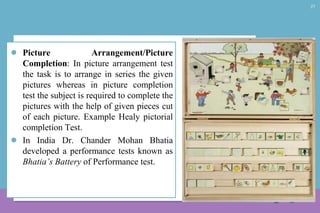
The document provides a comprehensive overview of intelligence, defining it as the capacity to think rationally and interact effectively with the environment. It discusses various types and theories of intelligence, including abstract, mechanical, and social intelligence, as well as individual differences influenced by heredity and environment. Furthermore, the document covers intelligence testing, highlighting significant tests such as the Stanford-Binet and Wechsler scales, and their applications in educational and psychological settings.