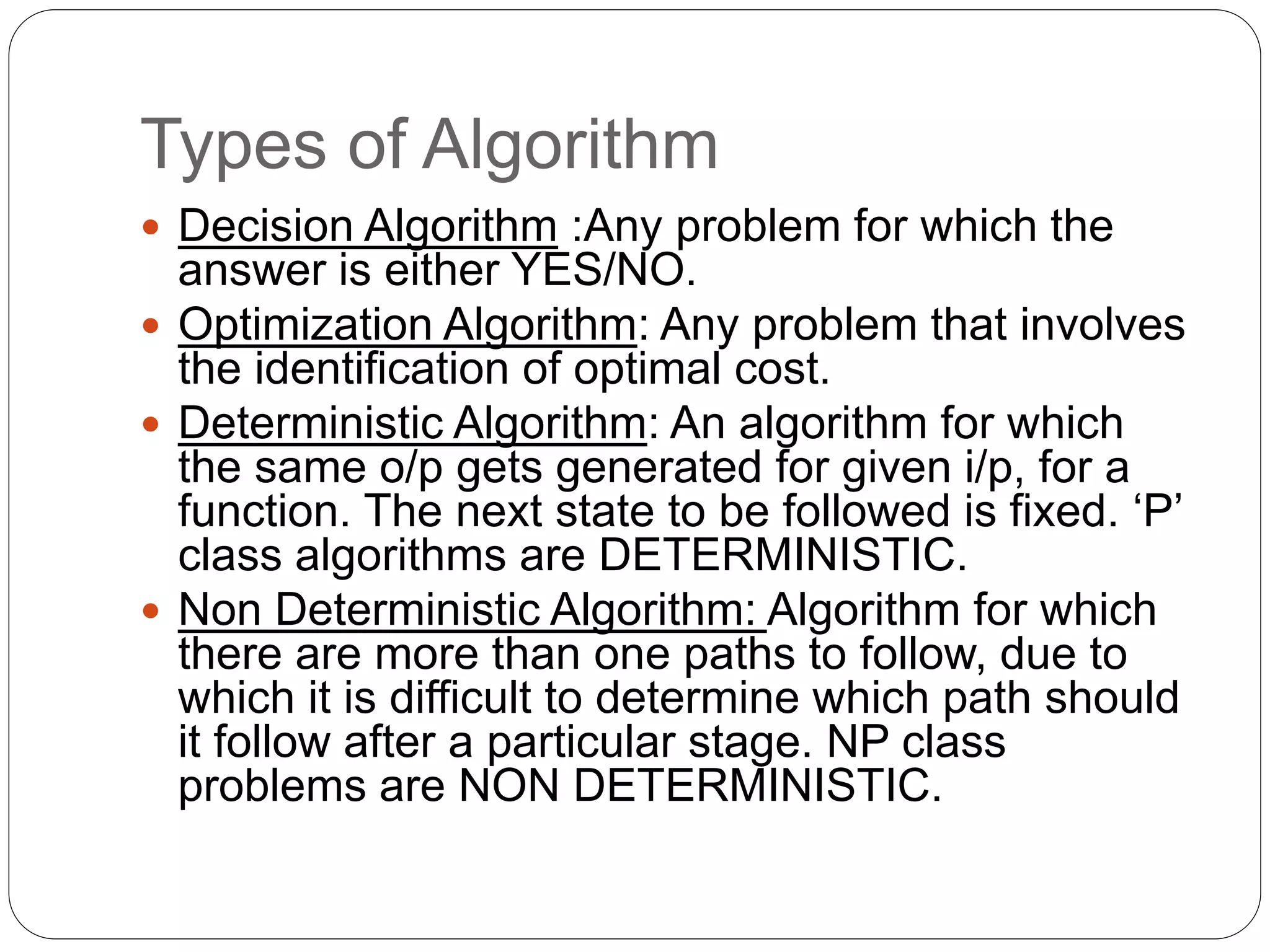
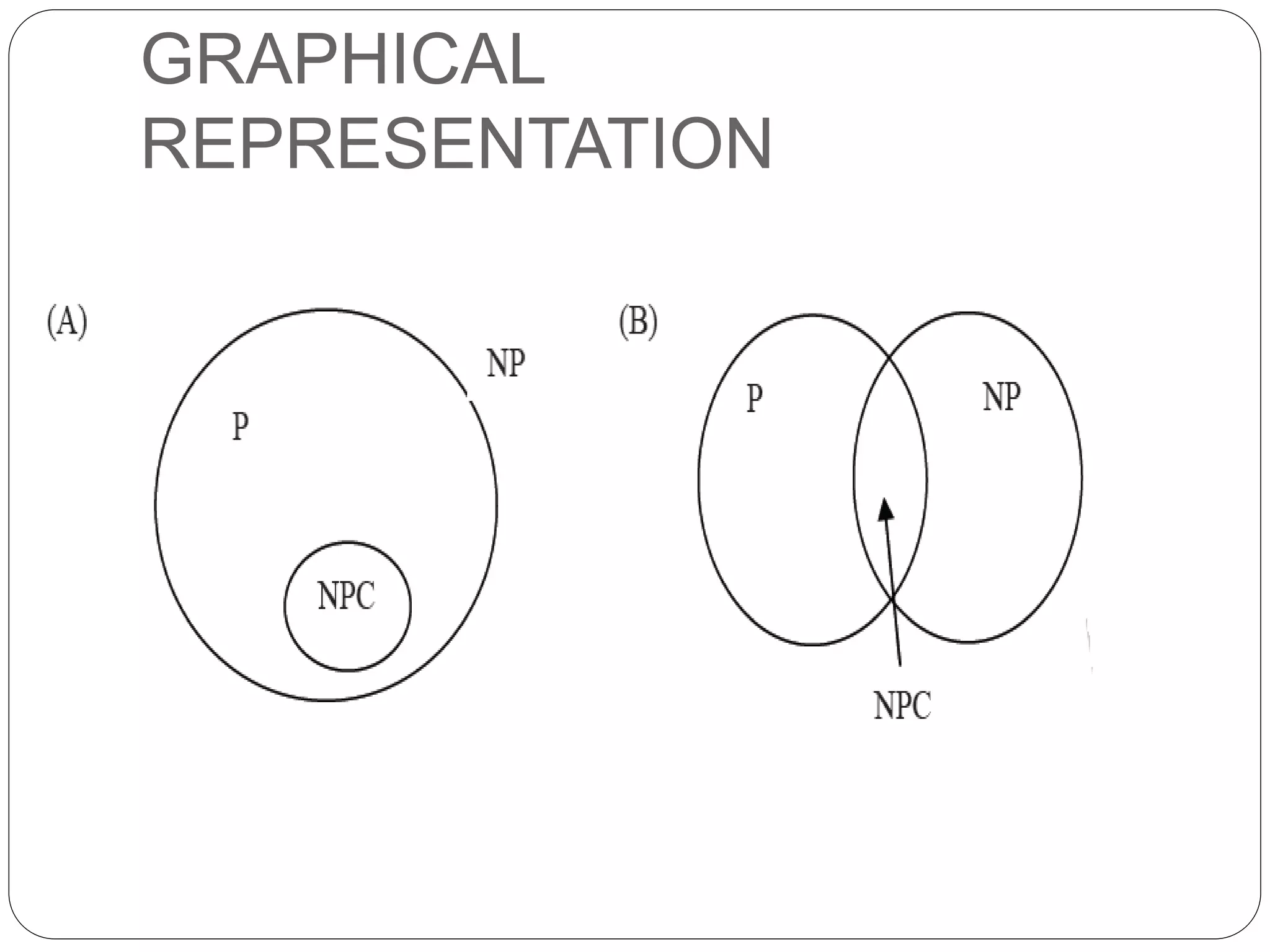
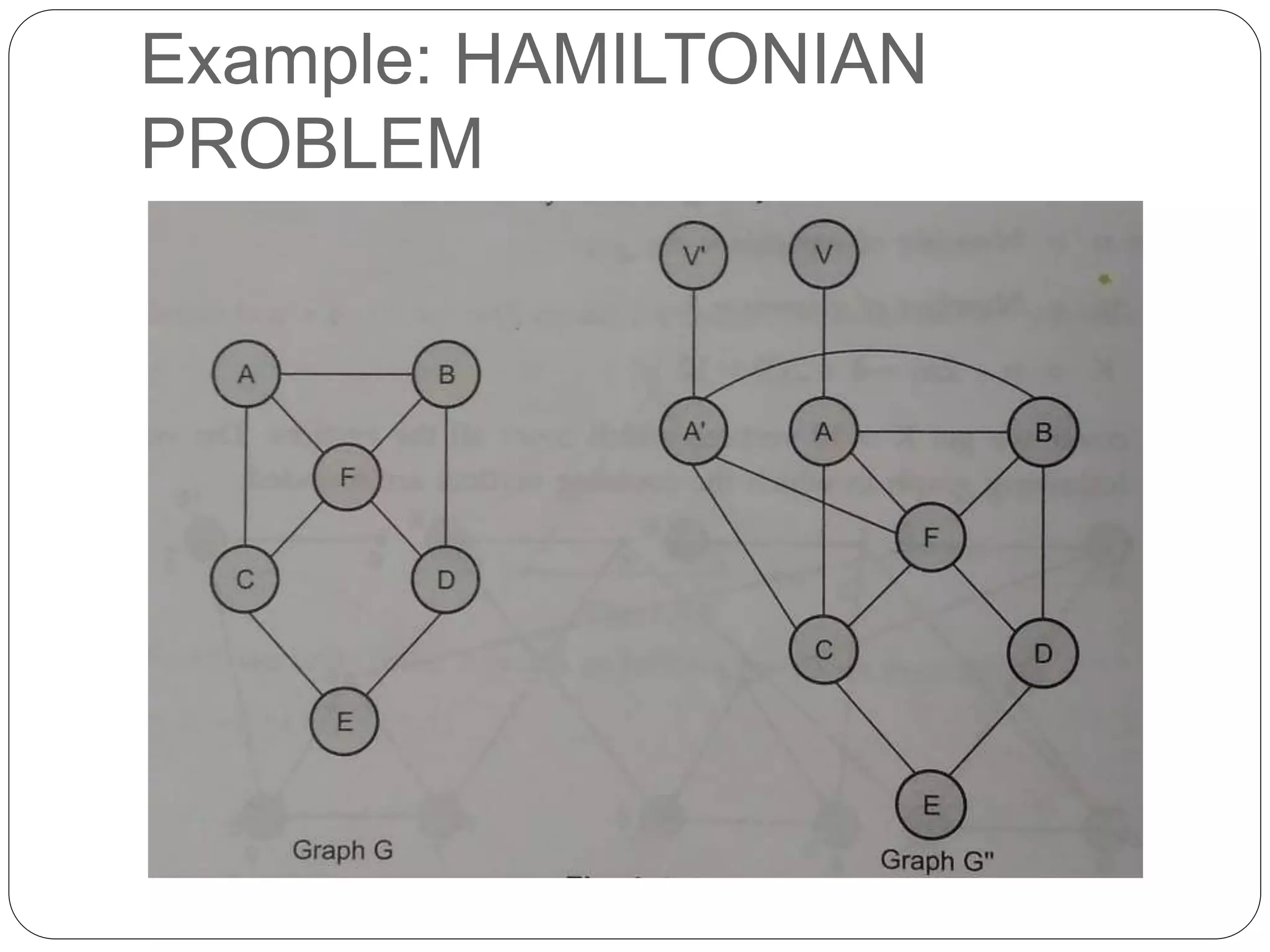
The document summarizes the concepts of P vs NP complexity classes. It states that P problems can be solved in polynomial time, like searching an array, while NP problems are solved in non-deterministic polynomial time, like the knapsack problem. It then defines different types of algorithms and complexity classes. The key classes discussed are P, NP, NP-Complete, and NP-Hard. It provides examples like sorting being in P, while the Hamiltonian problem is NP-Complete. A graphical representation is also included to illustrate the relationships between the complexity classes.