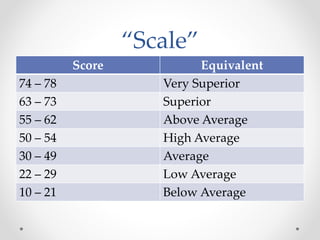
The document summarizes an IQ test called the Thurstone Test of Mental Alertness. It provides directions for taking the test, describing the testing environment as quiet, well-lit, and smoke-free. It notes the test assesses adjusting to new situations, learning new skills quickly, understanding complex relationships, and thinking flexibly. Scores are derived in verbal, quantitative, and total scores. The document lists similar IQ tests and notes some criticisms of IQ tests in general, such as cultural biases.