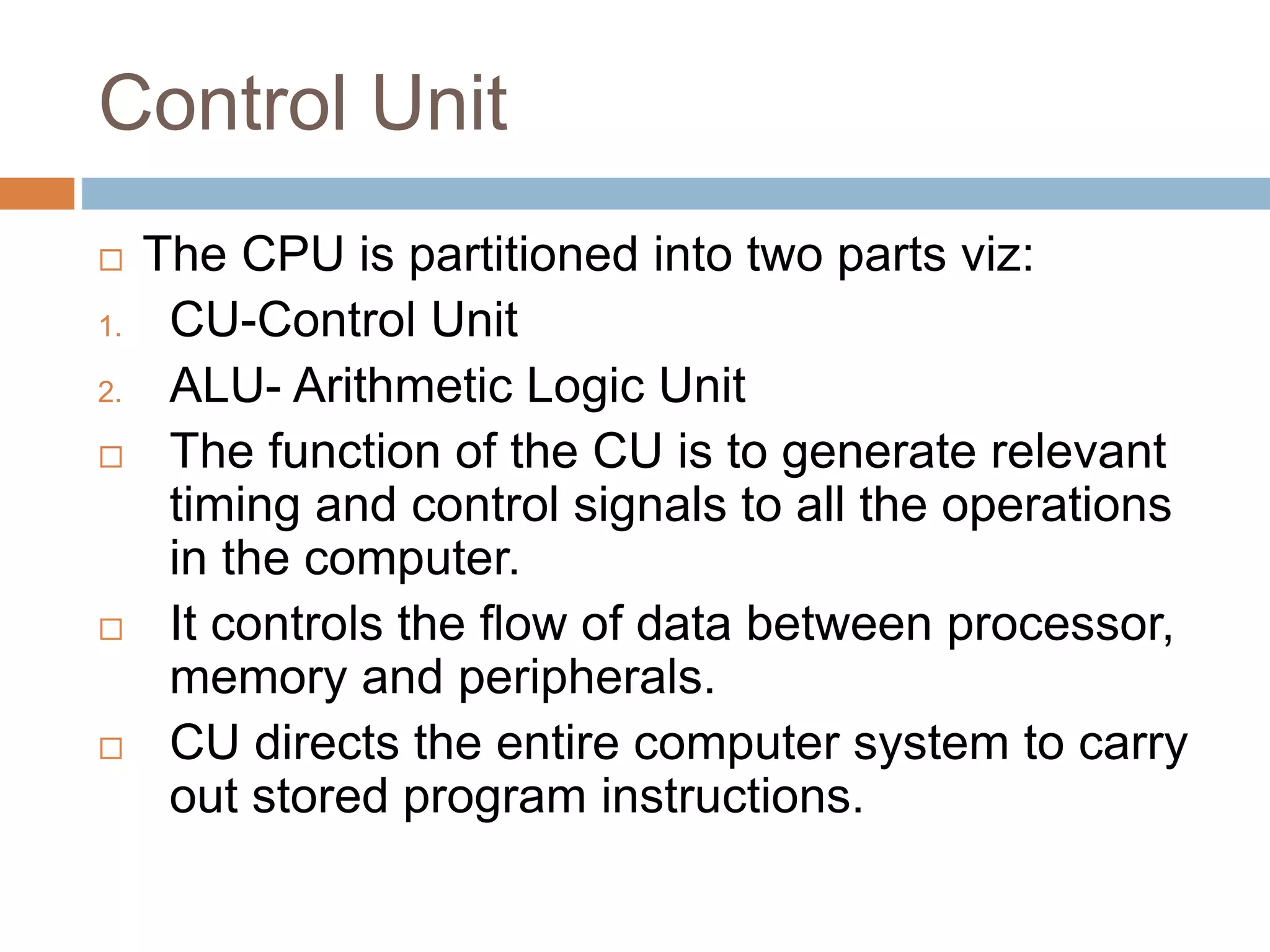
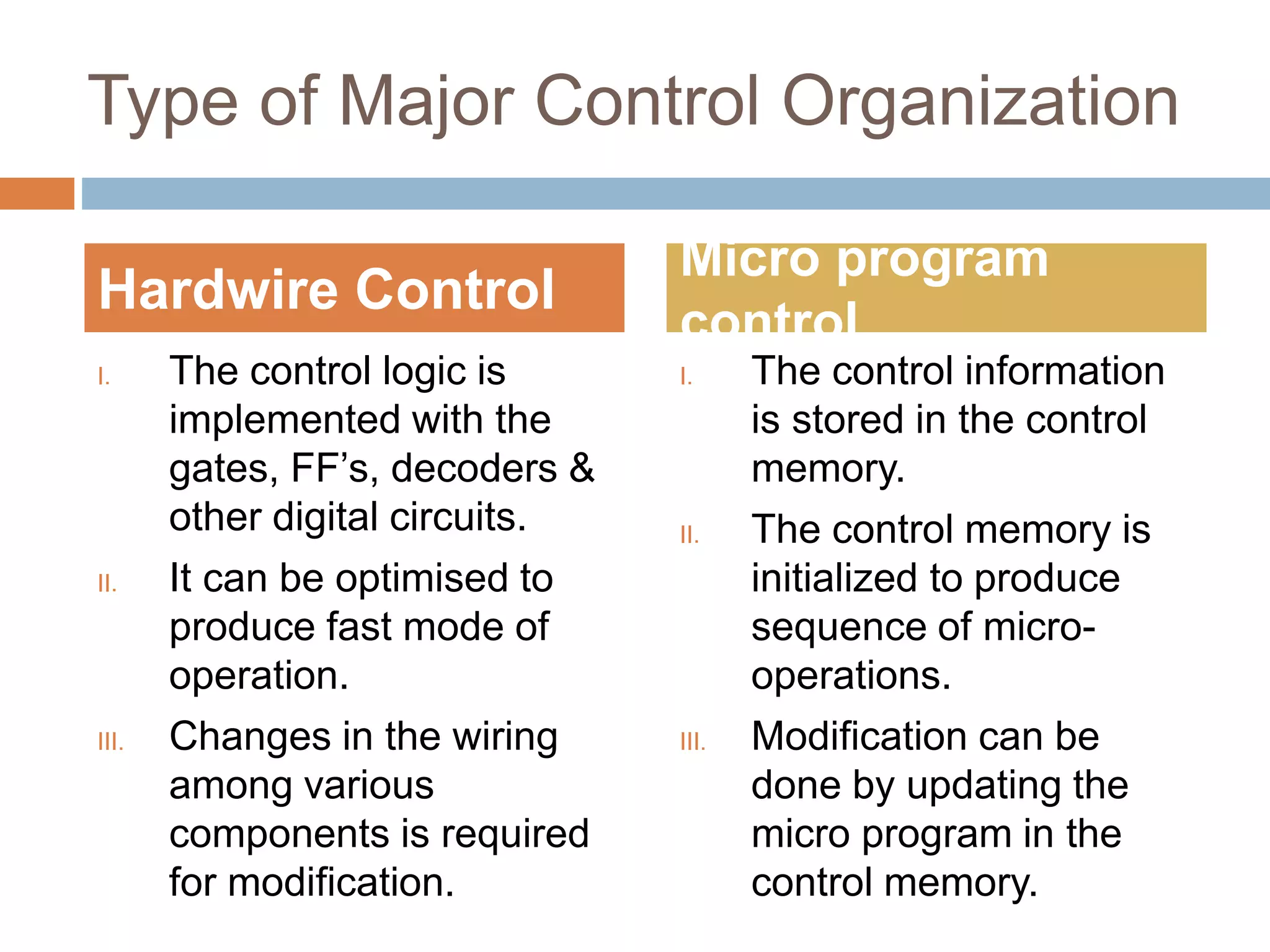
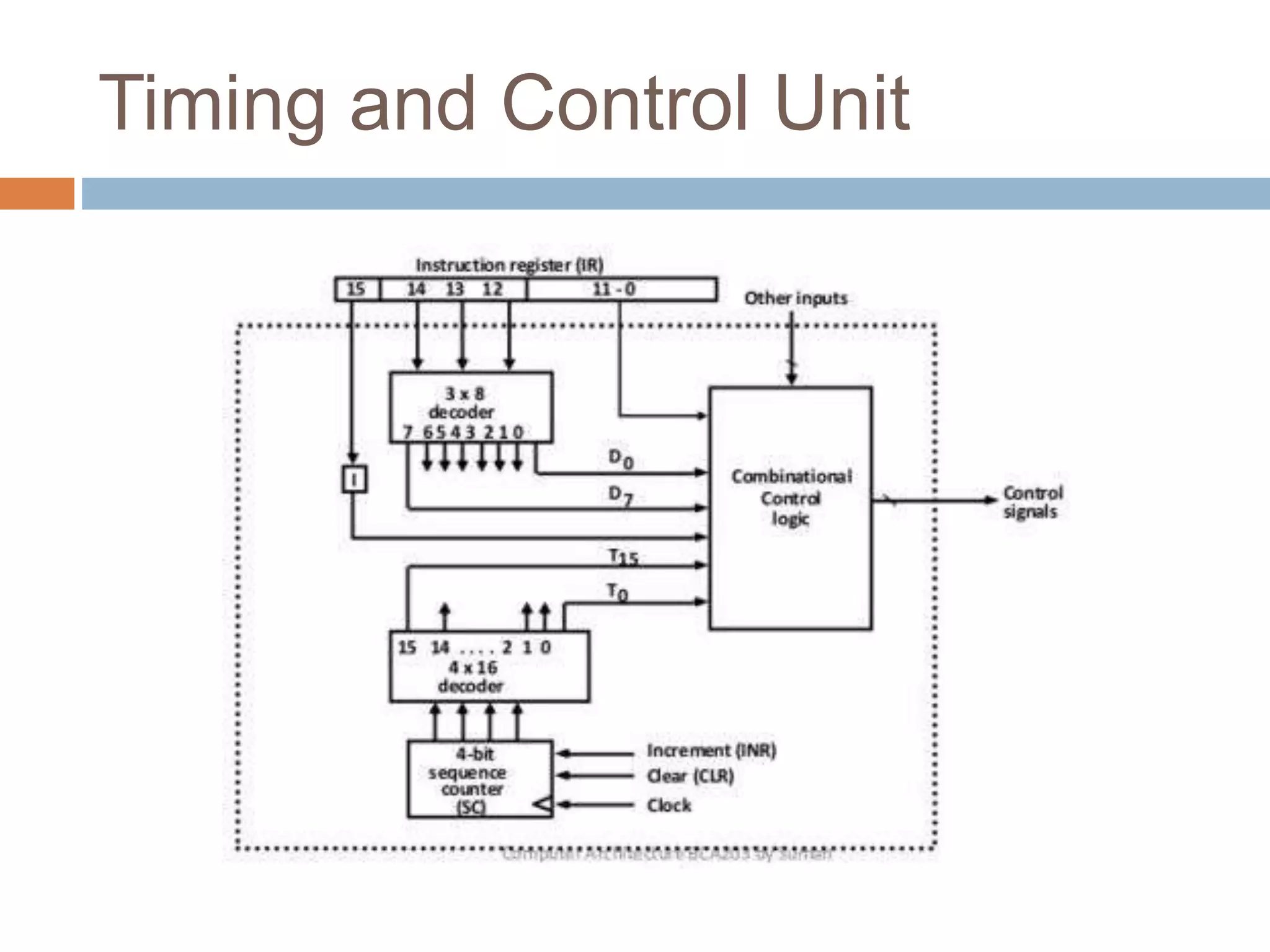
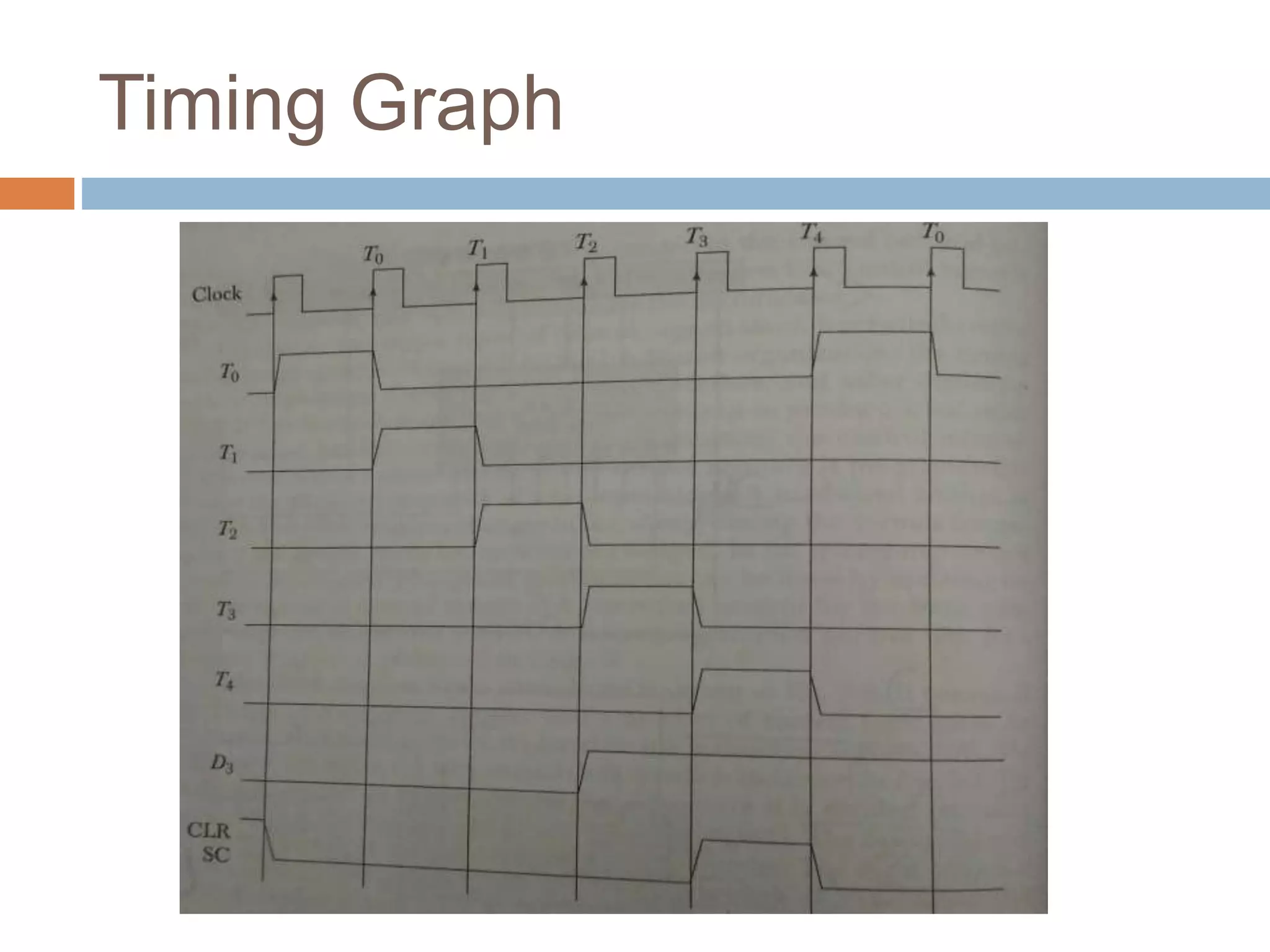
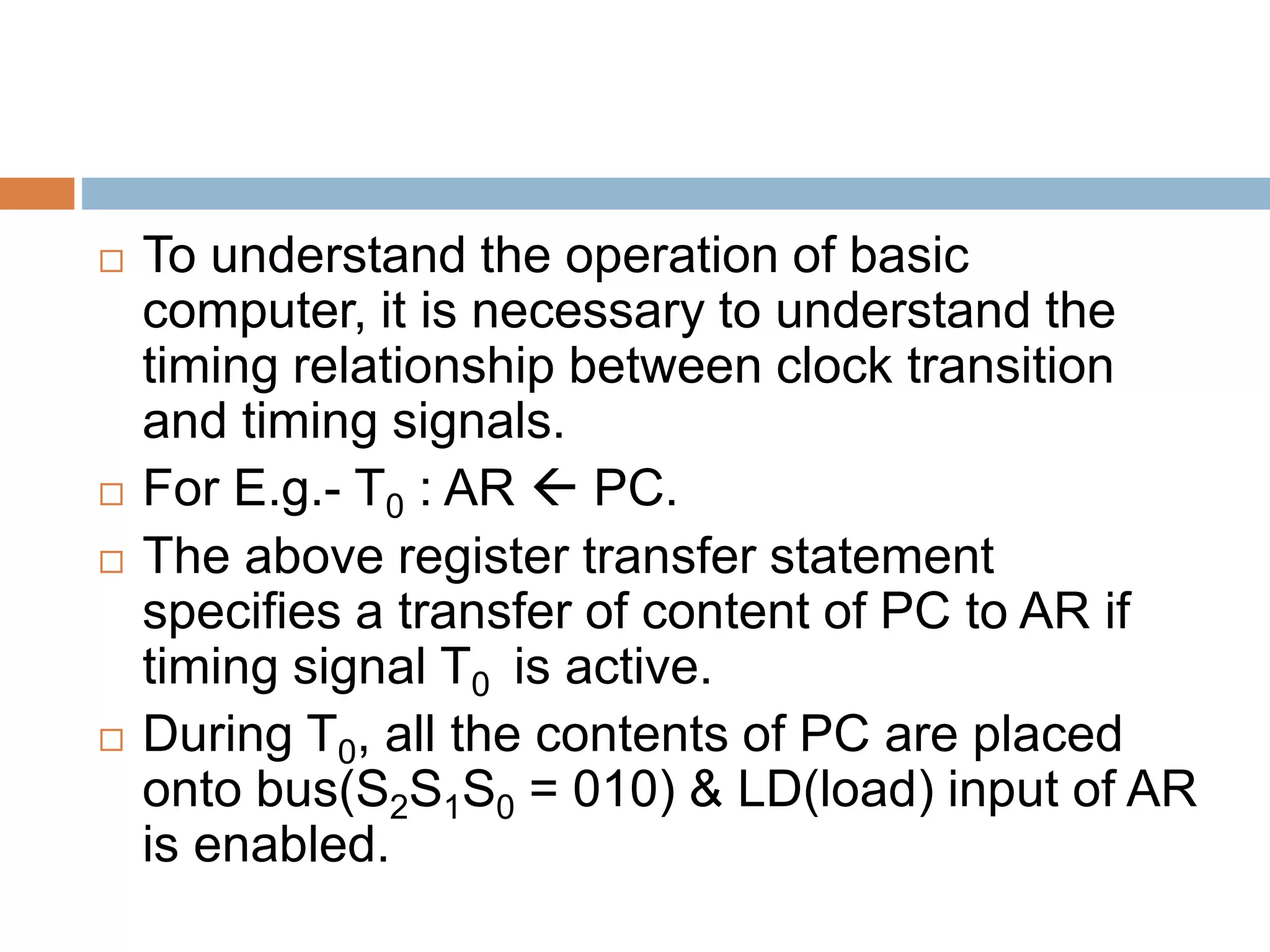
The control unit (CU) generates timing and control signals that coordinate operations in the computer. It controls data flow between the processor, memory, and peripherals, and directs the system to carry out instructions. Timing is controlled by a master clock generator that applies signals to registers and flip-flops. The CU generates control signals that provide inputs to the multiplexer on the common bus and processor registers. There are two major types of control organization: hardwired control uses gates and digital circuits while microprogram control stores control information in a control memory that is initialized to produce a sequence of micro-operations and can be modified by updating the microprogram. A memory read/write cycle is initiated on the rising edge of a