The document discusses the timing and control, and instruction cycle of a basic computer. It contains the following key points:
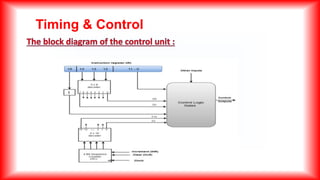
1. The timing of all registers is controlled by a master clock generator which provides clock pulses to flip-flops and registers. Control signals are generated in the control unit to provide inputs for operations.
2. There are two types of control organization: hardwired and microprogrammed. Microprogrammed control stores control information in a control memory.
3. An instruction cycle consists of fetching an instruction from memory, decoding it, reading the effective address if indirect, and executing the instruction before fetching the next one. The program counter loads the first instruction address.













![Instruction Cycle
The micro operations for the fetch and decode phases can be specified
by the following register transfer statements.
T0 : AR <--- PC
T1 : IR <--- [AR],PC = PC + 1
T2 : D0,,,,D7 <--- Decode IR(12--14),AR <--IR(0--11),I <---IR(15)
• Since only AR is connected to the address inputs of memory, it is
necessary to transfer the address from PC to AR during the clock
transition associated with timing signal T0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timingcontrol-231116100411-6ab74542/85/Timing-Control-pptx-16-320.jpg)
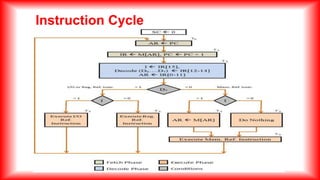

![Instruction Cycle
• Control then inspects the value of the first bit of the instruction, which
is now available in flip-flop I.
• If D7 = 0 and I = 1, we have a memory reference instruction with an
indirect address.
• It is then necessary to read the effective address from memory. The
micro operation for the indirect address condition can be symbolized
by the register transfer statement AR <-- M[AR]
• Initially, AR holds the address part of the instruction. This address is
used during the memory read operation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timingcontrol-231116100411-6ab74542/85/Timing-Control-pptx-19-320.jpg)


