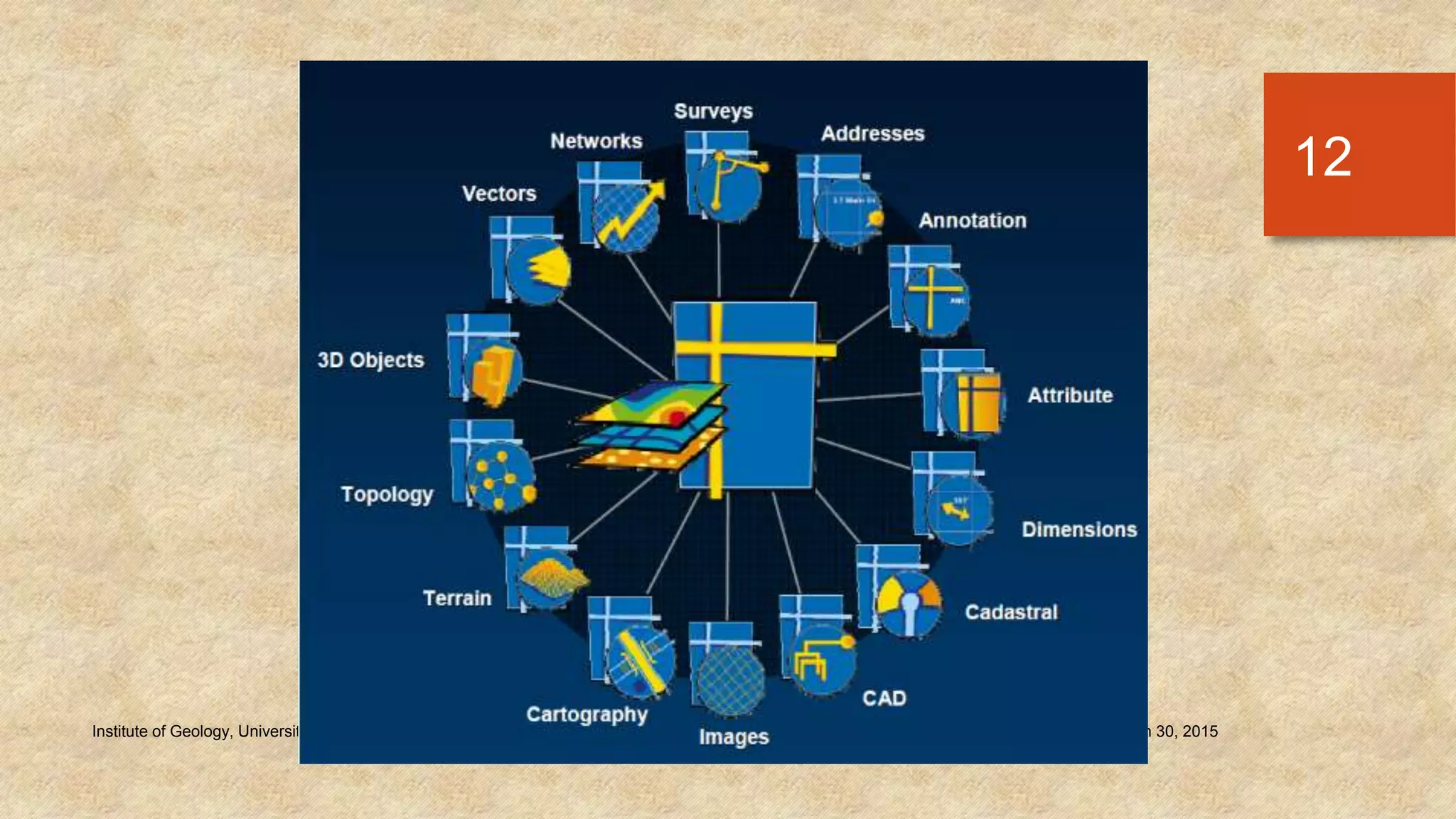
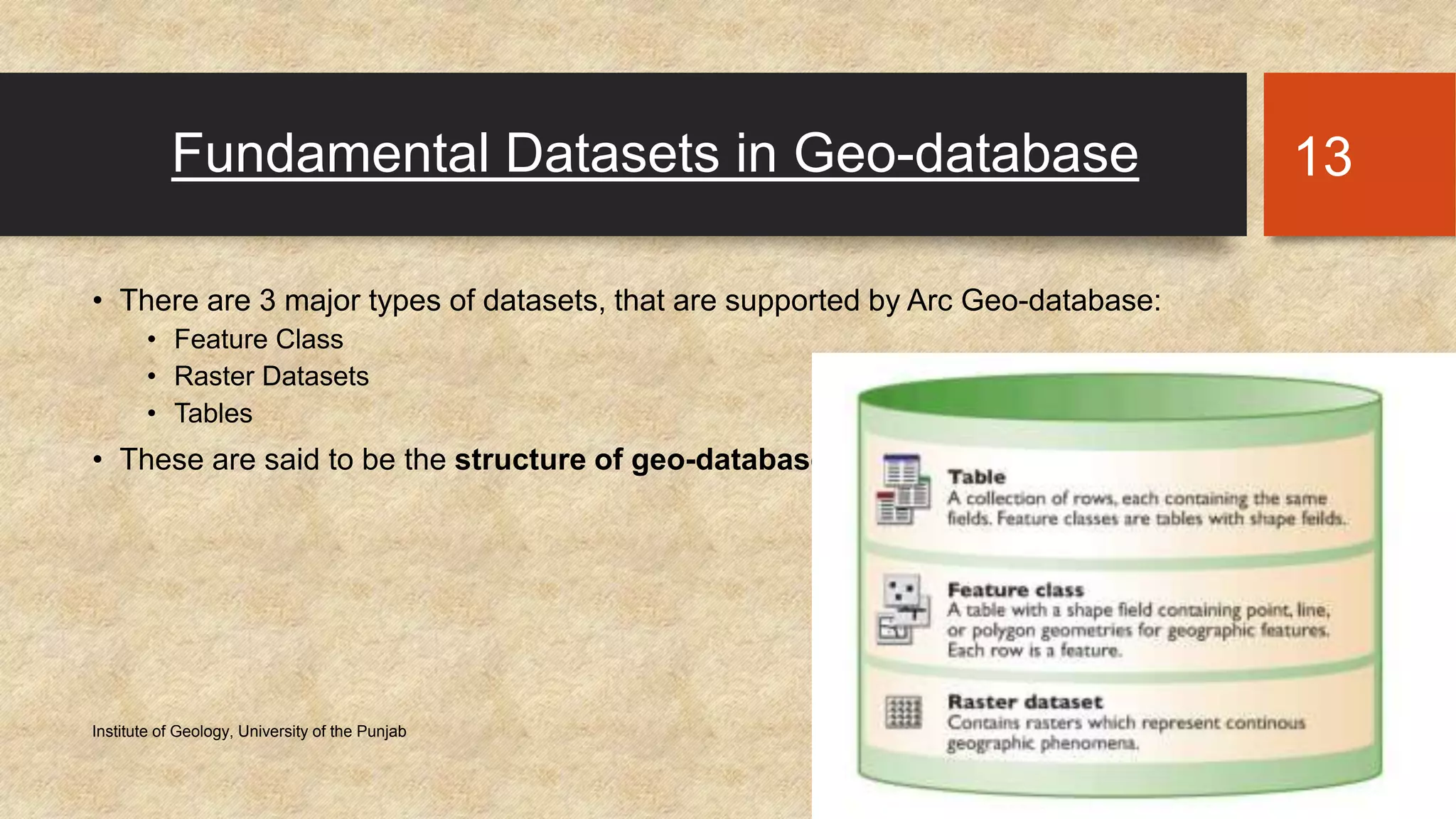
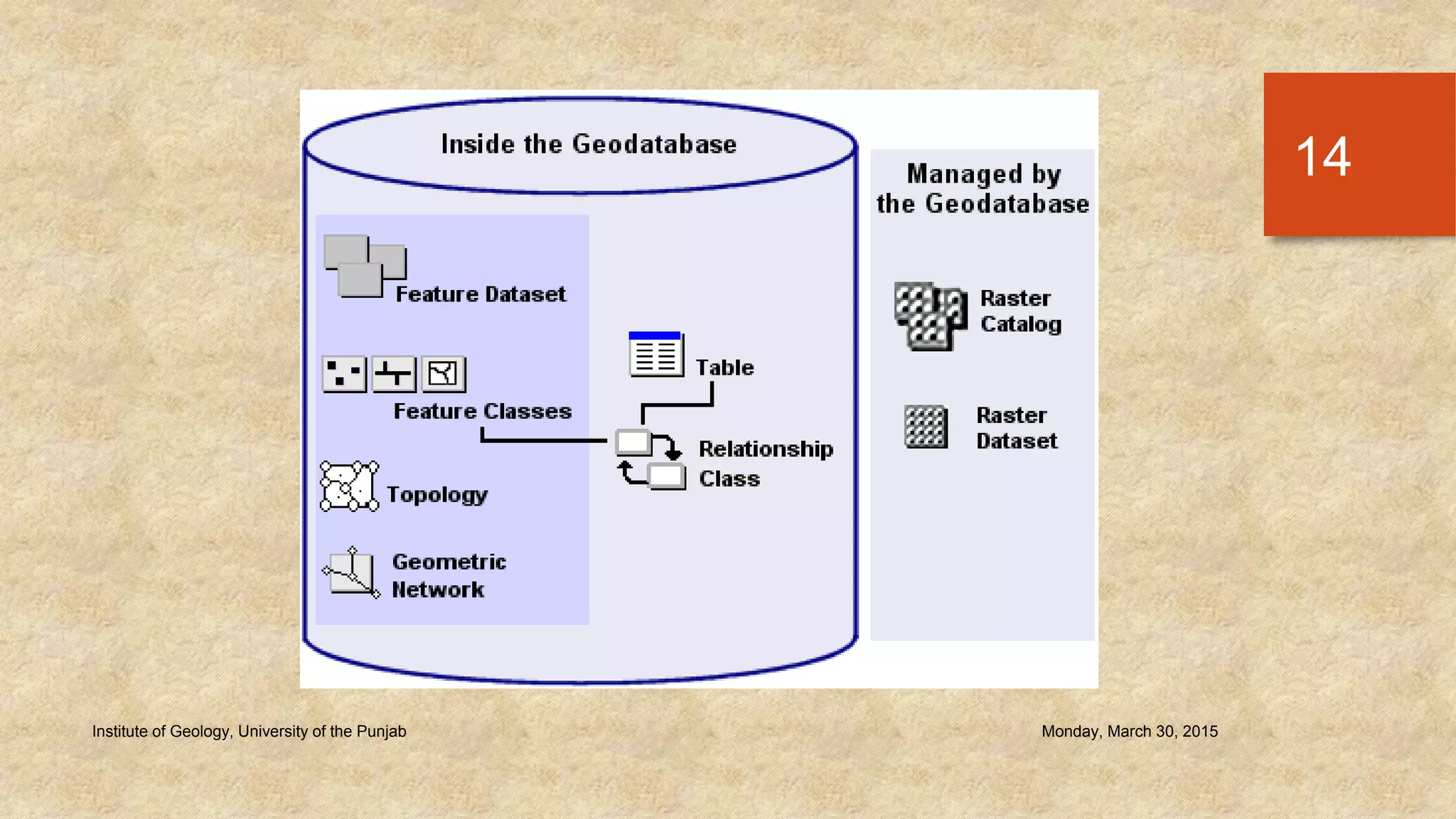
