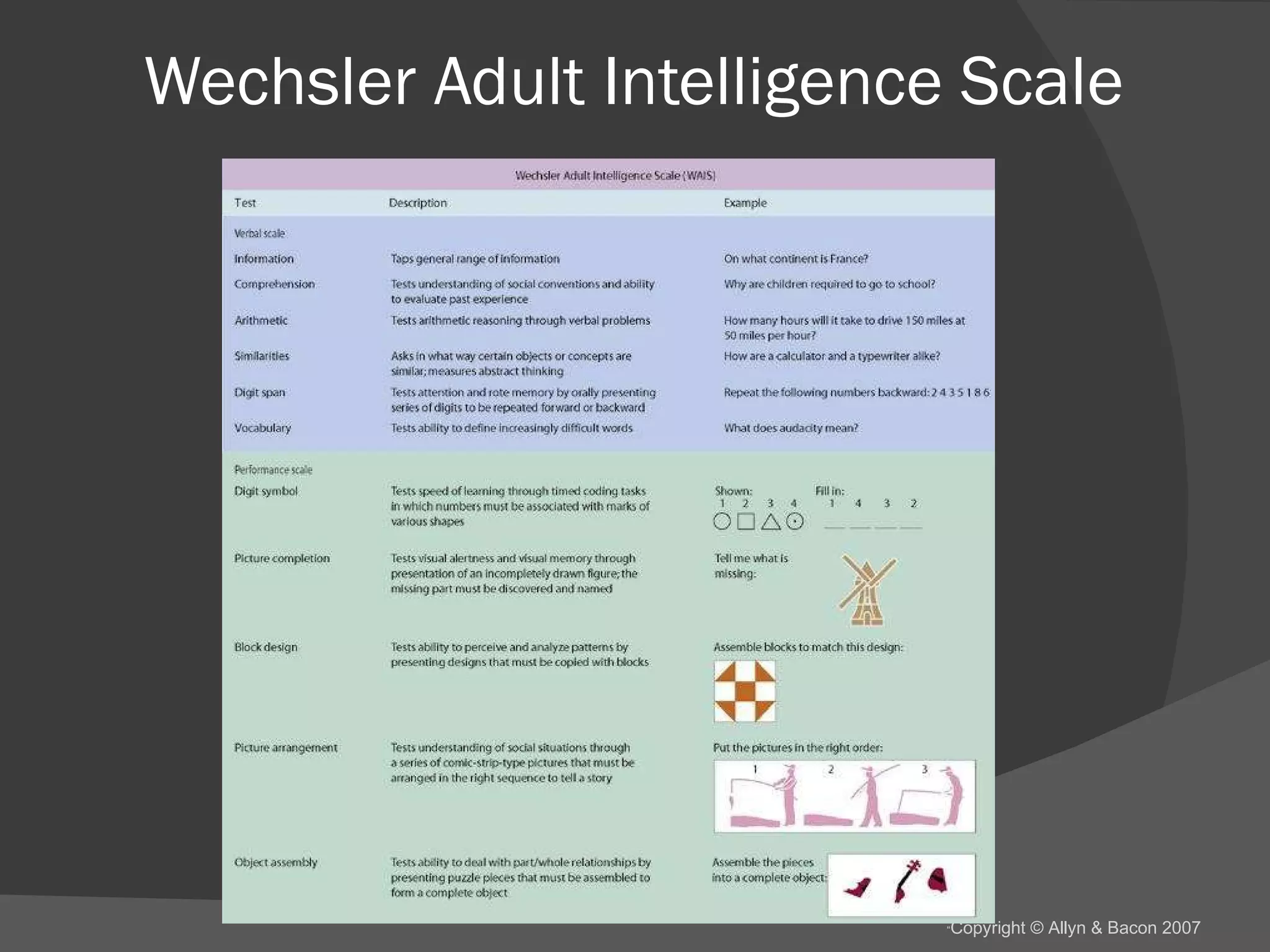
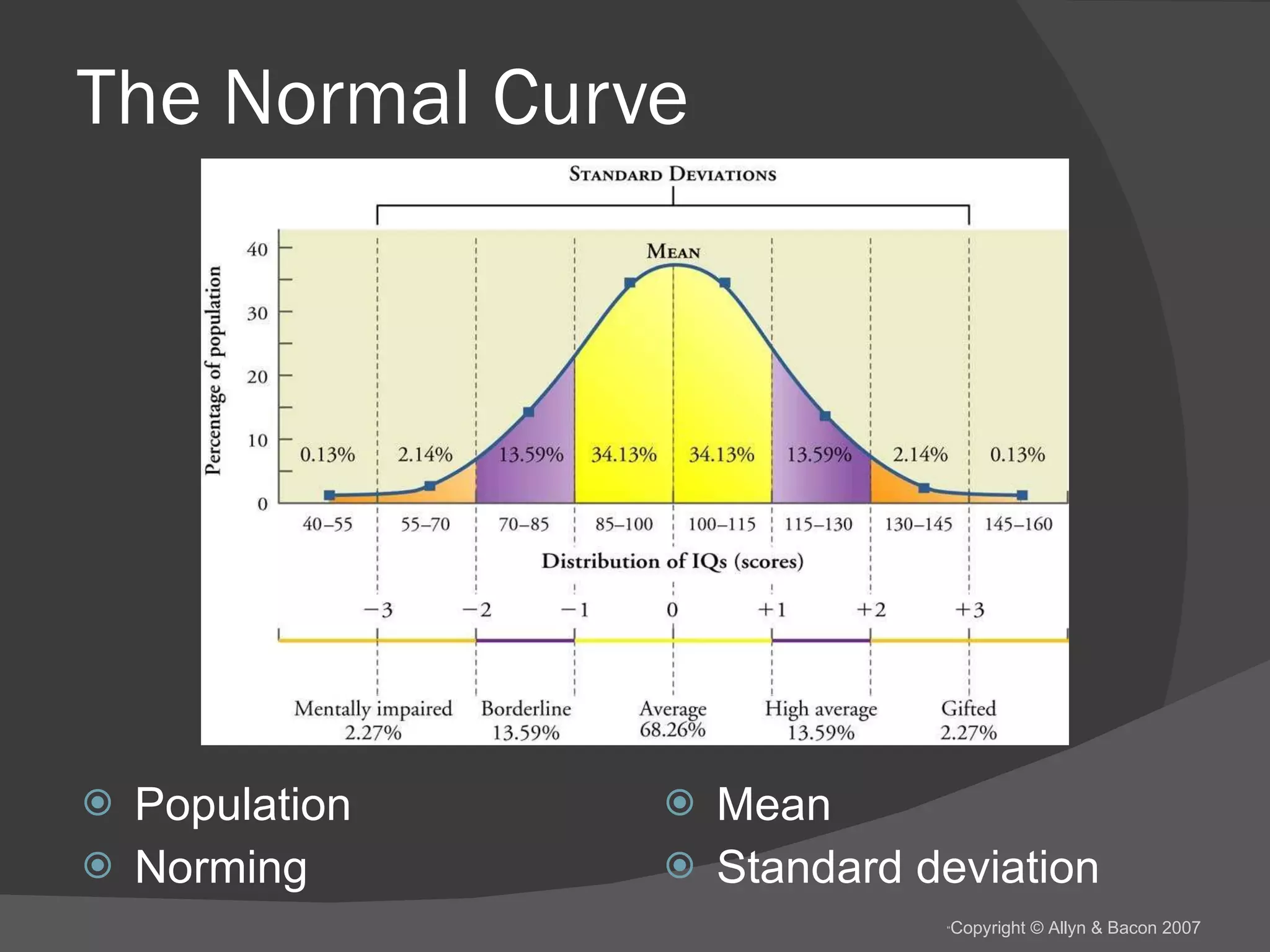
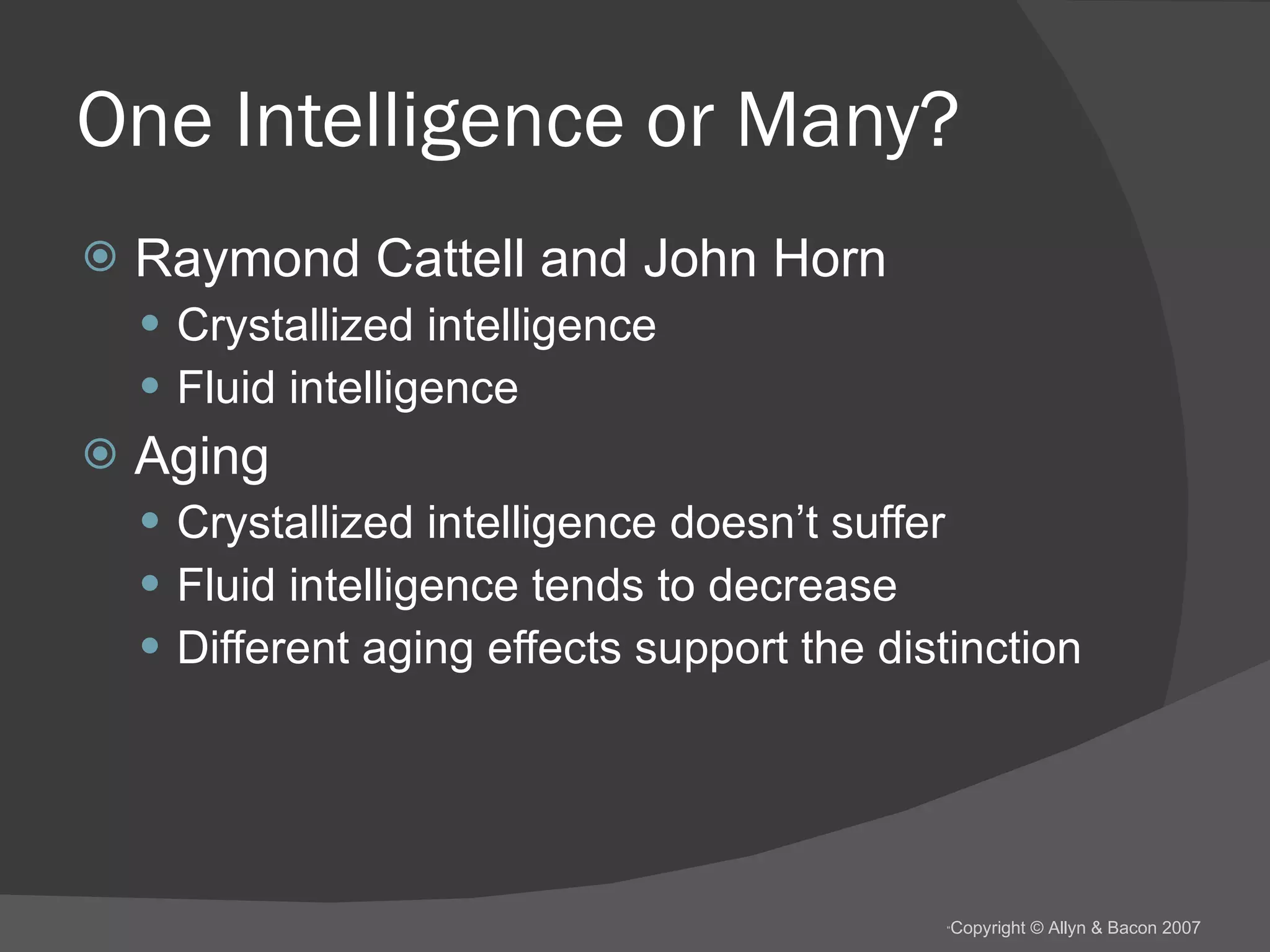
