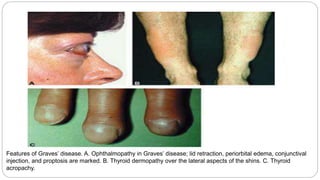
Graves' disease is the most common cause of thyrotoxicosis, accounting for 60-80% of cases. It is an autoimmune disorder causing hyperthyroidism due to thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins that activate the TSH receptor. Symptoms include anxiety, heat intolerance, palpitations, weight loss and goiter. Treatment involves antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine therapy or surgery to control the hyperthyroidism. Radioactive iodine is often the preferred treatment option. Graves' disease can also cause eye changes and pretibial myxedema. Managing the condition during pregnancy requires careful titration of antithyroid medications.