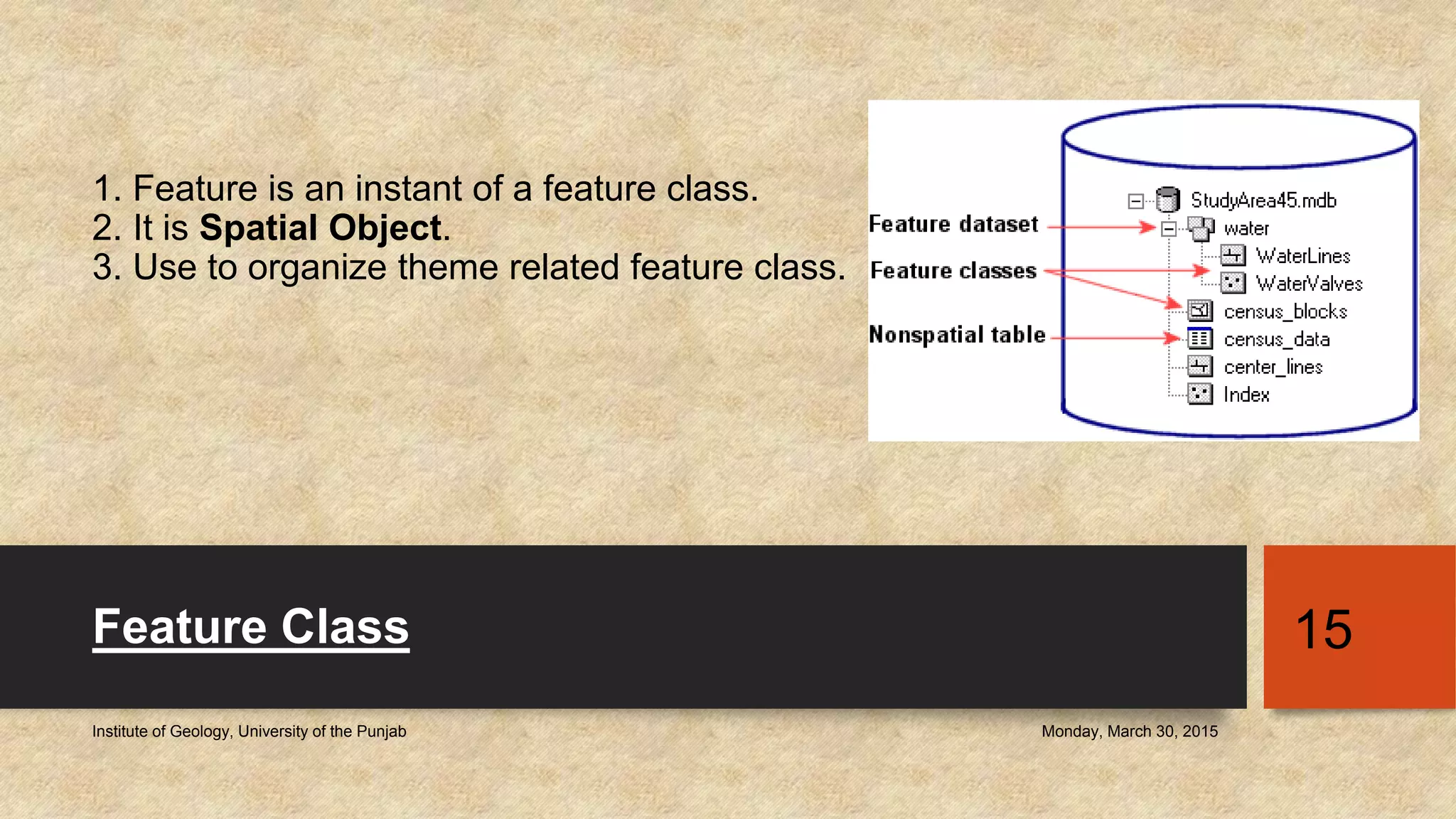
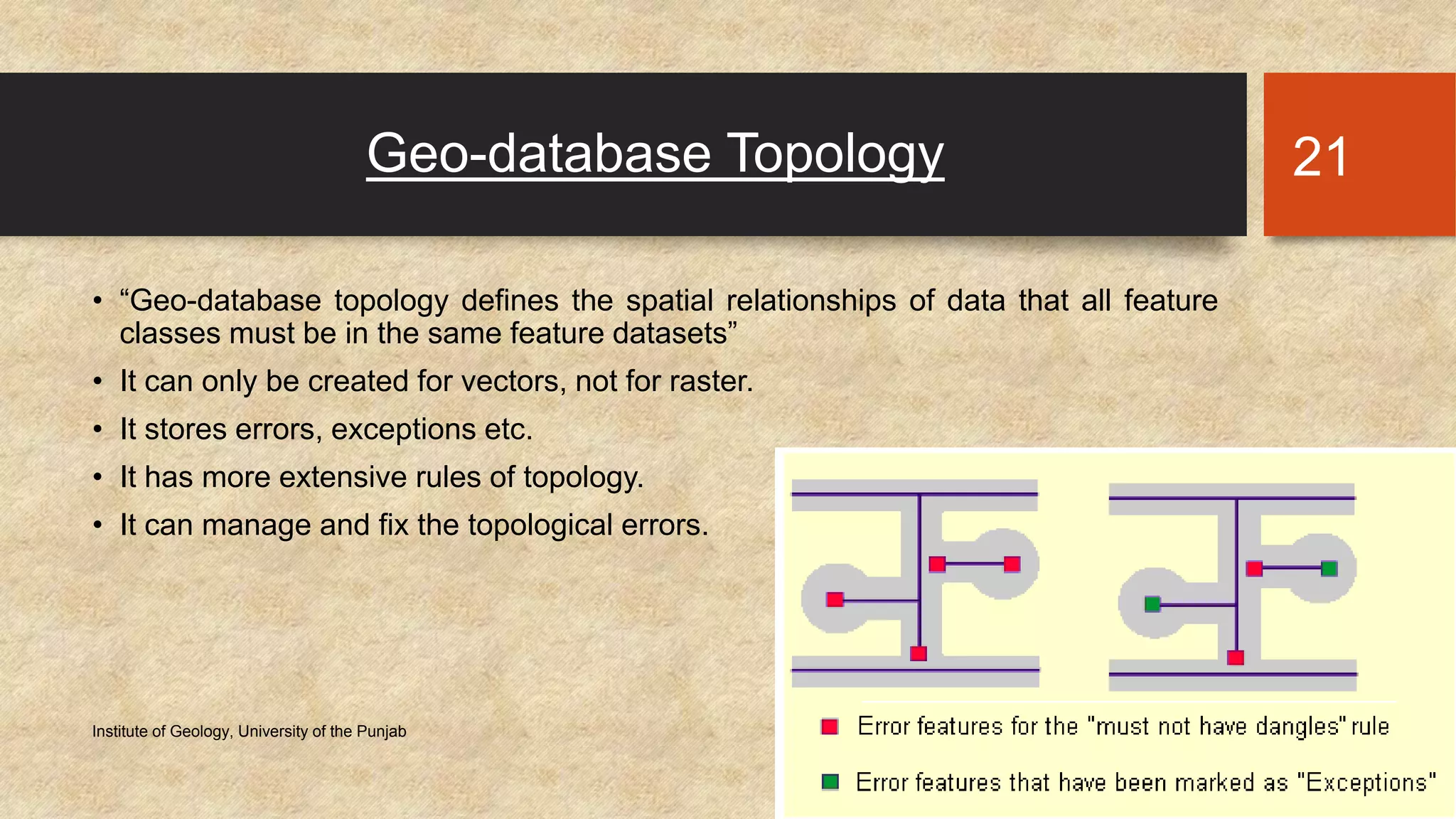
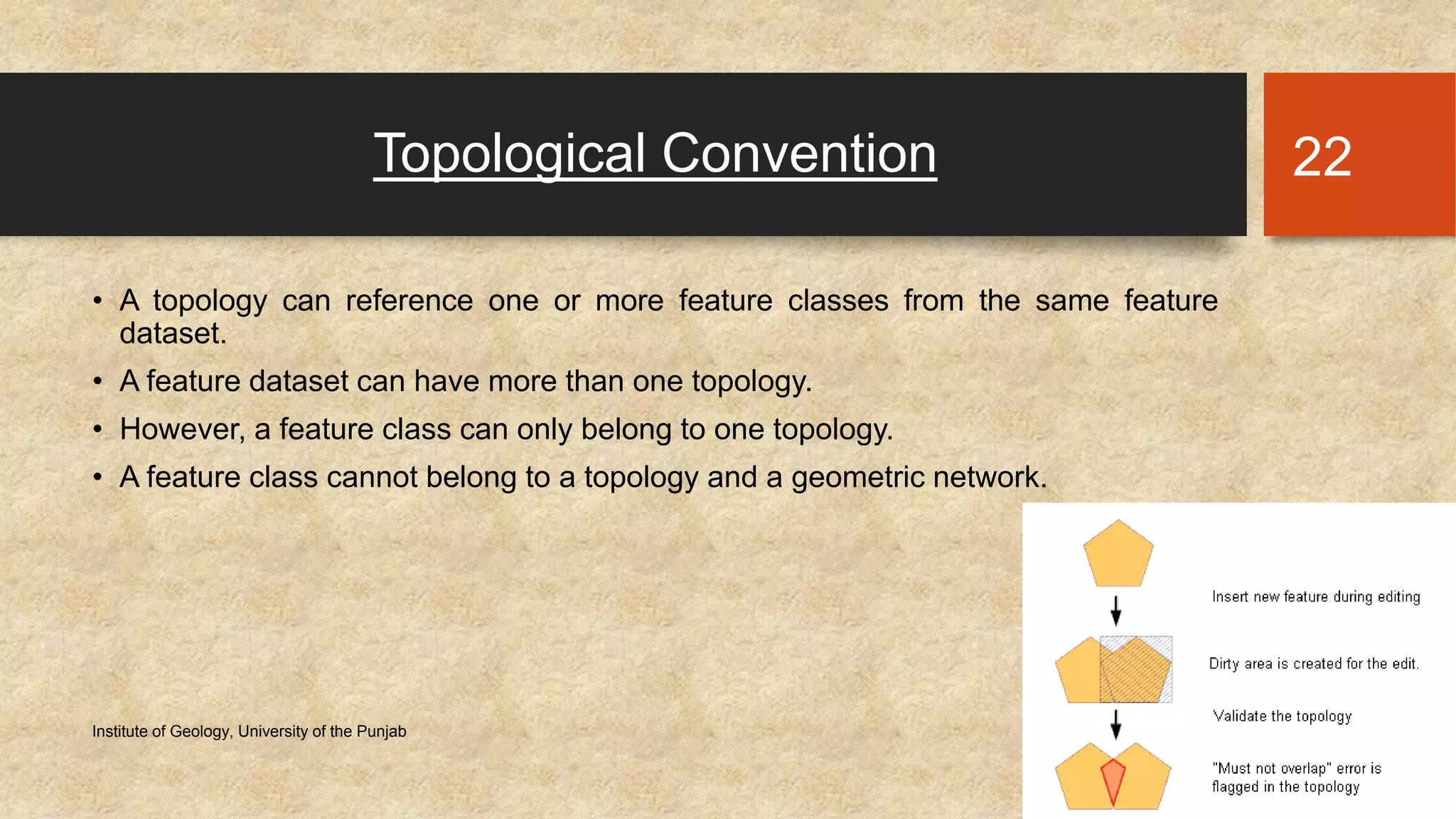
The document provides an introduction to geo-databases and topology. It defines a geo-database as a collection of geographic datasets held in a common file system folder that stores geometry, attributes, and behavioral rules. It discusses the history of linking spatial and non-spatial data, and describes how an ArcGIS geo-database maintains data integrity and supports editing topology. The document outlines the key components of a geo-database including feature classes, raster datasets, and tables, and describes the benefits of using a geo-database over other formats.