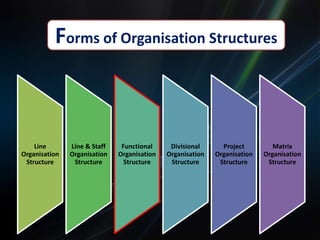
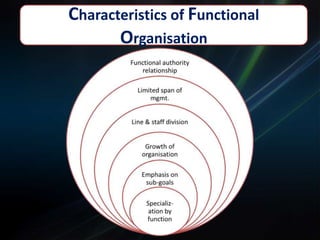
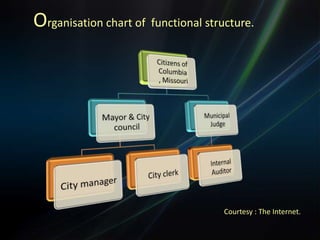
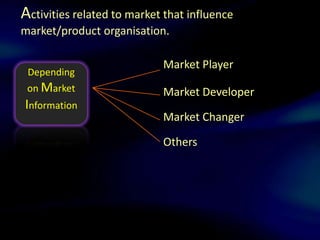
The document discusses functional and product/market organization structures. It describes functional structure as organizing resources by specialized tasks and departments, with advantages being specialization and order but disadvantages including slow decision making. Product/market structure organizes by products and customer groups, allowing a focus on products but with potential for sub-optimization. The document provides details on each structure type, including their suitability for different situations, characteristics, and strengths and weaknesses.