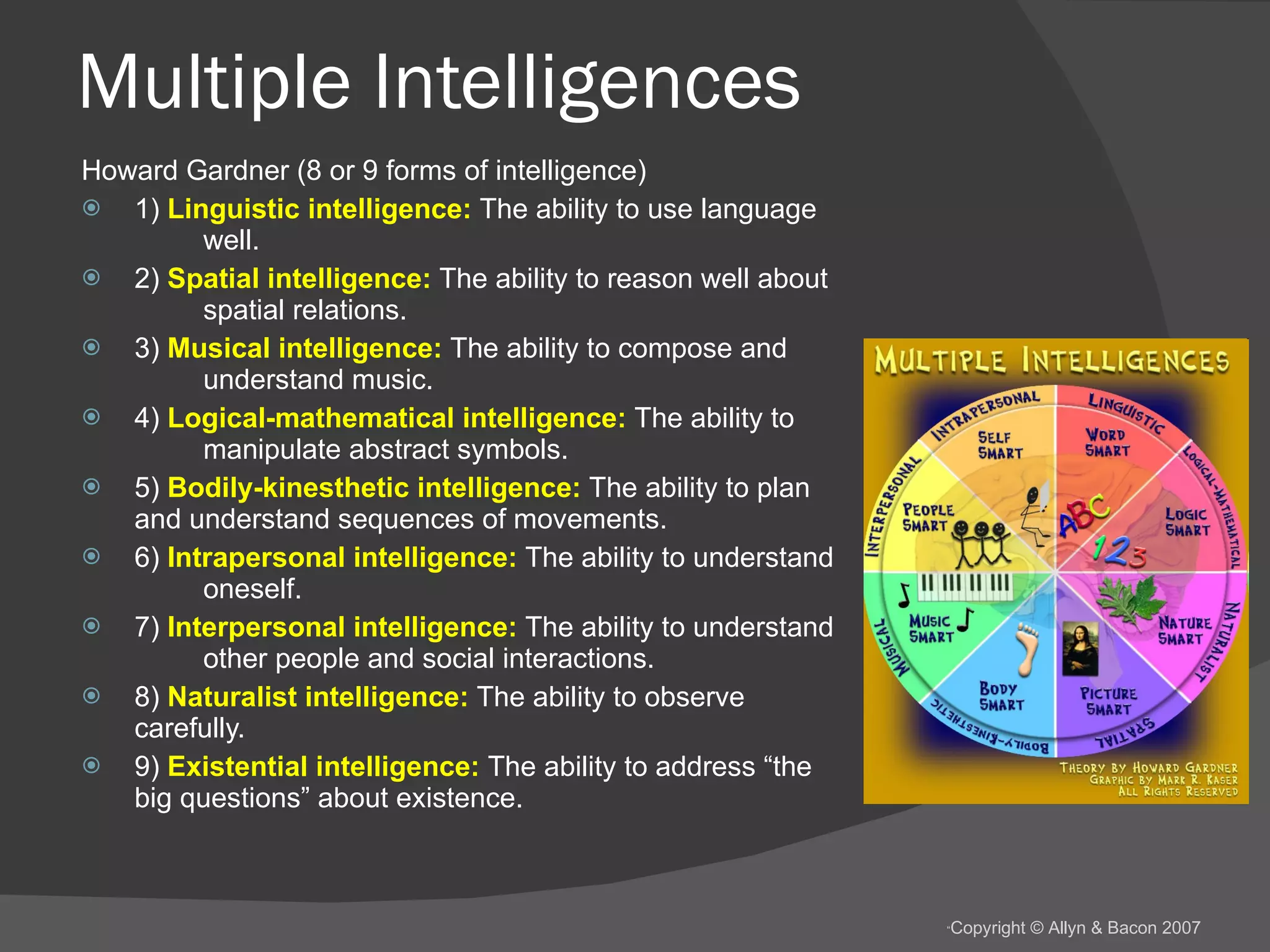
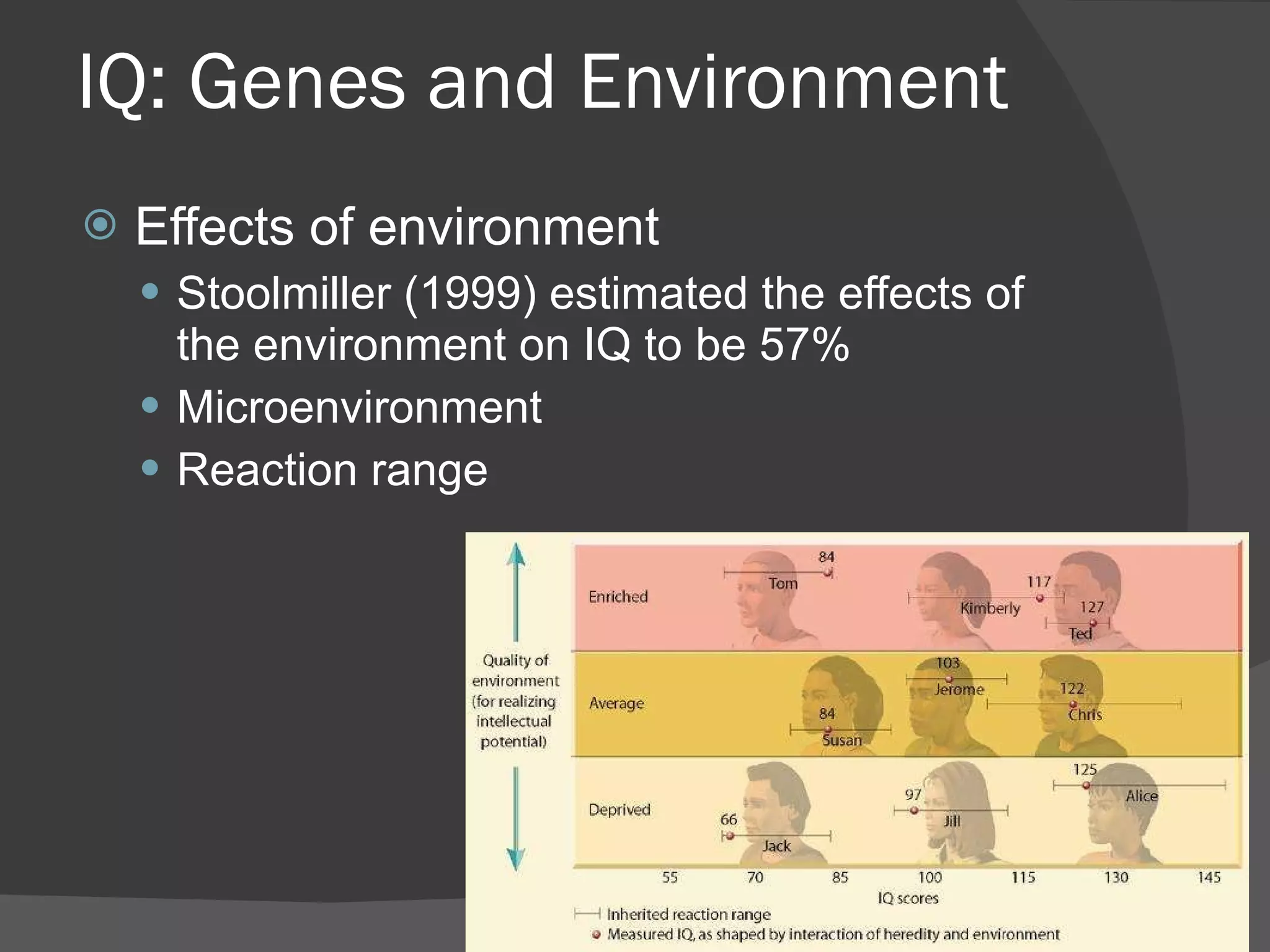
There are several theories about the nature of intelligence. Some psychologists believe there is a general intelligence factor, while others argue there are different types of intelligence, such as fluid intelligence and crystallized intelligence. Intelligence can be measured through IQ tests, but the concept of IQ and what it measures is debated. Factors like genes, environment, education and culture all likely influence a person's intelligence, but their relative impacts are still being studied.