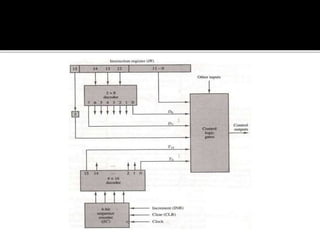
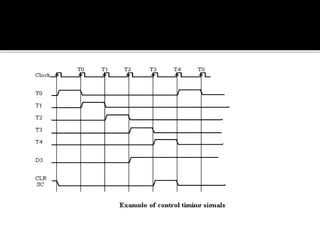
The CPU is divided into an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and a control unit (CU). The CU generates timing and control signals to coordinate the flow of data between the CPU, memory, and peripherals. It directs the entire computer system to carry out instructions by communicating with the ALU and memory. The CU instructs the ALU on which operations to perform and coordinates all computer components. The CU can use either a hardwired or microprogrammed organization to generate control signals. A microprogrammed CU implements control through a program of microinstructions stored in control memory.