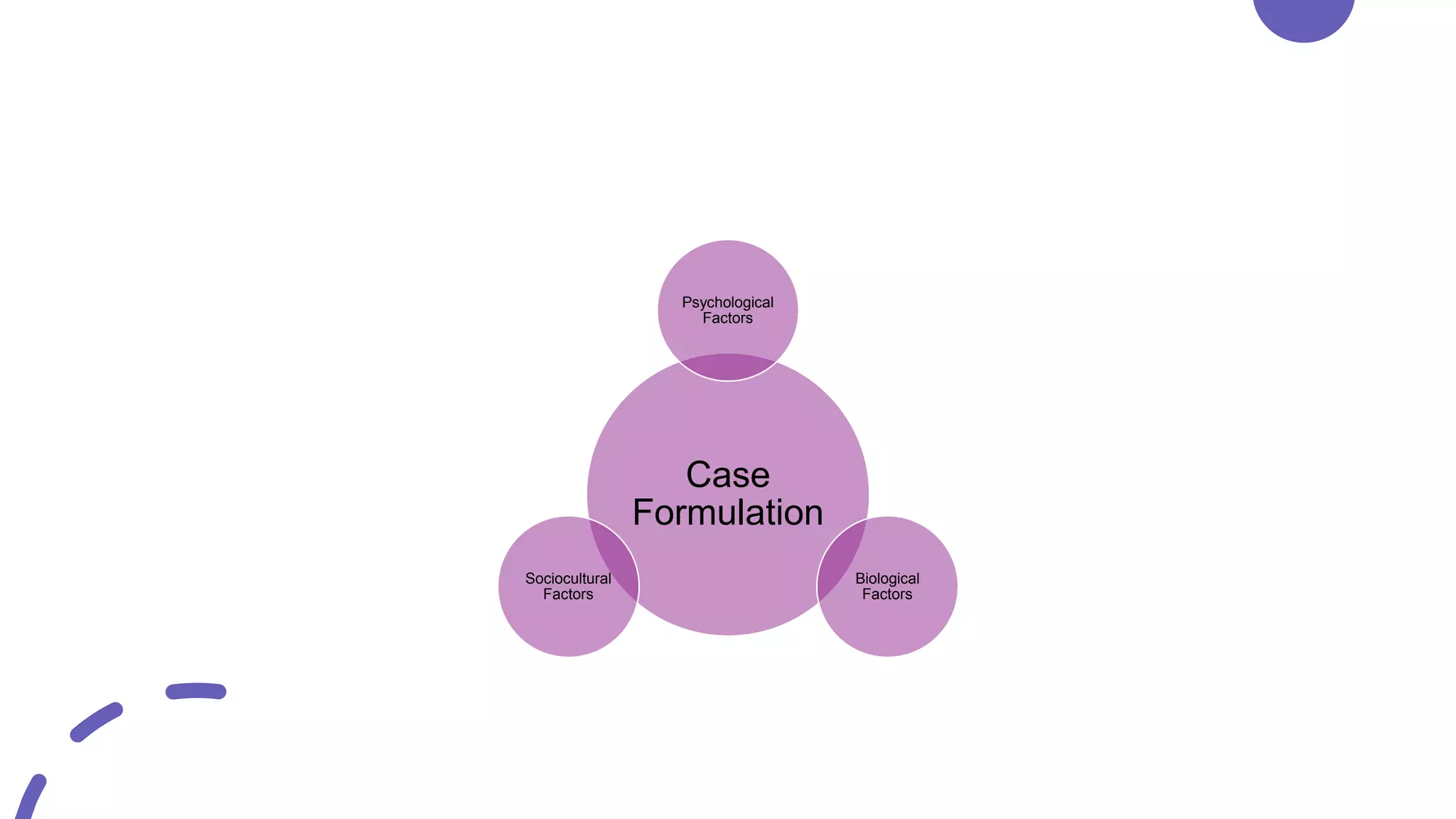
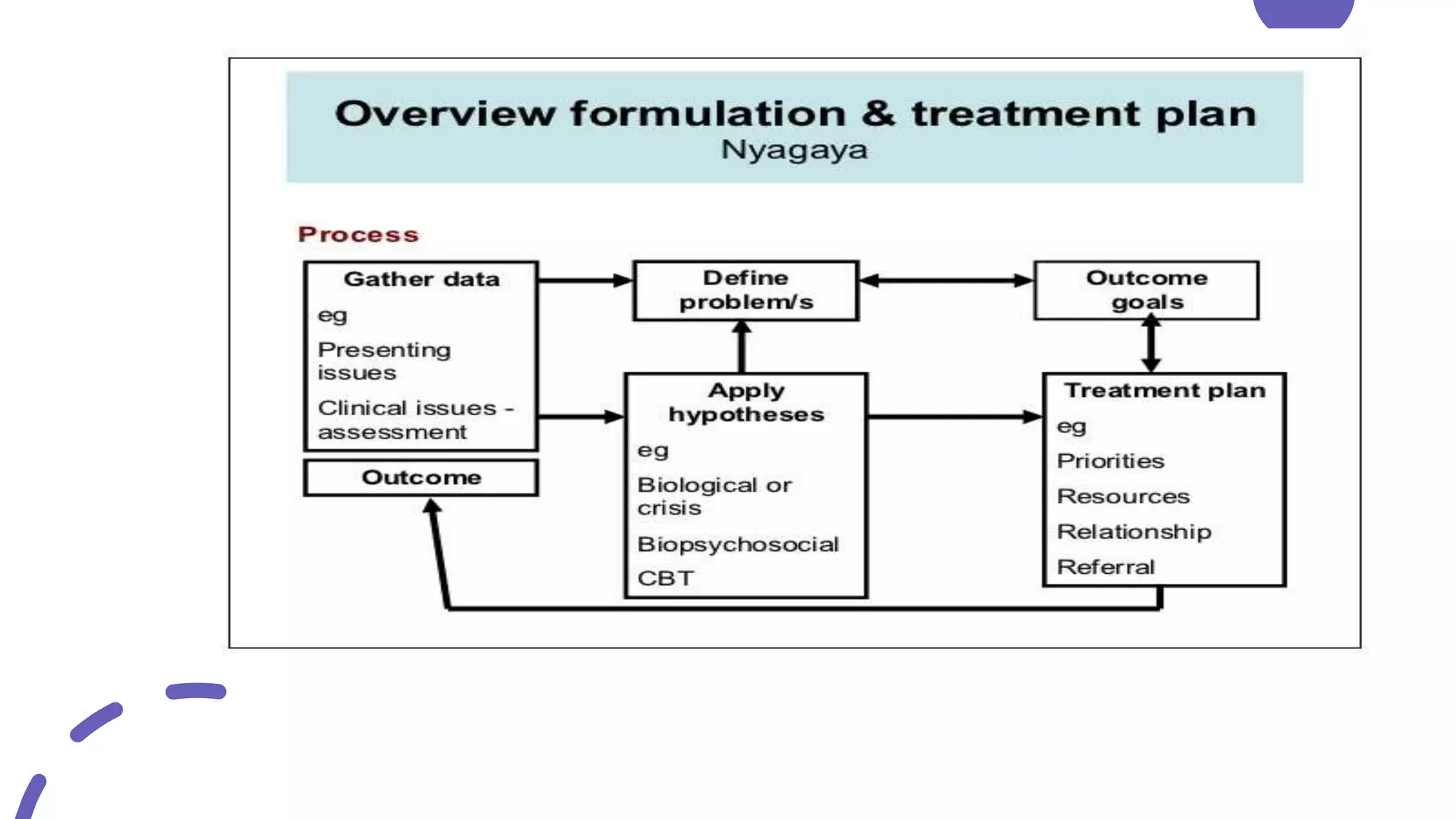
This document discusses case formulation, which involves developing a hypothesis about the factors that cause and maintain a client's problems. It outlines the key components of case formulation using the DSM-5, including the presenting problem, predisposing factors, precipitating factors, perpetuating factors, and protective factors. The document provides an example case formulation for a client named Nasira who is experiencing depression. It analyzes the precipitant, predisposing factors, and perpetuating factors for Nasira based on her history and symptoms. The case formulation would then inform the treatment plan.